From Outreach Ideas to Action in Three Easy Steps
A good idea is great. A good idea that’s executed perfectly can change the world. But a simple idea alone is useless.
A Good Idea That’s Executed Perfectly Can Change the World
There’s an idea that flops and an idea that becomes the next biggest thing. It’s all about how it’s executed. If it doesn’t come with a plan, or if it appears too difficult to introduce, someone else will do it, leaving you with a has-been idea that can no longer be implemented. This is why every ‘brainwave’ ‘eureka’ moment idea needs to be teamed together with a worthy execution”¦if not, don’t expect much.
Pushing an innovative idea forward into something else remains one of our biggest challenges. Admittedly, it can be a super exhausting process, which is why it’s always a great idea to invite the crowd to not only come up with the wonderful ideas, but to also help develop them as well.
There are a few key stages that need to be followed when it comes to getting your crowd in on the idea decision-making and development game.
1. Create a Unique Team
Almost anyone can research and refine new innovative ideas. However, you can take it a step further and invite the crowd to join in the fun and be a part of your team. This will give your idea more validation. It will also decrease any potential risk, and at the same time it could be a huge timesaver when it comes to marketing and finances.
In short, each and every idea should be unique enough to sway people to join a team that supports the idea.
2. Fine Tune that Idea
They say that behind every great idea catapulted onto the market, there was an equally great plan. Every idea requires some sort of plan. It could be just a basic one that briefly outlines the various possibilities connected to it, or it could be a more complex plan that delves into the intricacies of it.
A good plan should include a business plan. This might seem like a given, but you’d be surprised as to how many people don’t have a good business plan to back up their ideas. Plans should also include target audiences, marketing ideas and much more.
You need to approach every idea in a methodical way. You’ll need a unique set of criteria that pertains to one idea – it’s not a case of one-size fits all. You’ll need to answer any question that arises, and until this is done, you can’t move forward and successfully turn your idea into reality.
Use and involve your crowd. Ask them to research various aspects of the idea, and then have them report back and share their ideas and findings with the rest of the group.
3. Don’t Stand for Mediocre
There are literally hundreds upon hundreds of okay ideas. There are even hundreds of great ideas. But, an average or good idea is not enough, which is why it’s absolutely essential to select only the best of the best ideas. It doesn’t matter if it’s only one mind-blowing idea because as the old adage goes, quality is better than quantity.
Quality Is Better than Quantity
The good and even the great ideas might struggle. Such ideas are difficult to get funding for, and it’s more challenging to prototype and deliver them. If you want to make your idea come alive, you need to have defined criteria, which allows for choosing the best idea to follow up on. After the criteria has been established, it’s time to use the crowd again aka Christian community. Ask them to respond accordingly and honestly – does the idea meet all the listed criteria?
If yes, that’s great, you’re moving towards success. If not, it’s back to the drawing board to get it right.
You need to act now and remember this: it’s okay to simply start by putting just one outreach idea into action.
What kinds of challenges do you and your team face when trying to develop your ideas further?
