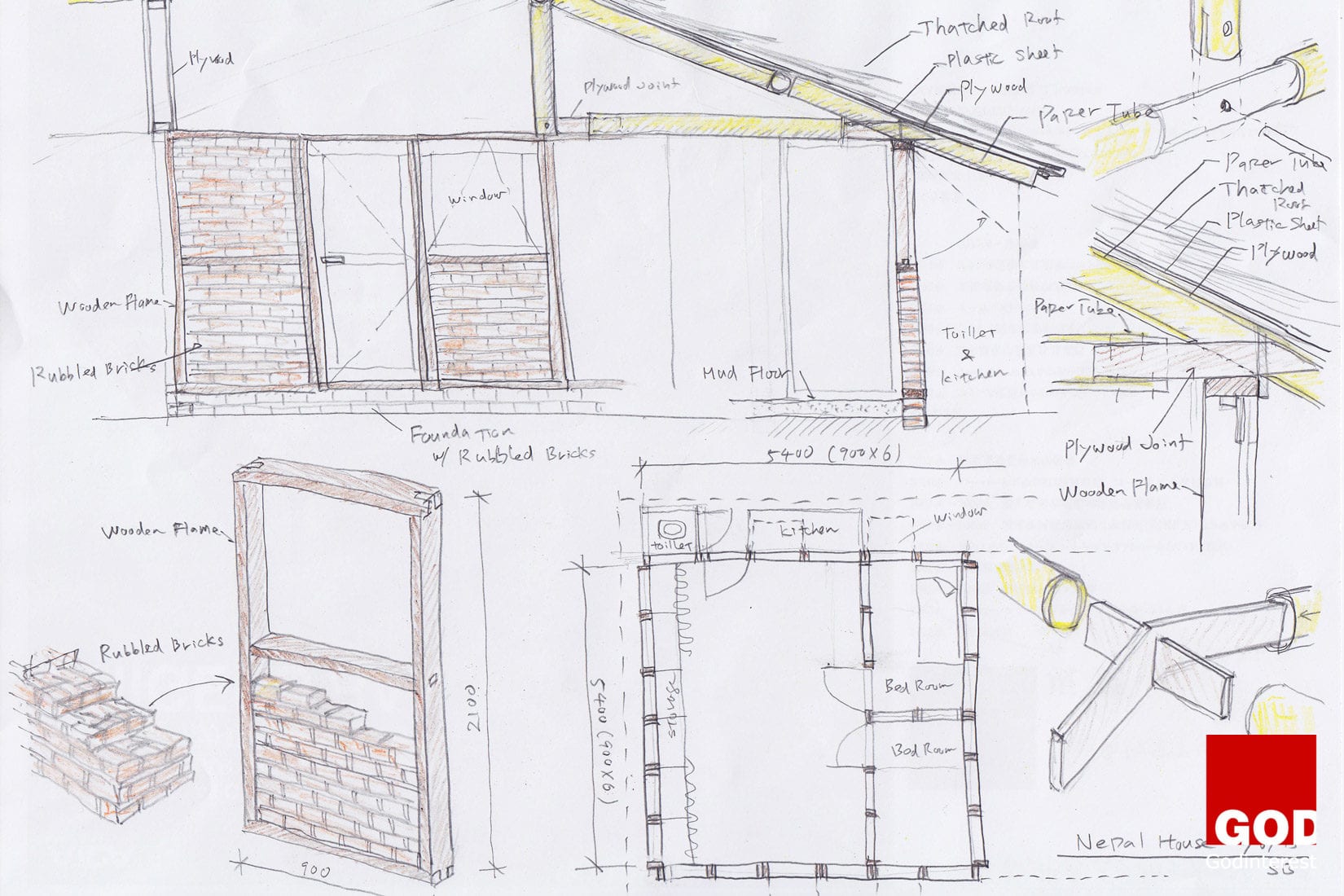
We all know that project managers are responsible for managing projects through to completion while remaining on time and within budget, but how exactly do they do it? What does a typical day look like for a project manager?
Here’s a sample of what a typical day might look like for a project manager.
The Early Bird Gets the Worm, Success Comes to Those Who Prepare Well and Put in Effort
8.30 am: Starting the day
After settling in for the day’s activities, it’s time to plan out the day. Start up the computer, email clients, draft team schedules, organize time sheets and create the to-do list.
To-do lists help managers and their teams stay on track. If a manager notices that one team member has yet to deliver an assignment, they can address this issue first thing in the morning; otherwise, delays can build up and affect the project. Likewise, lists help managers see the next course of action for projects.
