A Compendium of Project Management Humour to Make You Laugh
Successful People Always Leave the Office on Time?
Politics and Project Management, a Lesson in Leadership
We all know that the more power you have, the better you are able to get the job completed. The problem is most project managers have lots of responsibility, but hardly any authority and since most projects exist outside core business structures, they are forced to develop other methods of influence.
One unspoken evil that is often ignored on project management training courses is the politics of project management. While most of us view politics with disgust; there is no refuting that effective project managers are often seen as those who are equipped and able to employ fitting political strategies to further their project goals.
“In a Perfect World the Best Workers Would Be Promoted on Merit Alone and the Best Ideas Would Be Adopted Regardless of Personal Interest – but We Do Not Live in Utopia”
Have you ever included ‘office politics’ as a risk on your risk register? Probably not. Though, consider the potential implications of ignoring the ugly stepchild of project management?
“The Objective of Office Politics Is to Manipulate a Situation in Order to Achieve an Outcome That Will Benefit One Individual or Group at the Expense of Other Individuals or Groups.”
While it is unlikely that ‘office politics’ would be listed directly as a risk on your risk register, it is quite likely that one or more of the outcomes of it would. As a result, if you want to survive and prosper in the real world you need to combine good work with smart politics to ensure your own success and that of your projects. The biggest mistake a project manager can make is to assume that politics in project management doesn’t exist. After all, politics is human nature and has played an integral part in history since the dawn of civilization.
In a group where working interactions are fraught with tension and individuals have their own personal agendas or want to be “top dog” personal conflicts will often get in the way of the project aims. Issues between members of the team become the over-riding concern both for the individuals afraid and sometimes even the project manager. Meetings can consist of jostling for power or simply trying to justify your position and when that happens progress on the project will undoubtedly suffer.
For most project managers, playing politics is a form of slow, soul-destroying torture where logic, self-control, transparency and trustworthiness are replaced by deception, concealment, and sabotage. However, ignoring the external and internal politics surrounding your project or organization is dangerous. Successful project managers need to understand organizational politics and how to make them work for project success.
In the case of project politics you can use these key techniques in a constructive manner:
Carefully Manage Your Own Conduct
- The first rule is to at all times act in a way that commands respect and beyond that, respect others. That means not gossiping, spreading rumors or getting sucked into interpersonal conflicts and arguments. Maintain your honesty!
- Be positive as a positive outlook is a choice that you can always make and remain professional.
- Be confident and firm but not hostile and make sure you take organizational perspectives, not a personal one when voicing objections or giving criticism.
- Always assume things will be disclosed, so don’t rely on confidentiality.
- Over time you will learn what works in your organization’s culture and what doesn’t. Try to watch other people and identify successful behaviors that you can model to navigate the political minefield.
Review the Organization Chart
- Sit back and watch for a while. Identify the real influencers, those who are respected, champions, those who have authority but don’t use it, the mentors and last but not least the true brains behind the organization. Then re-map the organization chart in terms of political influence as politics will often bypass the formal organization chart.
Understand the Social Network
- Once you know who’s who in the organization, you have to understand the social networks. This involves identifying who gets along with whom, groups or cliques that have formed and ongoing interpersonal conflicts. Over time you will learn who has the most trouble getting along with others and the basis for the interrelationship whether it be friendship, respect or manipulation, including how the influence flows between all parties.
Build Good Relationships
- Now you need to build multiple networks but avoid aligning yourself with one group or another this way you can keep your finger on the pulse of the organization.
- Don’t be afraid of politically powerful people and instead, develop relationships that cross the formal hierarchy in all directions.
- Build your relationships on trust and respect and avoid empty flattery.
Use Your Social Network
- You will need to learn to use your social network to stay clear of negative politics. You can do this through positive political action.
- Use your network to gain access to information, build visibility of your achievements and improve difficult relationships.
- Attract opportunities where you can shine and seek out ways to make yourself, your team and your boss look good.
Counteract Negative Play
“The Expression, Keep Your Friends Close and Your Enemies Closer” Couldn’t Be Any Truer When It Comes to Office Politics.”
- Your mapping of the organization will help you to identify those people who use others for their own political purposes, and not for the common good. Know that these people typically have low self-worth (that’s why they rely on destructive politicking to get ahead). Always be very careful what you say to them. Understand what motivates them, their goals, and how to avoid or counter the impact of their politics
- Remember loyalty is not a reliable factor in the workplace!
“It is easy to become a target if you’re ambitious or if you strive for change. One of the biggest mistakes we make in our career is to assume that everyone likes progress. This is not true’Å —’Å many are content with the status quo and will defend it with their life.”
Projects are rarely easy and office politics can compound other sorts of problems that arise so they need to be dealt with swiftly and firmly.
Atkins Appointed as Sustainability Adviser for Major Regeneration Project in the UK
Atkins has been chosen as the sustainability consultant to develop an environmental sustainability target for Old Oak Common, a £26bn urban redevelopment in London.
“Gentrification has profoundly influenced religion. In the context of Christianity, of course, gentrification takes on a new, existential dimension.”
At five times the size of the King’s Cross redevelopment, Old Oak and Park Royal is London’s largest opportunity area and urban regeneration investment project with an estimated worth of £7bn per annum to the UK economy. Old Oak and Park Royal has the potential to create up to 25,500 homes and some 65,000 jobs, constructing a transport hub to link Crossrail, National Rail and High Speed 2.
Atkins will create a set of sustainability targets to be used for the development in partnership with Old Oak and Park Royal Development Corporation (OPDC) and its cost control and project management advisor Faithful+Gould. The sustainability targets will be based on six core themes comprising urban form and public space, transport, energy, waste and materials, water, and access to nature, watercourses and green spaces.
Flexibility and adaptability will be a key focus area when developing the sustainability targets together with the combination of green infrastructure with urban planning and design, and the role of fast developing smart technologies.
“The Sustainability Targets Are Expected to Be Used for Anything up to 20 to 50 Years’ and Will Involve a Sensible Combination of ‘Open-Minded Thinking with Real-World Analysis.”
Sean Lockie, sustainability director at Faithful+Gould, said: “Old Oak and Park Royal is a massive opportunity for London to do things that haven’t been done before. “It means creating a vision which sets out clear goals, such as being healthy to live in, flexible over time, affordable, comfortable, and being energy and resource efficient, and then taking a systematic approach to delivery. “We’ll need to come up with some new business models to achieve this but in doing so we have a great opportunity to make a real difference in people’s lives.”
Atkins will lead stakeholder engagement workshops with the OPDC, designers and the local authority until August 2016 and is set to deliver its sustainability report to the OPDC in September 2016.
“Is urban regeneration about more than the material?” It’s about a piece of heaven on earth ”¦ where true expressions of what Jesus did or how he lived actually articulates itself into society.”
The Nature of Good ‘Project Chemistry’
Has Nigeria Become the World’s Junk Yard of Abandoned and Failed Mega Projects worth Billions?
Dim1, N. U., Okorocha2, K. A., & Okoduwa3 V. O.
The Nigerian construction industry is mostly concerned with the development and provision of projects such as roads, bridges, railways, residential and commercial real estates, and the maintenance necessary for the socio-economic developments contributes immensely to the Nigerian economic growth (Bureau of Statistics, 2015). Butcher and demmers (2003) described projects as an idea which begins and ends by filling a need. However, a project fails when its idea ends without meeting the needs and expectations of its stakeholders.
Nigeria Has Become the World’s Junk – Yard of Abandoned and Failed Projects worth Billions of Naira!
Hanachor (2013), revealed that projects form part of the basis for assessing a country’s development. However, a damming report from the Abandoned Projects Audit Commission which was set up by the Ex-President Goodluck Jonathan in 2011 revealed that 11,886 federal government projects were abandoned in the past 40 years across Nigerian (Abimbola, 2012). This confirmed the assertion by Osemenan (1987) “that Nigeria has become the world’s junk –yard of abandoned and failed projects worth billions of naira”.
Abandoned projects including building and other civil engineering infrastructure development projects now litter the whole of Nigeria.
Physical projects do not only provide the means of making life more meaningful for members of the community where the projects are located, successful projects also result in empowerment and collective action towards self improvement (Hanachor, 2013).