Hidden Sins of Using Spreadsheets to Manage Projects
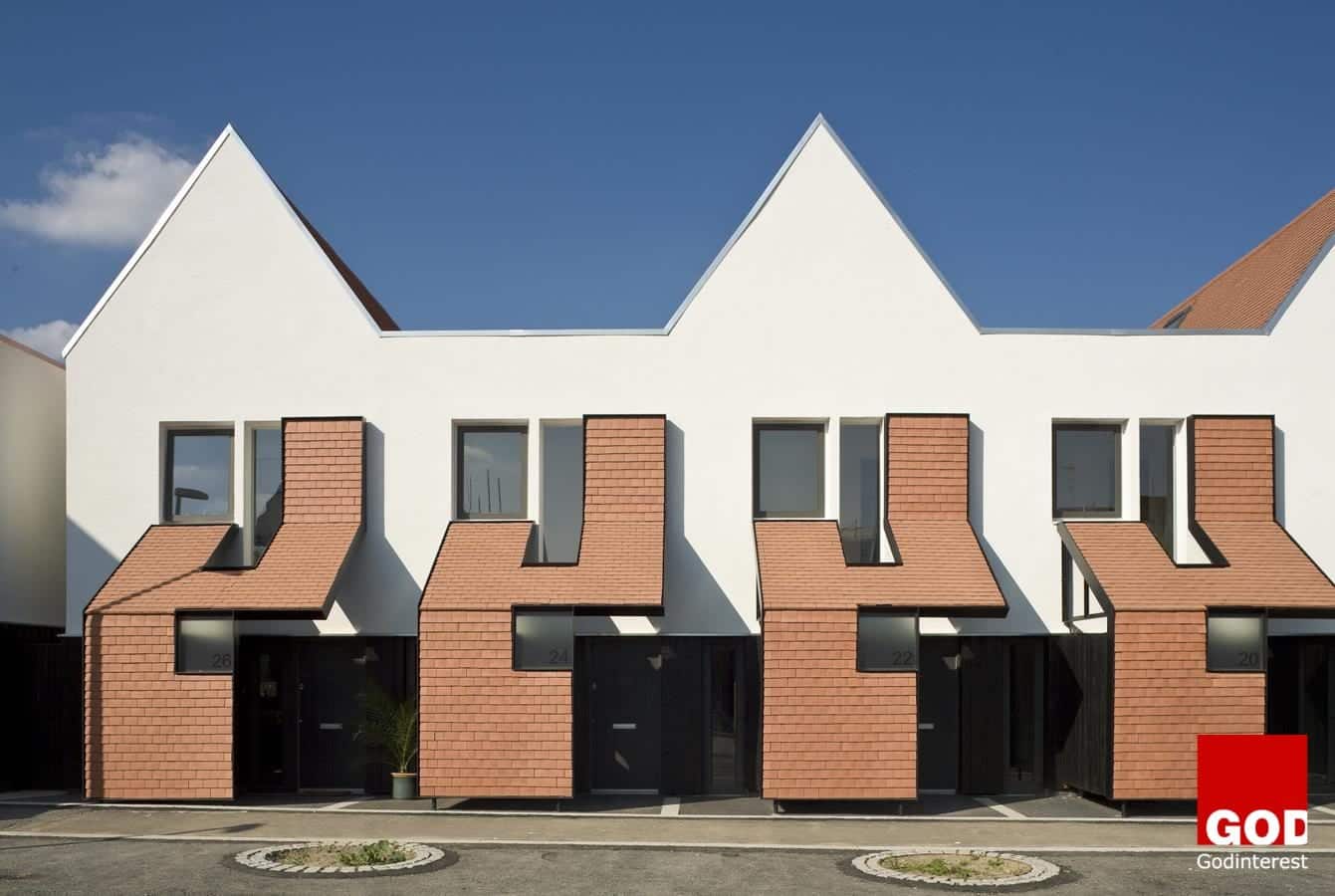
Prefab Comeback
Prefab housing suffers from bad stigma due to the fact that some people saw the prefabs as ugly and characterless, and were afraid they would become slums – hardly the promised housing fit for heroes following the second World War. However, building homes from pre-made parts can save time and money. The term prefab or prefabrication often evokes thoughts of poor construction, substandard living conditions and a long-standing “temporary” solution.
Prefab dwellings are making a comeback driven by a lack of affordable housing, a rapidly growing economy and changing demographic trends.
Methods Methods of Construction (Mmc) Offer Significant Potential to Minimise Construction Costs
The term ‘Modern Methods of Construction‘ refers to a collection of relatively new building construction techniques that aim to offer more advantages over traditional construction methods. Off-site construction (OSC) is a modern method of construction, based on off-site manufacturing of building elements.
With exponentially lower construction costs, quicker construction, reduced labor costs and having the ability to achieve zero defects, MMC is gaining a lot of attention as the potential answer to the UK’s housing crisis.
In a valiant attempt to strip away prefabricated housings’ bad rep are MMC with contemporary sleek designs, and constructed to withstand the test of time. MMC housing has the capability to deliver both quality and quantity housing to the tune of ‘ £50,000 per unit.
MMC units hold the promise of being extremely energy efficient and environmentally sustainable. Many versions of MMC take into account how to utilise natural resources and reduce each unit’s carbon footprint. In addition, MMC also addresses environmental concerns by creating much less waste than a standard brick-and-mortar project. While it is plausible that a traditional build could hire a waste removal company who would have the ability to recycle up to 90 percent of the construction waste; with MMC projects, this will automatically happen.