9:15 am: Time to get moving
Efficiency is a must and there is no time to be wasted in project management. After a quick review of project plans and to-do lists, the manager must be prepared to get his team moving right away.
Round up team members, review the project’s current position and emphasize the next course of action. In order to get the team moving on assignments, strong project managers set deadlines throughout the day.
Morning team meetings are also necessary to make sure each member understands the project and their assignments. It’s also a time to answer any questions for clarity or to get feedback or concerns from individuals.
While daily group meetings can be important, they are not always necessary and can be counter-productive. If the team is on the same page and everyone is ready to tackle the tasks of the day, spend a short period re-grouping so that the team can get on and complete their assignments. There’s no need to spend hours planning and reviewing.
10 am: Meetings, meetings, meetings
More than one project manager will be more than likely in the office and they will all need to work together for the benefit of the programme. This is why meetings with other managers and higher ups are necessary in a project manager’s day.
Meetings allow each project manager to go through the status of their respective projects and to track the weekly schedule and other deadlines. It is also a time to address any business-critical tasks that might come up.
It’s worth considering that only 7% of communication is spoken. The other 93% is made up of tone (38%) and body language (55%). So although facts and figures are easily communicated via email, letter or phone, an actual discussion or negotiation is best handled where you can see the other person and therefore are able to see for yourself what their tone and body have to say on the matter.
10:30 am: Tackling the small stuff
Meetings will be on and off throughout the day for project managers, which is why it’s important to tackle the small tasks in between appointments. Small tasks include wrapping project reports, booking future meetings, answering correspondences with other colleagues, reviewing items and team reports among other things.
It’s also important to schedule post-mortem meetings with the project team to review the success of projects in order to apply any lessons learnt to future projects.
11 am: Project kick-off meeting
When one project ends, another begins, which means it’s time for yet another project kick-off meeting. Kick-off meetings can take on various forms, depending on the type of business. However, they all share the same basic needs.
Every individual involved with the new project should be in attendance and have the latest version of project specifications in written form. As project manager, it might be wise to send this to team members several days before the kick-off meeting to ensure everyone has time to review.
During a kick-off meeting, it’s important to review the overall goals for the project, both commercial and technical details, break down functional requirements, and spend time for discussion and questions. By allowing team members to communicate questions and share ideas, it opens the lines of communication and may bring up potential concerns that might have been missed in the initial planning stages.
Conclude kick-off meetings with a definition of the next steps and be sure individuals are aware of deadlines and their assignments.
11:30 am: Reviewing project specs, budgets and scheduling submissions
Other important tasks to tackle in between meetings include reviewing specifications and budgets and schedules for future projects. If a project begins that day, now would be a good time to apply the finishing touches to the project documentation before presentation and approval.
When it comes to establishing project estimates and budgets, a project manager must bring all of his experience into play in order to create a realistic budget that includes wiggle room for factors such as project complexity, team experience and skill levels, stakeholders involvement, time needed, third-party services needed, and contingency allowances among many other things.
It’s Not Easy to Squeeze in a Lunch Break, but It’s Often Necessary for the Project Managers Health and Sanity
12 pm: Lunch
In the midst of the seeming chaos that is project management, be sure to fuel up for the rest of the day’s work. Lunch is also a great span of time to check in with team members to make sure they are still on target for later-day deadlines.
2 pm: Launching the next project
After digesting lunch, it’s time to launch the next project. Get the whole team ready to go live and present the project to the client and begin testing aspects of the project in a live environment. It’s a time to spot problems and address them and review schedules and deadlines and other project needs.
3 pm: Time for everything else
The final two hours in the office are spent addressing everything else on the project manager’s plate. A project manager must be good at multi-tasking and whatever duties couldn’t be accomplished throughout the day are reserved for the final hours. Most of the time, lower priority tasks are reserved for afternoon hours. These tasks could include project update meetings with various departments, logging finances, reviewing monthly project schedules, approving time sheets, writing weekly reports, sorting purchase orders and communicating with suppliers. There are so many other small to-do list items that project managers are responsible for, but are often overlooked.
Spending Time at the End of the Day as Well as the Beginning to Review and Plan Will Only Help You Succeed as a Project Manager
5 pm: Review the day, plan for tomorrow
Before heading home, review the day’s list and what’s been accomplished. Anything that has been added or was left unfinished should be scheduled for the next day or sometime throughout the week. Reflect on your team’s work and clear the email inbox. Use a filing system that makes sense for you and be ruthless about deleting stuff. The beauty of an empty inbox is a thing to behold. It is calming, peaceful and wonderful.