This Issue of Abandonment Has Been Left Without Adequate Attention for Too Long, and Is Now Having a Multiplier Effect on the Construction Industry in Particular and the Nigeria’s National Economy as a Whole. (Kotngora, 1993)
PROJECT FAILURE
Project Failure might mean a different thing to different stakeholders. A project that seemed successful to one stakeholder may be a total failure to another (Toor and Ogunlana, 2008). Some stakeholders, more especially the project users and some private owners, think of failed projects as a situation where a completed building project collapsed, a situation where by a completed dam project stopped working after few days of completion, or a completed road project that broke down after few months of completion. Other experienced stakeholders, such as engineers and architects conform to the iron triangle by Atkinson (1999) which states that the most strategically important measures of project failure are “time overrun”, “cost overrun”, and “poor quality”.
Turner (1993) noted that a project fails when the project specifications are not delivered within budget and on time; the project fails to achieve its stated business purpose; the project did not meet the pre-stated objectives; the project fails to satisfy the needs of the project team and supporters; and the project fails to satisfy the need of the users and other stakeholders. Lim and Mohamed (1999) cited in Toor and Ogunlana (2009) clarified that there are two possible view points to project failure namely; the macro-level and the micro-level. They further explained that the macro view point reviews if the original objectives and concepts of the project was met. Usually the end users and the project beneficiaries are the ones looking at the project failure from the macro view point, where as the project design team, the consultants, contractors, and suppliers review projects from a micro view point focusing on time of delivery, budget, and poor quality.
In the early 1990s, the failure as well as the success of any project was determined by the project duration, monetary cost, and the performance of the project (Idrus, Sodangi, and Husin, 2011). Belout and Gauvrean (2004), also confirmed that the project management triangle based on schedule, cost, and technical performance is the most useful in determining the failure of a project. Moreover, a project is considered as an achievement of specific objectives, which involves series of activities and tasks which consume resources, are completed within specifications, and have a definite start and end time (Muns and Bjeirmi 1996, cited in Toor and Ogunlana, 2009). Reiss (1993) in his suggestion stated that a project is a human activity that achieves a clear objective against a time scale. Wright (1997) taking the view of clients, suggested that time and budget are the only two important parameters of a project which determines if a project is successful or failed. Nevertheless, many other writers such as Turner, Morris and Hough, wateridge, dewit, McCoy, Pinto and Slevin, saarinen and Ballantine all cited in Atkinson (1999), agreed that cost, time, and quality are all success as well as failure criteria of a project, and are not to be used exclusively.
FACTORS OF PROJECT FAILURE
Cookie-Davies (2002) stated the difference between the success criteria and the failure factors. He stated that failure factors are those which contributed towards the failure of a project while success criteria are the measures by which the failure of a project will be judged. The factors constituting the failure criteria are commonly referred to as the key performance indicators (KPIs).
Time and Cost Overrun
The time factor of project failure cannot be discussed without mentioning cost. This is because the time spent on construction projects has a cost attached to it. Al-Khali and Al-Ghafly, (1999); Aibinu and Jagboro, (2002) confirmed that time overrun in construction projects do not only result in cost overrun and poor quality but also result in greater disputes, abandonment and protracted litigation by the project parties. Therefore, focus on reducing the Time overrun helps to reduce resource spent on heavy litigation processes in the construction industry (Phua and Rowlinson, 2003). Most times, the time overrun of a project does not allow resultant system and benefits of the project to be taking into consideration (Atkinson, 1999). Once a project exceeds the contract time, it does not matter anymore if the project was finally abandoned or completed at the same cost and quality specified on the original contract document, the project has failed. Furthermore, Assaf and Al-Hejji, (2006) noted that time overrun means loss of owner’s revenue due to unavailability of the commercial facilities on time, and contractors may also suffers from higher over heads, material and labour costs.
Poor quality/Technical Performance
The word “Performance” has a different meaning which depends on the context it is being used and it can also be referred to as quality. Performance can be generally defined as effectiveness (doing the right thing), and efficiency (doing it right) (Idrus and Sodangi, 2010). Based on this definition of performance, at the project level, it simply means that a completed project meets fulfilled the stakeholder requirements in the business case.
CAUSES OF PROJECT FAILURE
A lot of research studies have investigated the reasons for project failures, and why projects continue to be described as failing despite improved management. Odeh and Baltaineh, 2002; Arain and Law, 2003; Abdul-Rahman et al., 2006; Sambasivan and Soon, 2007; all cited in Toor and Ogunlana, 2008, pointed out the major causes of project failures as Inadequate procurement method; poor funding and availability of resources; descripancies between design and construction; lack of project management practices; and communication lapses
The contract/procurement method
A result obtained from two construction projects which were done by the same contractor but using different procurement methods showed that rework, on the design part which occurs when the activities and materials order are different from those specified on the original contract document, makes it difficult for the project to finish on the expected time (Idrus, Sodangi, and Husin, 2011). This is as a result of non-collaboration and integration between the design team, contractor, and tier suppliers. The rework on the design portion has a huge impact on project failure leading to the time overrun. The traditional method of procurement has inadequate flexibility required to facilitate late changes to the project design once the design phase of the construction project has been concluded.
Nigerian most widely used procurement method is the traditional method of procurement (design-bid-construct) which has been confirmed to be less effective to successfully delivery of a construction project (Dim and Ezeabasili, 2015). And, the world bank country procurement assessment report (2000) cited in Anigbogu and Shwarka, (2011) reported that about 50% of projects in Nigeria are dead even before they commence because they were designed to fail.
The way the construction projects are contracted, in addition to the way the contracts are delivered, contributes to the causes of projects failure. Particularly, among the methods of project contracting is lump-sum or a fixed-price contracting method, in which the contractor agrees to deliver a construction project at a fixed price. The fixed-price contract can be low-bid or not however, once the contract cost has been agreed upon the contract award, it cannot be changed. And, contractors are expected to honor and deliver the contract agreement, failure to do so can result in a breach of contract which can result in the contractor being prosecuted.
Awarding a contract to an unqualified personnel also contributes to project failures. When a contractor places more emphasis on money and the mobilization fee after a construction project has been initiated instead of getting the right workforce and skilled professionals that will execute the project. Instead the workforce chosen will often not be base on competence and required skills rather it will be based on availability. Moreover, poor strategy and planning by contractors who have overloaded with work also contributed to one of the causes of project failure.
Poor funding/Budget Planning
A lot of public projects in the Nigerian construction industry failed as a result inadequate funding, and the difference between the national annual budget and the budget actual released. Most of the Nigerian public projects are signed even before the actual release of the national budget. The difference in budget of the contracted project and the actual budget release can get the contracted company stuck as a result of inflation of prices, scarcity of construction material at the time of the budget release and mobilization to site. Also un-planned scope of work which can be as a result of the contractor working on another contract when he is called back to mobilization to start work. Moreover, poor budget planning is a regular mistake made by some contractors by not undertaking feasibility assessments before starting the design. The construction project should be planned according to the available resources and not according to the unrealistic expectations a client has in mind.
Discrepancies Between the Design and Construction
Limited collaboration between the contractors, engineers, and the architect results in discrepancies between the project designs and construction on site, and further leads to rework. Changes on a project designs, and changing to the scope of work in the middle of construction processes on site can be dangerous, and can lead to time overrun, increase in cost, and most of all can lead to abandonment. Moreover, many cases have been seen where the designs from the architects are not buildable on site, while In some cases, most contractors are unable to adequately specify the scope of work for the construction processes on site. Therefore any default on the design by the architect can be an opportunity for the contractor to make more money which might cause the project duration to exceed the time specified on the contract document.