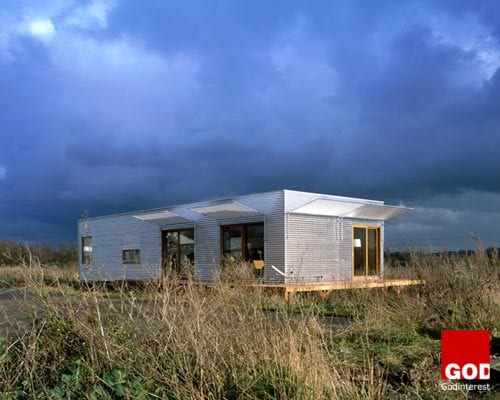

There have already been a number of successful examples of MMC housing constructed in various parts of the United Kingdom. The M-house (pronounced “mouse”) is designed and constructed to last an upwards of 100 years. While Architect Alford Hall have created quality MMC apartment buildings proudly showcasing a patio and private entrance for each flat.


While many of the MMC homes are still in their early years the upkeep and maintenance will be reduced by 50% since the OSC process lowers the risk of non-conformities.
MMC homes are being fabricated and designed to accommodate many different lifestyles, such as, two-story homes, tall six-story apartment buildings, single-family homes and log cabins are all available options for families looking at MMC.
While there is a plethora of design options available all MMC OSC projects have a common theme. The internal workings of the homes are fabricated off-site, while only the “outer skin” comes to fruition on-site. To even further streamline the process, it has been suggested that having a “catalog of pre-selected materials increases supplier relationships and makes the design process more streamlined.”
With the small sample available with progressive MMC systems, it is currently reasonable to conclude that using modern methods of construction to build homes can cost more than traditional home building procedures; due to the need for specialised MMC design consultants. However, outside of costs, MMC remains a faster home building method than traditional brick and block house building and is slowly becoming a relevant front-runner to answer the UK’s housing shortage.
75 of the Most Inspirational Leadership Quotes
MoVoCoSy – Modular Volumetric Construction System
Momo Apartments
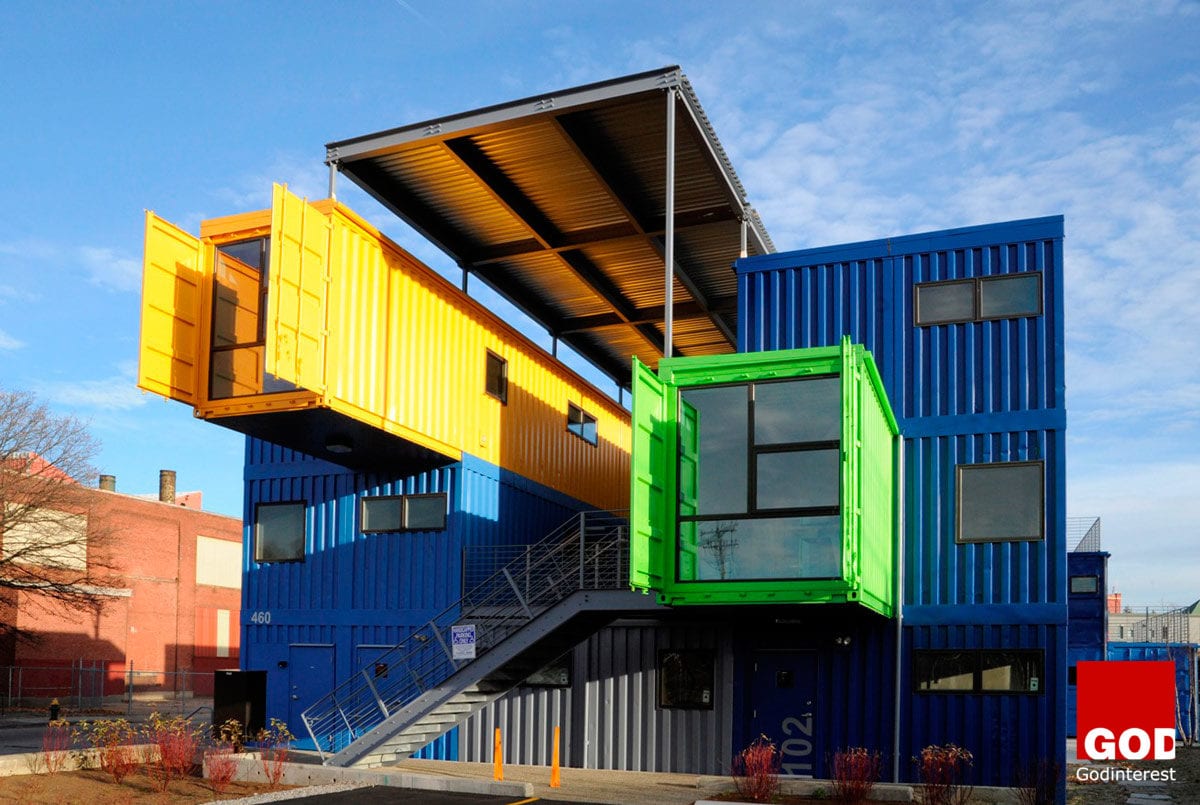

Zero defects are the primary battleground between traditional and modern construction methods. A relative concept, zero defects is, however, a target that the construction industry has set for itself. Primary considerations are structural stability and keeping the water out. Proper functioning of services, components, fixtures, and fittings are essential.
Energy and sound performance are also vital, as well as issues of safety, access, and security. This is a campaign which will be fought in years to come… and in the meantime here is another prefab scheme which feature’s in these skirmishes.
Mobile Modular (MoMo) is a research development project for a relocatable system of mass housing constructed from specially fabricated shipping containers. This type of system allows flats to be erected speedily on short-life sites and to be demounted and re-assembled in different configurations on other sites in the future.
The key objectives:
Remove MoMo apartments from a site where housing has been provided for 5 years.
Refurbish Each module at the supplier’s yard or an alternative temporary site.