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
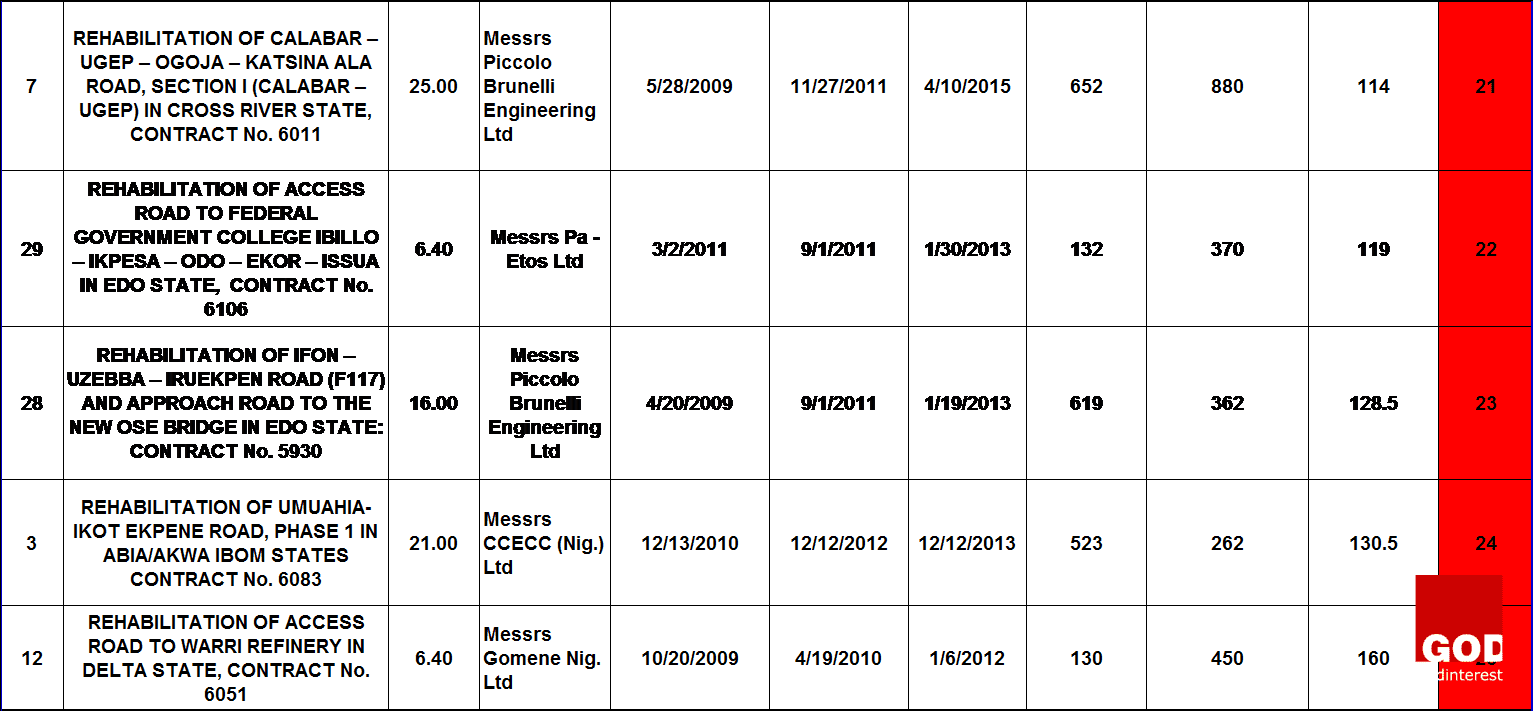
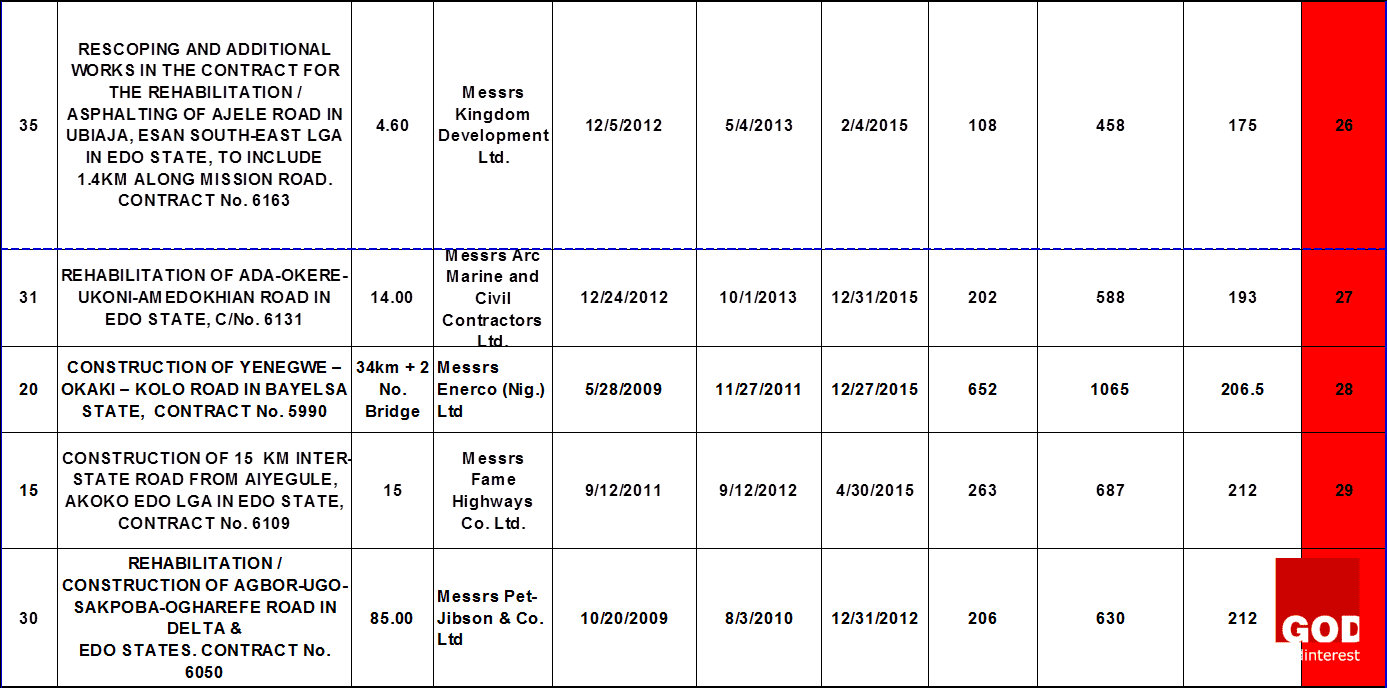
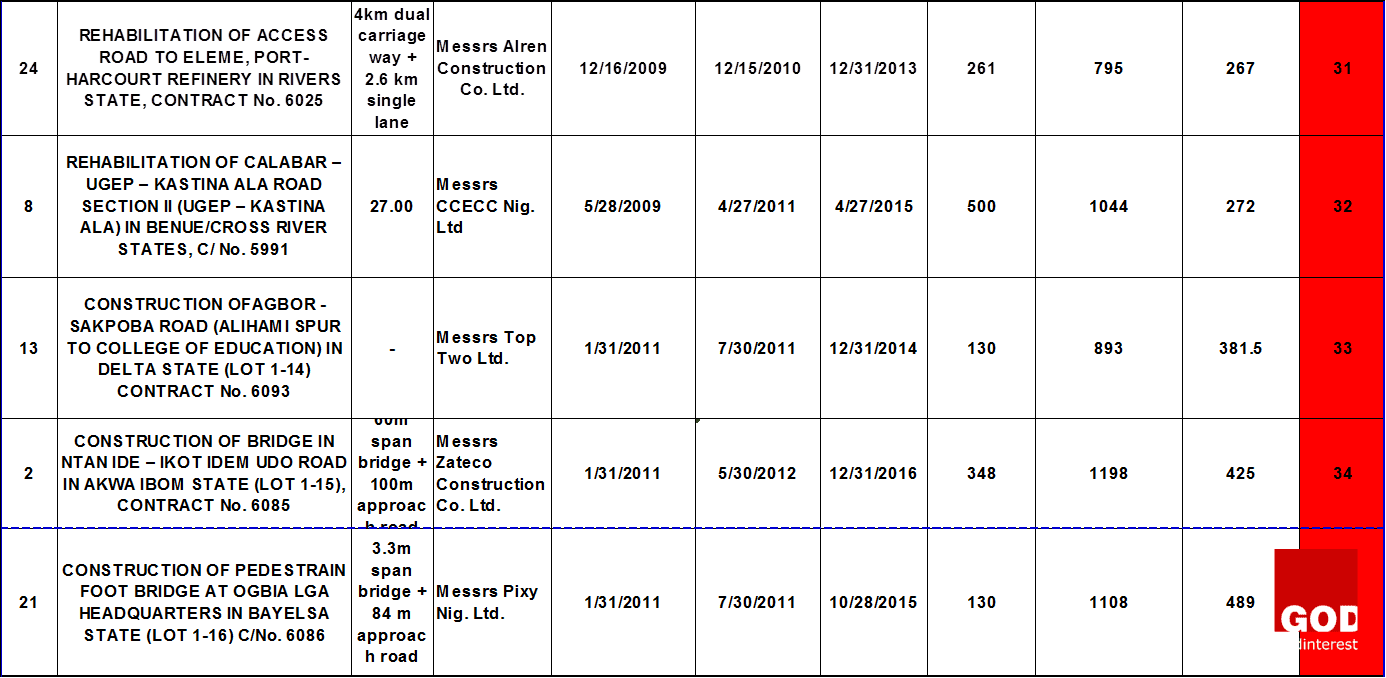
This research starts with a general reasoning or theory which says that the major cases of project failure in the Nigerian construction industry are defined based on time overrun and cost overrun. The findings from the data analysis will help on the decision to accept the theory or not. The research data was collected from the progress report for the month ending of October, 2015 published by the Nigeria of Federal Ministry of works on thirty-nine on-going highway construction projects at the South-South geopolitical zone. The table 1 below shows the information on the data collected which comprises of the project title, contract Number, project description, the contractor that was awarded the projects, the date of project commencement, date of completion and the extended date if any. The scheduled time for each project was specified as follows: project commencement date labeled as “a”, project completion date labeled as “b”, and the extended date labeled as “c”.

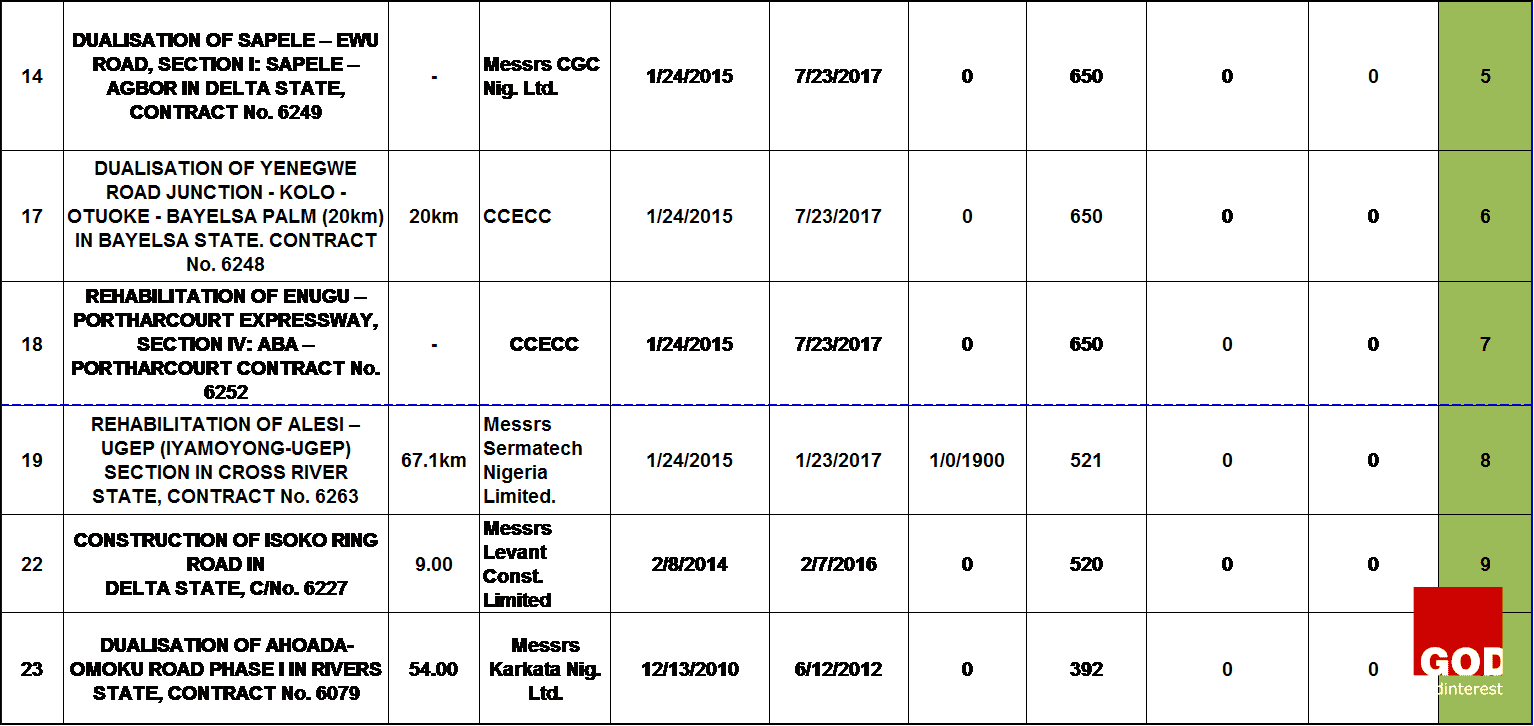
DATA ANALYSIS
The data analysis was done with the use of Microsoft excel. The analysis started by obtaining the number of days between the date of commencement of each project and the date of completion to show the duration of each highway project. And, the number of days between the project completion date and the extension date showed the time-overrun. The project duration and the extended days were obtained with the use of NETWORKDAYS function in Microsoft Excel which calculates the number of working days between two dates excluding weekends and any dates identified as holidays.
The standard deviation between the specified project duration for each highway projects and the extended days was calculated to obtain the extent to which each highway project contract failed on its time of delivery. This was denoted as the degree of failure. The table 1 above showed the projects ranking which was done based on the degree of failure of all the highway projects. The highway projects that were ranked from one to sixteen have low degree of failure and are represented with green color, while the rest are those with high degree of failure and are represented with red color.
FINDINGS
The findings made showed that the successfully completed highway projects have no extended days or time overrun, and the successful on-going highway projects are still on schedule and have no extended days unlike the on-going highway projects that have already failed as a result of the extended dates. Other projects have been abandoned because they have exceeded the delivery date as specified on the contract document, and have no extended date of completion. Thus, no work is going on.
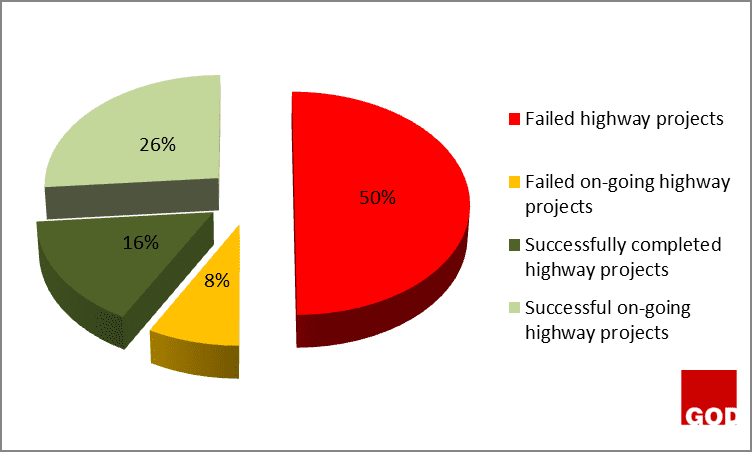
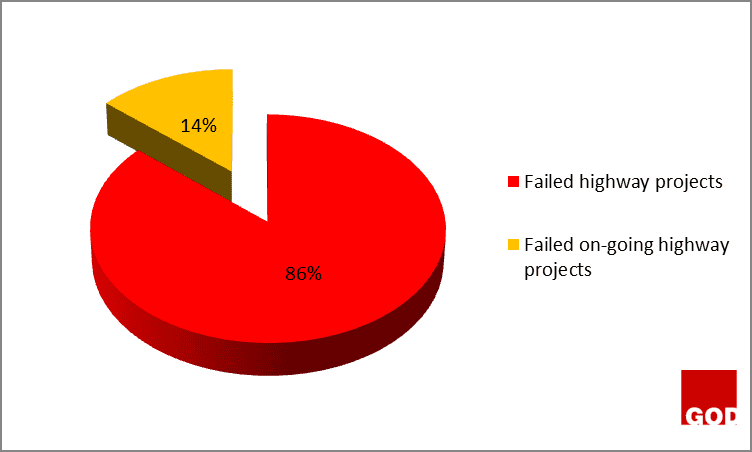
Figure 2 above showed that 14% of highway projects are still on-going projects because they have not exceeded the original date of completion as specified on the contract document. However, they are heading towards failure because they have been given an extended date of completion which can be as a result of some critical activities running behind schedule, causing delay on the critical path network of the projects. Moreover, the other 86% completely failed because they have exceeded their completion date specified on the contract document.