Re-locate The apartments in any new configuration to provide decanting, short-term housing, permanent apartments. This type of system can also become a permanent housing solution.
Originally commissioned by the Peabody Trust, after feasibility stage, the team was invited to take the project forward with their own initiative. The team formed a consortium with the aim of developing a prototype to demonstrate the principles, and to market the MoMo scheme as a one-stop shop package to interested parties.
Modular Penthouse, New Inn Yard, Shoreditch
A modern approach to prefabrication is flourishing in the capital with a new generation of designers and manufacturers building on the pioneering work of organisations such as the Peabody Trust. City apartments lend themselves well to factory built components where the quality of construction needs to compensate for higher densities and restricted space for accommodation.
Offsite construction is also less disruptive in the city environment with increased construction speeds bringing a corresponding reduction in noise and transport and material handling in the neighbourhood.
It is evident that many designers are also promoting the modular unit not only as a way of producing affordable housing but also as a fashionable lifestyle product.
No more connotations of the stigmatised post-war temporary housing; the prefab is now an aspirational dwelling which is becoming increasingly desirable.
3D-modelling has also opened up mny possibilities for housing construction. The software and expertise now exists to construct houses and apartments as a virtual model before any construction work begins. It is therefore possible to join up the process of construction starting with the purchaser/occupier who make choices of layout, fittings and furnishings from the computer visualisation. Data from the virtual model then becomes specification and fabrication data which is passed to the factory and eventually delivered to site.
Modular Penthouse, New Inn Yard, Shoreditch High Street



Material efficiency and ease of construction were prime functional objectives. The Shoreditch Penthouse project explored the possibilities of inserting structures into a dense urban fabric by re-using roof tops of existing buildings. Four prefabricated volumetric units provide for various functions; they interlock on site to generate an integral live/work space in conjunction with the existing floor below. Starting with the simple idea of maximising capacity through optimisation of the existing structure, they integrate new spaces whilst sharing foundations, services and circulation areas. Core principles of sustainable construction can therefore be applied from the very beginning. Finally, through off-site construction expensive site management can be kept to a minimum, whilst maintaining a high quality of craftsmanship in a controlled factory environment.