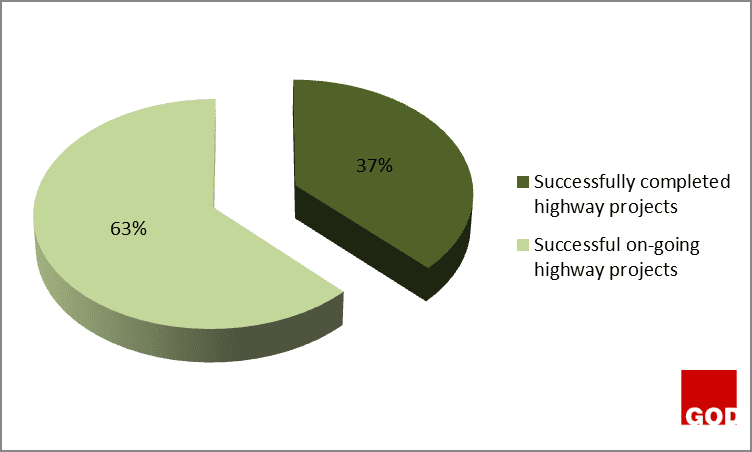
The figure 3 above showed that 63% of the successful highway projects are still on-going because they have not exceed their completion dates, and they are not yet completed. However, those on-going highway projects might end up as failed projects as a result of poor funding, discrepancy between the design and the construction on site, and conflict between the construction parties or stakeholders.
“Say what you will do, and do what you said” or “Say as you will do it, and do it as you said”
CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION
The idea of knowing what a failed project is, the factors and the causes is very important in project management. Success in project management can neither be achieved nor measured without the knowledge of project failure, its factors, and causes in the Nigerian construction industries. This work has shown that project failure is as a result of exceeded time of delivery, cost overrun, and poor quality. However, the analysis was only done based on exceeded time of project delivery because of the nature of the data collected.
This work suggested a few approaches to help reduce the number of failed projects in the Nigerian construction industry if properly implemented. Firstly, Having good collaboration between the project stakeholders involved in a construction project at the early stage of project conception is most important in order to accomplish the project objectives, and deliver the project on time, within budget, and quality specified on the original contract document (Othman, 2006).
Secondly, Adopting the ISO 9000 technique which is used for quality management will also help in achieving a successful project delivery. This technique states “ say what you will do, and do what you said” or “say as you will do it, and do it as you said”. This technique is not an indication of high quality but it promotes control and consistency which leads to specialization, and improved productivity and quality. Also, adopting the principles of lean construction will help to reduce waste within the construction and stream-line activities in order to improve the on-time delivery of projects.
Thirdly, Learning from the precedent failed projects, how those projects failed, and the reason for their failures. This will help the project manager to plan and mitigate the risks of project failures in the future. And, finally, more seminars and workshops will help to educate and enlighten clients (the federal government representatives), users, contractors, engineers, and architects on what is project failure, the factors that contributes to abundant failed projects, and their causes.
REFERENCE
Abimbola, A. (Novermber 24, 2012). About 12,000 Federal Projects Abandoned across Nigeria. Premium times (November 16, 2015). Retrieved from www. Premium timesng.com/news/108450-about-12000-federal-projects-abandoned-across-nigeria.html.
Al-Khali, M.I and Al-Ghafly, M.A. (1999). Important Causes of Delays in Public Utility Projects in Saudi Arabia. Construction management and Economics, 17, 647-655
Aibinu, A.A and Jagboro, G.O. (2002). The Effects of Construction Delays on Project Delivery in Nigeria Construction Industry. International journal of Project management, 20(8), 593- 599.
Anigbogu, N. and Shwarka, M. (2011). Evaluation of Impact of the Public Procurement Reform Program on Combating Corruption Practices in Public Building Project Delivery in Nigeria. Environtech Journal, 1(2). 43-51.
Assaf, S. and Al-Hajji, S. (2006). Causes of Delays in large Construction Projects. International Journal of Project Management, 24, 349-357.
Atkinson , R. (1999). Project management: Cost, time, and quality, two best guesses and a Phenomenon, it’s time to accept other success criteria. International Journal of project Management, 17(6), 337-342.
Belout, A and Gauvrean, C. (2004). Factors Influencing the Project Success: The impact of human resource management. International Journal of project Management, 22, Pp. 1-11.
Butcher, N. and Demmers, L. (2003). Cost Estiumating Simplified. Retrieved from www.librisdesign.org.
Cookie-Davies, T. (2002). The Real Success Factors on Projects. International Journal of Project management, 20(3), 185-190.
Dim, N.U. and Ezeabasili, A.C.C (2015). Strategic Supply Chain Framework as an Effective Approach to Procurement of Public Construction Projects in Nigeria. International Journal of Management and Susutainability, 4(7), 163-172.
Hanachor, M. E. (2012). Community Development Projects Abandonment in Nigeria: Causes and Effects. Journal of Education and Practice, 3(6), 33-36.
Idrus, A., Sodangi, M., and Husin, M., H. (2011). Prioritizing project performance criteria within client perspective. Research Journal of Applied Science, Engineering and Technology, 3(10), 1142-1151.
Idrus, A. and Sodangi, M. (2010). Framework for evaluating quality performance of contractors in Nigeria. International Journal of Civil Environment and Engineering. 10(1), 34-39.
National Bureau of Statistics (January, 2015). Nigerian Construction Sector Summary Report: 2010-2012.
Kotangora, O. O. (1993). Project abandonment, Nigerian Tribune.
Osemenan, I. (1987). Project Abandonment. New Watch Magazine, Vol. 1, pp. 15.
Othman, M.,R. (2006). Forging main and sub-contractor relationship for successful projects. Retrieved from http://rakanl.jkr.gov.my/csfj/editor/files/file/projek/lessonslearned/MAIN&SUB_2.pdf
Phua, F.T.T and Rowlinson, S. (2003). Cultural Differences as an Explanatory Variable for Adversarial Attitude in the Construction Industry: The case of HongKong. Construction Management and Economics, 21, 777-785.
Reiss, B. (1993). Project Management Demystified. London: E and FN Spon Publishers.
Toor, S. R. and Ogunlana, S. O. (2008).Problems causing Delay in Major Construction Projects in Thailand. Construction management and Economics, 26, 395-408.
Toor, S. R. and Ogunlana, S. O. (2008). Critical COMs of Success in Large-Scale Construction Projects: Evidence from Thailand constructuction industry. International Journal of Project management, 26(4), 420-430.
Toor, S. R. and Ogunlana, S. O. (2009).Beyound the “Iron Triangle”: Stakeholder perception of key performance indicators (KPIs) for large-scale public sector development projects. International Journal of Project management, doi: 10.1016/j.ijproman.2009.05.005.
Toor, R. and Ogunlana, S. (2009). Construction Innovation: Information, process, management. 9(2), PP. 149-167.
Turner, J. R. (1993). The Handbook of project-Based Management: Improving the process for achieving strategic objective. London, McGraw-Hill.
Wright, J., N. (1997). Time and Budget: The twin imperatives of a project Sponsor. International Journal of Project Management, 15(3), 181-186.
15 Shocking Project Management Statistics
The project management landscape is changing with an increased emphasis on productivity, reporting, and information technology. A number of studies have been completed that look into the success and failure rates of projects.
Below are 15 shocking statistics that reveal how project management has changed and is performing across various industries over the last 5 years.
- There is projected to be 15.7 million new project management roles to be added globally across seven project-intensive industries by 2020 reaching an economic impact of over $18 trillion, across seven project-intensive industries including Manufacturing, Finance & Insurance, Information Services, Utilities, Business Services, Oil & Gas and Construction (Project Management Institute)
- 75% of IT executives believe their projects are “doomed from the start. (Geneca)
- The healthcare industry is projected to increase project management roles by 30%, a higher growth rate than any current project intensive industry between 2010 and 2020. (Project Management Institute)
- A third of all projects were successfully completed on time and on budget over the past year. (Standish Group)
- 80% of “high-performing” projects are led by a certified project manager. (PricewaterhouseCoopers, Insights and Trends: Current Programme and Project Management Practices 2012)
- One in six IT projects have an average cost overrun of 200%. (Harvard Business Review 2004)
- 44% of project managers use no software, even though PWC found that the use of commercially available PM software increases performance and satisfaction. (Pricewaterhouse Coopers)
- More than 90% of organizations perform some type of project postmortem or closeout retrospective. (The Standish Group: CHAOS Research Report 2013)
- On average, it takes 7 years in the profession to go from entry-level to managing large, complex projects. (ESI International: Annual Salary Survey 2013)
- The average large IT project runs 45% over budget, 7% over time, and delivers 56% less value than expected. (Project Management Institute: Pulse of the Profession 2015)
- Only 64% of projects meet their goals. (Project Management Institute: Pulse of the Profession 2015)
- 60% of companies don’t measure ROI on projects. (KPMG New Zealand: Project Management Survey 2010)
- The United States economy loses $50-$150 billion per year due to failed IT projects. (Gallup Business Review)
- In just a 12 month period 49% of organizations had suffered a recent project failure. In the same period only 2% of organizations reported that all of their projects achieved the desired benefits. 86% of organizations reported a shortfall of at least 25% of targeted benefits across their portfolio of projects and many organizations failed to measure benefits so they are unaware of their true status in terms of benefits realization. (KPMG – Global IT Project Management Survey 2005)
- According to an IBM study, only 40% of projects meet schedule, budget and quality goals. (Harvard Business Review 2004)
If you have any other project management statistics please share them with us.
7 Tips You Need to Be a Super Project Manager
You Were Never Made to Be ‘Productive’
Compared to people in other industrialized nations, Americans work longer hours, take fewer vacation days, and retire later in life. Busyness, once seen as the curse of the disadvantaged, has become equated with status and importance. Our work increasingly defines who we are.
“Godly rest (distinct from play, relaxation, or sleep) is inextricably tied to our identity as children of God.”
The solution perhaps is to be “Lazy Intelligent”? That sounds like something an unsuccessful, lazy slacker would say, isn’t it? Actually, it’s the opposite. One of America’s most influential and controversial science fiction authors Robert Heinlein uttered these words during his time. Despite his nod to laziness, Heinlein went on to pen hit titles such as Starship Troopers and Stranger in a Strange Land.
Productive laziness is not about doing absolutely nothing at all. It’s not about just sitting around and drinking coffee or engaging in idle gossip while watching the non-delivered project milestones disappear into the horizon. In fact, this behavior would lead to a very short-lived project management career.
Laziness Is Not Synonymous with Stupidity
Instead, productive laziness should be viewed as a more focused approach to management. Adopting this mindset means concentrating efforts where it really matters, rather than spreading yourself thing over unimportant, non-critical activities that in some cases don’t need to be addressed at all.
According to the Pareto Principle — Also Known as the “80/20 Rule” — 80 Percent of the Consequences Stem from 20 Percent of the Causes.
While the idea has a rule-of-thumb application, it’s also commonly misused. For example, just because one solution fits 80 percent of cases, that doesn’t mean it only requires 20 percent of the resources needed to solve all cases.
The principle, suggested by management thinker Joseph M. Juran, was named after Italian economist Vilfredo Pareto, who observed that 80 percent of property in Italy was owned by 20 percent of the population. As a result, it was assumed that most of the result in any situation was determined by a small number of causes.
Rest Is at the Center of God’s Design
Every smart but lazy person should consider the 80/20 Rule each day. For managers, the principle is a reminder to concentrate on the 20 percent of work that really matters.
Contrary to belief, 80 percent of success is not just showing up. In fact, only 20 percent of what you do during the day will produce 80 percent of your results. Therefore, it is important to identify and focus on that 20 percent during the working day.
When genius and laziness meet, the results can be magical. Being just the right combination of smart and lazy can bring you to have a real edge over others. Interestingly enough, smart lazy people are generally better suited for leadership roles in organizations. These people make great strategic thinkers and leaders. They do things in a smart way in order to expend the least effort. They don’t rush into things, taking that little bit of extra time to think and find the shortest, best path.
They question, contradict, and show dissent against inefficient methods or unnecessary tasks.
“Whenever There Is a Hard Job to Be Done, I Assign It to a Lazy Man; He Is Sure to Find an Easy Way of Doing It. — Bill Gates”
Bill’s not the only guy, who believes that laziness doesn’t necessarily have to be a bad thing. German Generalfeldmarschall Helmuth Karl Bernhard Graf von Moltke was the chief of staff for the Prussian Army for 30 years. He is regarded as one of the greatest strategists of the latter 1800s among historical scholars and is the creator of the more modern method of directing armies in the field.
Moltke observed his troops and categorized them based on their intelligence, diligence and laziness. If soldiers proved to be both lazy and smart, they were promoted to leadership because they knew how to be successful with efficiency. If soldiers were smart and diligent, they were deployed into a staff function, focusing on the details. Soldiers who were not smart and lazy were left alone in hopes they would come up with a great idea someday. Finally, soldiers who were not smart but diligent were removed from ranks.
Like Moltke’s army, the lazy manager is all about applying these principles in the delivery and management of work. You’re likely not stupid since you’ve landed the management position, but how are your lazy skills? Applying smart-lazy tactics will not only allow your work to be more successful, but you will also be seen as a successful individual and a top candidate for future leadership roles.
Think return on investment (time spent versus money earned ratio) rather than busy work and don’t restrict yourself to a certain way of doing things just for the sake of the status quo.
These people make great strategic thinkers and leaders. They do things in a smart way in order to expend the least effort. They don’t rush into things, taking that little bit of extra time to think and find the shortest, best path.
In the wise words of Bill Gate’s and American automotive industrialist Walter Chrysler, “Whenever there is a hard job to be done, assign it to a lazy man or woman for that matter; as he or she is sure to find an easy way of doing it.”
For an overachieving people-pleaser like me, thinking of rest as an innate part of who we were created to be—not as a discipline or something to be earned—is compelling. It is yet another form of God’s infinite grace, one that’s needed today more than ever.
Co-Author Peter Taylor
Described as “perhaps the most entertaining and inspiring speaker in the project management world today”, Peter Taylor is the author of two best-selling books on ‘Productive Laziness’ – ‘The Lazy Winner’ and ‘The Lazy Project Manager’.
Fighting Gender Discrimination in The High-Tech World
New research suggests that tech-savvy women might face gender discrimination in jobs at high-tech firms, partly due to mismanaged projects.
It shows gender discrimination is still as prevalent in the UK as it was 20 years ago, and comes as International Women’s Day will be celebrated this week on March 8, for the 103rd year.
The book “The Recruitment, Retention and Advancement of Technical Women: Breaking Barriers to Cultural Change in Corporations” by the Anita Borg Institute for Women and Technology, a Palo Alto-based nonprofit organization focusing on the role of women at high-tech firms.
“More than a Quarter of Women Have Experienced Some Form of Gender Discrimination in the Workplace, a New Study Shows.”
Tech firms typically rely on a “hero mindset” to save poorly organised runaway coding projects. As a result, employees with family responsibilities (generally considered to be women) are left out, the report said.
The Research Also Suggests out of 1,500 Office Workers in the Uk, 26% of Women Felt That Having Children Held Them Back in Their Career
The research also suggests that there is evidence of bias against women in recruitment and job assignment in places where high-tech corporate cultures thrive on this “hero mindset” that “rewards a ‘last minute’ crunch where 24/7 work becomes necessary to ‘save’ a project.” However, these environments fail to acknowledge family responsibilities and flexibility needs, the report said.
This fly-by-the-seat-of-your-pants workday culture represents a pattern that’s grown mainly because an organization poorly defines project management and requirements.
For example, Silicon Valley’s sometimes frantic fire-fighting pace and in-your-face communication style produces many technical cultures that often “leave women feeling isolated and crushed,” notes the report.
The study also reflects what 59 senior business and tech managers — both men and women from companies like Cisco, Facebook, Goldman Sachs, Google, HP, IBM, Intel, Microsoft and Symantec — shared during a closed forum organized by the Anita Borg Institute. According to the report, it’s common in the high-tech world to find the modern equivalent of the “good old boys network” that tends to hire “people who are like them.”
Technical women these days are “still a rarity,” said Dr. Carolyn Simard, author of the report. She added that in the United States, women earn just 18 percent of computer science degrees in college. That figure is sharply down from the 37 percent observed in 1985. Yet technical demand is still expected to grow as much as 32 percent by 2018.
The Institute published a second report titled “Senior Technical Women: A Profile of Success,” which surveyed approximately 1,800 participants from seven unidentified high-tech firms in Silicon Valley.