Architect: Oceans Group
Structural Engineer: Atelier One
New Urban Homes
A 3-dimensional system involving modules or pods which is the basic building block of much prefabricated construction. Several designers are experimenting with making this form adaptable to more than apartments. The majority of new high-density developments in London provide only flatted accommodation and ignore the needs of families. While the argument for more homes at a higher density is understood, should this policy exclude families? And what sort of city would London become?
For the past three years the architects have been examining opportunities for high-density urban family housing on a number of initiatives in Southwark, Ealing and Harrow. Using modular construction techniques the ‘courtyard’ homes deliver more space for less cost. Arranged in typical urban blocks and at no more than three storey densities they produce some 80 dwellings per hectare.
The house delivers flexible open plan ground floors with circulation spaces that are naturally lit. With both a courtyard and an upper terrace each house benefits from at least 40m2 of external space. More importantly this space is entirely private to the dwelling and is directly related to the kitchen, living and bedroom spaces. These are external rooms, a far cry for a patch of green, sandwiched between close boarded fencing and overlooked by the neighbours.


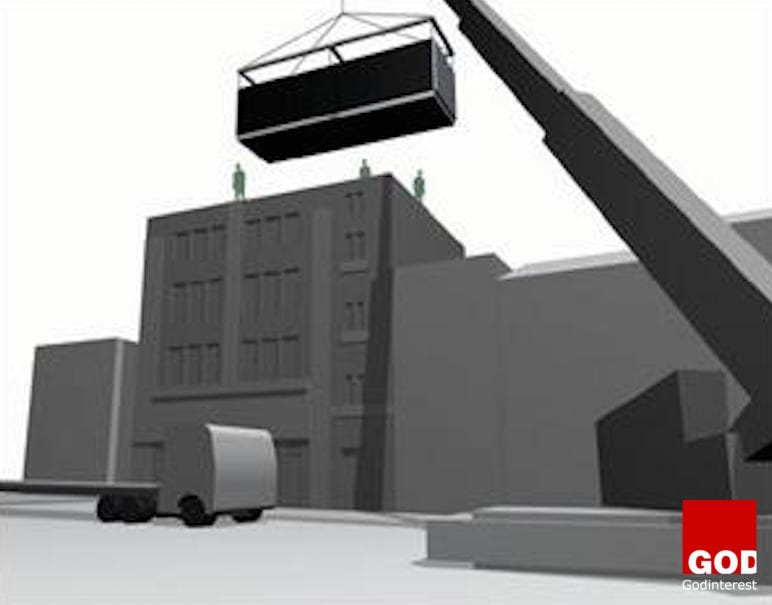
The five steel modules required for each house are delivered on low loaders and craned onto preprepared footings. All modules are fully fitted-out in the factory. The technology allows different fenestration arrangements, cladding options and roofing forms.
Architect: Proctor and Matthews
Principal Supplier: Spaceover
The Ideal Home Exhibition: Live-in Quarters
The Ideal Home exhibition has not always been the first place to look for cutting edge housing design in recent years. But in 2002 two ground-breaking apartments were demonstrated – the Live-in Quarters concept house and the Space over keyworkers prototype. Over 10,000 visitors to the exhibition registered their interest in gaining further information when construction started, thus proving the enormous demand for high-quality accommodation of this kind.
Live-in Quarters (LQ) is both developer and manufacturer waiting to supply the London market. It has produced a family of concept houses for low-cost accommodation designed to suit single people and key workers. It has been set up specifically to deal with the problems of London and anticipates high rise schemes of six to 12 stories built in a galvanized lightweight steel frame. LQ propose to have their own factory located in East London. LQ customers are seen as those who wish to get on to the first rung on the property ladder, frequently key workers and single people earning less than £30,000 a year. They took a brief from Keep London Working, the result of which was the 26m2 flat exhibited at the Ideal Home Exhibition which provided total privacy and security with individual showers, WC, and kitchens. They also exhibited a two-story unit where the first floor contained an executive 33m2 studio. In addition to the normal options for mortgage purchase, shared equity and rent, they are planning to offer a new form of tenure called equity rent. In simple form, this enables residents to convert their rent into a percentage of the equity depending on the period of time they stay in the property without any risk of negative equity.
Architect: The Design Buro, Levitt Bernstein