It found that women now hold about four percent of the senior-level technical positions at high-tech firms and an estimated one-quarter of all tech jobs. On higher levels, women are more likely to end up in a managerial position compared to men (36.9 percent of women compared to 19 percent of men), who are more likely to hold “individual contributor positions” in technical coding jobs.
The second study also found that men and women in technical jobs value most of the same attributes for success, such as being analytical, questioning, risk-taking, collaborative, entrepreneurial, assertive, working long hours and being sociable.
Far more often than men, women generally have “primary responsibility for the household,” the study showed. However, senior-level tech women are much more likely to have a partner who holds primary responsibility for the household and children (23.5 percent of partnered senior women) compared to entry or mid-level women (13.4 percent). Senior-level tech women are also more likely than their male counterparts to forego a partner and children because they believe they might hinder their careers.
To improve work-life balance and stop any perceived gender bias against women in the high-tech world, the Anita Borg Institute is pushing a few ideas that will generate debate and controversy.
“The Equality Act 2010 Makes It Unlawful for an Employer to Discriminate Against Employees Because of Their Gender.”
One recommendation suggests that because there is evidence that women are eliminated in the hiring process at the resume review level, companies might consider “that all women candidates should at least get an interview.”
With backing from firms like HP, Google, Facebook, Intel and Intuit, the Anita Borg Institute even suggested that it might be possible to create a software tool designed to weed out any unconscious bias against hiring or promoting women in the tech world.
This “software tool for detecting bias” was proposed at the Institute’s forum. It can use language recognition to zero in on everything from performance evaluations to letters of recommendation that exhibit gender bias. An online tool like this can be found at Harvard’s Project Implicit.
“We envision building on such research to create a system where specific language can be fed and analyzed for the existence of bias,” the report said. “Using machine learning and text analysis methods would help organizations and individuals address the existence of bias before the damaging language is formally used in recommendations or evaluations.”
Additionally, the software would be a “high-impact diagnostic tool for calibrating organizations with regard to hiring and promotion decisions.”
A Day in the Life of a Project Manager
We all know that project managers are responsible for managing projects through to completion while remaining on time and within budget, but how exactly do they do it? What does a typical day look like for a project manager?
Here’s a sample of what a typical day might look like for a project manager.
The Early Bird Gets the Worm, Success Comes to Those Who Prepare Well and Put in Effort
8.30 am: Starting the day
After settling in for the day’s activities, it’s time to plan out the day. Start up the computer, email clients, draft team schedules, organize time sheets and create the to-do list.
To-do lists help managers and their teams stay on track. If a manager notices that one team member has yet to deliver an assignment, they can address this issue first thing in the morning; otherwise, delays can build up and affect the project. Likewise, lists help managers see the next course of action for projects.
9:15 am: Time to get moving
Efficiency is a must and there is no time to be wasted in project management. After a quick review of project plans and to-do lists, the manager must be prepared to get his team moving right away.
Round up team members, review the project’s current position and emphasize the next course of action. In order to get the team moving on assignments, strong project managers set deadlines throughout the day.
Morning team meetings are also necessary to make sure each member understands the project and their assignments. It’s also a time to answer any questions for clarity or to get feedback or concerns from individuals.
While daily group meetings can be important, they are not always necessary and can be counter-productive. If the team is on the same page and everyone is ready to tackle the tasks of the day, spend a short period re-grouping so that the team can get on and complete their assignments. There’s no need to spend hours planning and reviewing.
10 am: Meetings, meetings, meetings
More than one project manager will be more than likely in the office and they will all need to work together for the benefit of the programme. This is why meetings with other managers and higher ups are necessary in a project manager’s day.
Meetings allow each project manager to go through the status of their respective projects and to track the weekly schedule and other deadlines. It is also a time to address any business-critical tasks that might come up.
It’s worth considering that only 7% of communication is spoken. The other 93% is made up of tone (38%) and body language (55%). So although facts and figures are easily communicated via email, letter or phone, an actual discussion or negotiation is best handled where you can see the other person and therefore are able to see for yourself what their tone and body have to say on the matter.
10:30 am: Tackling the small stuff
Meetings will be on and off throughout the day for project managers, which is why it’s important to tackle the small tasks in between appointments. Small tasks include wrapping project reports, booking future meetings, answering correspondences with other colleagues, reviewing items and team reports among other things.
It’s also important to schedule post-mortem meetings with the project team to review the success of projects in order to apply any lessons learnt to future projects.
11 am: Project kick-off meeting
When one project ends, another begins, which means it’s time for yet another project kick-off meeting. Kick-off meetings can take on various forms, depending on the type of business. However, they all share the same basic needs.
Every individual involved with the new project should be in attendance and have the latest version of project specifications in written form. As project manager, it might be wise to send this to team members several days before the kick-off meeting to ensure everyone has time to review.
During a kick-off meeting, it’s important to review the overall goals for the project, both commercial and technical details, break down functional requirements, and spend time for discussion and questions. By allowing team members to communicate questions and share ideas, it opens the lines of communication and may bring up potential concerns that might have been missed in the initial planning stages.
Conclude kick-off meetings with a definition of the next steps and be sure individuals are aware of deadlines and their assignments.
11:30 am: Reviewing project specs, budgets and scheduling submissions
Other important tasks to tackle in between meetings include reviewing specifications and budgets and schedules for future projects. If a project begins that day, now would be a good time to apply the finishing touches to the project documentation before presentation and approval.
When it comes to establishing project estimates and budgets, a project manager must bring all of his experience into play in order to create a realistic budget that includes wiggle room for factors such as project complexity, team experience and skill levels, stakeholders involvement, time needed, third-party services needed, and contingency allowances among many other things.
It’s Not Easy to Squeeze in a Lunch Break, but It’s Often Necessary for the Project Managers Health and Sanity
12 pm: Lunch
In the midst of the seeming chaos that is project management, be sure to fuel up for the rest of the day’s work. Lunch is also a great span of time to check in with team members to make sure they are still on target for later-day deadlines.
2 pm: Launching the next project
After digesting lunch, it’s time to launch the next project. Get the whole team ready to go live and present the project to the client and begin testing aspects of the project in a live environment. It’s a time to spot problems and address them and review schedules and deadlines and other project needs.
3 pm: Time for everything else
The final two hours in the office are spent addressing everything else on the project manager’s plate. A project manager must be good at multi-tasking and whatever duties couldn’t be accomplished throughout the day are reserved for the final hours. Most of the time, lower priority tasks are reserved for afternoon hours. These tasks could include project update meetings with various departments, logging finances, reviewing monthly project schedules, approving time sheets, writing weekly reports, sorting purchase orders and communicating with suppliers. There are so many other small to-do list items that project managers are responsible for, but are often overlooked.
Spending Time at the End of the Day as Well as the Beginning to Review and Plan Will Only Help You Succeed as a Project Manager
5 pm: Review the day, plan for tomorrow
Before heading home, review the day’s list and what’s been accomplished. Anything that has been added or was left unfinished should be scheduled for the next day or sometime throughout the week. Reflect on your team’s work and clear the email inbox. Use a filing system that makes sense for you and be ruthless about deleting stuff. The beauty of an empty inbox is a thing to behold. It is calming, peaceful and wonderful.
Why Should I Hire a Project Manager for My Church Project?
Is it worth hiring a project manager when any seemingly knowledgeable pastor or church member might do?
The truth is, project managers can be a valuable asset to any organization. Whereas the average church member who is only familiar with certain tasks might be overwhelmed by the complexity of major organizational assignments, project managers are trained to handle programs with elaborate factors such as high budgets, increased manpower and layers of duties.
An Astounding 97% of Organizations Believe Project Management Is Critical to Business Performance and Organizational Success. (Source: PricewaterhouseCoopers)
On the flip side, some professional bodies disagree, arguing that professionals like pastors, marketers, and accountants are able to manage projects just as well as any project manager with some effort.
Barely over Half (56%) of Project Managers Are Certified (Source: Wrike)
“It’s a raging debate,” said Tony Marks, author of the 20:20 Project Management guide.
“Some industries, such as oil and gas, are hesitant to hire outside project management specialists because they may lack industry knowledge. Instead, these industries prefer to employ technical experts and put them through project management training.”
“The danger is that these people are more likely to get sucked into their comfort zone dealing with the nitty-gritty and technical detail they understand and are fascinated by when they should be managing the project,” said Tony Marks.
In addition to being trained to juggle tasks efficiently, project managers spend an enormous amount of time honing their skills. Much more goes into the craft than obtaining Prince2 or APM certifications.
According to Mike Savage of Thales Training and Consultancy, the International Project Management Association requires its professionals to have at least 15 years of experience and training. The association has four grades from D to A. At the A level, project managers must have a minimum of five years project management experience, five years of program management and five years of portfolio management.
“So to Say That Anyone Can Be a Project Manager Is like Saying Anyone Can Be a Brain Surgeon, Said Savage.”
But just because there are individuals specializing in project management doesn’t mean non-specialists can’t learn the techniques as well. Ian Clarkson of training course provider QA encourages everyone to learn project management practices.
“The skills, leadership, planning and stakeholder engagement techniques are vital to all disciplines,” he said.
“Projects which are run by engineers with project management training are less likely to be successful than the reverse,” said Lloyd’s Register energy program director Roger Clutton. “If there is a lack of technical expertise that will show up in the risk assessment. But a lack of project management skills is much less likely to be detected.”
With that, it seems that the argument on whether or not hiring an outside project management is necessary will continue. But the debate only seems relevant to rival professions as there is projected to be 15 million new project management jobs within the decade. (Source: Project Management Institute).
No matter how you look at it, though, it seems that trained and experienced project managers must be worth their weight in gold.
The Good, the Bad and the Ugly of Project Management for Christian Leaders
It’s Monday afternoon at the office. The week has only begun, but you’re already swimming in a sea of memos, spreadsheets, and schedules. Just as you’re daydreaming about what leftovers you might reheat for a late dinner, your boss pokes his head into your office. He or she mutters something about quotas and deadlines before he or she drops the bomb about a “little project” he or she needs you to complete by the end of the week. And just like that, you know you’ve been handed a nightmare but for whatever reason accept the challenge.
“According to the Cranfield School of Management in the Uk, 68% of Projects Are Destined for Failure Before They Even Start.”
The lack of project management training or experience of many Christian leaders can be an enormous stress factor for them. Whilst natural organizational ability is enormously helpful, in itself it is no guarantee of any project being both successful and low stress.
What is a nightmare project? It’s something we’re all familiar with. The boss assigns us some vague task and a deadline but leaves the means to a solution up to our creative intellect.
So how do you solve the problem of this dreaded “project”?
1. Understand the scope of the project
First things first, create a list to layout your ideas on how to go about the job at hand. Write out questions you might have that need to be answered, people you might need to work with or talk to in order to understand what work must be done.
Without fully understanding what work must be done, it is impossible to accurately estimate a project’s schedule or budget.
After creating a list, share your ideas with colleagues. Work with peers who have the same goal and share the same work ethics as you. Too often, when faced with an unrealistic project, we tend to work with just about anybody who wearily agrees to have their name on board. The enthusiasm of a new project quickly fades when actual work is needed. Instead of “How can I help?” were met with “I’m busy right now” and “Can it wait until next week?” The sponsor, project manager, and project team must share a common understanding of the scope of the project.
2. Get estimates from the people who will be doing the work
To avoid the stress of friendly fatigue, create a solid plan of action with your co-workers. Assign duties and responsibilities and set a deadline for each task.
4. Re-estimate as soon as you realize an estimating assumption was wrong
Don’t get discouraged if people and other things fall through. Even though it’s frustrating with the broken promises, missed deadlines, mistakes, and poor quality outputs. As soon as you realize a mistake was made, assess the impact and re-estimate the project.
“Unfortunately When Project Managers Spend the Majority of Their Time Trying to Achieve the Unachievable, the Result Is Frustration and Potential Burnout.”
But say you’ve followed those steps and were able to remain positive throughout this grueling week. You completed the assignment, whether enthusiastically or completely drained of all energy, only to be told the higher-ups decided to go a different route and don’t need the results of your project after all. “Good effort, though,” your boss tells you as he or she hands back your laminated report.
If you find yourself in this situation, just remember to never say “yes” to a “little project without first taking a look at what you’ve been handed.
Top 6 Most Impressive Megaprojects of 2015
Megaprojects are crucial to the future of most cities, states, and individual livelihoods, however, they also attract a lot of public attention because of the substantial impacts they have on communities, environments, and government budgets. The objective of these projects is to unlock higher growth paths for the economy, as such, they require care in the project development process to reduce any possible optimism bias and strategic misrepresentation.
The problem is that these projects often go off the rails, either with regard to budget, time or both.
The risks associated with MegaProjects, those costing 1 billion or more, are well documented. In one influential study, Bent Flyvbjerg, an expert in project management at Oxford’s business school, estimated that nine out of ten go over budget.
The first factor is that the size of a MegaProject can be so large and unique that it is difficult to model the costs and logistics. Another factor is that MegaProjects are backed by governments which are not typically known for their success in budgeting or efficiency.
In today’s post, we’ve identified the Top 6 most impressive MegaProjects of 2015. These MegaProjects will transcend time and continue to bestow wonder upon new generations.
1. Mall of the World, Dubai

Dubai has a very ambitious project on its hands. Dubai’s Mall of the World will have its very own Oxford Street and Broadway. It will also have galleons and waterfalls. However, the most challenging part of this project is that the area will be covered by a giant retractable roof during the summer months and be climate-controlled creating the world’s first temperature controlled city.
Dubai Mall of the World Set to Put Uae Retail ’20 Years Ahead’ of Gulf Region
Launched with a fanfare by the emirate’s ruler, Sheikh Mohammed bin Rashid al Maktoum, it is the first state-sponsored mega-project to emerge from Dubai since the pre-crash bubble. After years of stalled projects the big plans are back and they are more ambitious than ever before.
It is thought the huge construction will attract 180 million visitors a year and developers hope it will secure Dubai’s futures as a tourism hub.
The Mall of America (MoA) is a gigantic shopping mall owned by the Triple Five Group and is by far the largest mall in the United States. However, the $325 million expansion of the nation’s largest shopping center is now underway. The project consists of a luxury 342-room hotel, an office tower and more than 50 shops and restaurants. Some 1,000 jobs are expected to be created during the construction phase of the project, and 2,500 permanent jobs from retail, hotel and office operations.
The Triple Five Group, owned by Canada’s Ghermezian family, owns and manages the Mall of America, as well as the West Edmonton Mall. MoA is located in Bloomington, Minnesota (a suburb of the Twin Cities).
3. Zurich North America, Chicago, IL


The $333 million site is currently under construction and will be the largest build-to-suit office project in Chicago. Zurich a north america insurance company headquarters includes a 735,000 square foot building rising to 11 stories at its tallest, shaped something like the letter A resting on its side.
Zurich looked at a multitude of factors and in the end made the decision that investing in a new state of the art regional headquarters would be the right choice. The project is due to be completed late summer of 2016.
4. Dubai World Central Airport


This massive $32 billion structure sent its first commercial jet into the air in late October 2013. The project isn’t scheduled for full completion until 2027 and is expected to become the world’s busiest airport, however, with plenty of other contenders quickly taking shape in Asia and the Middle East, it’s has stiff competition.
Dubai World Central Airport is expected to shuttle 160 million passengers through Dubai every year making it the busiest airport on earth.
5. Bao’an International Terminal 3

Bao’an plays a pivotal role in the Pearl River Delta: It serves both Shenzhen and Hong Kong, via a connecting ferry. Terminal 3 is an expansion project designed by the Italian architect Massimiliano Fuksas. The centrepiece of the expansion is a new runway, which is built on a 108,000-foot piece of land reclaimed from the River Delta.
6. Crossrail

Crossrail tunnelling began in 2012 and ended at Farringdon, London in May with the break through of tunnelling machine Victoria. Eight 1,000 tonne tunnelling machines bored 26 miles or 42 km of new 6.2m diameter rail tunnels under London.
London is the fastest growing capital city in Europe and today it is home to 8.6 million people with the population expected to reach 10 million by 2030. TfL’s work is critical to supporting the continued growth and regeneration of London.
As we reflect upon these impressive feats by mankind, we can only imagine what the next big wonder will be. Is it the secretive Nicaragua canal? Could it be Elon Musk’s proposed Hyperloop concept? Or perhaps it will be a new state of the art high speed train developed by China, USA or the UK?
Did we miss one? Please let us know by commenting below.