7 Secret Things You Didn’t Know About Successful Procurement Teams
Some senior members of staff see procurement expenses as a necessary evil and overlook any efficiency improvement methods for this sector. This is not an uncommon way of thinking, as procurement and the supply chain is a massive part of any company’s costs and can total up to 70% of an organisation’s total spend.
These managers are missing out on effective changes that can shift procurement to a significant supplier of growth and profit for any business.
Follow these 7 steps to improve your procurement team.
1. Embrace Change
It’s so important for procurement managers to embrace and invest in technology changes currently taking place in the industry.
Managers should hold a full assessment of deficiencies in their processors and search for technology that meets the needs of the business, rather than fitting the business around new technology. For example, if you are having trouble with historic and retrospective analysis, invest in predictive analytics.
2. Consider Outsourcing
Outsourcing may not be an avenue you have ever considered in regards to procurement, even though it happens all the time with HR and IT departments. Even so, many procurement managers are still apprehensive to apply it to their supply chain.
Outsourcing certain aspects of procurement can be a way of improving existing systems and processors rather than a cost reduction measure. It can also allow your business to access highly skilled procurement experts when it would be counter-productive to hire someone internally. These individuals are often very focused on delivering results, and if you plan outsourcing correctly, the increase in productivity will outweigh the costs of outsourcing.
If a procurement manager feels like there are areas in the business where costs can be cut, it might be worth bringing in a consultant. There are also outsourcing services that offer expert domain knowledge and vendor contact opportunities.
3. Ensure Your Supply Chain Is Properly Staffed
The efficiency of a supply chain is very much dependent on the quality of its staff. As a procurement manager, it’s important to ensure that the supply chain is staffed with highly skilled individuals, and that these staff have regular access to education and training.
Procurement professionals will be tasked with a wide variety of roles, including:
- Planning delivery timetables
- Ensuring stores have enough stock
- Overseeing the arrival of shipments
When hiring employees, it’s important to ensure they have skills such as communication, attention to detail and teamwork. They must also be willing to learn and improve throughout their career.
4. Create Risk Management Policies
One of the key ways of making a procurement team more efficient is to prepare for the unexpected. Procurement managers should establish proper levels of control to manage risk and ensure that all these policies are periodically reviewed. These risk management fail safes should include:
- The financial impact a risk might have
- The likelihood to the risk occurring
- A priority list for managing risks
All staff members should be aware of these risks, and the processes in place if the risks occur. For example, if a major supplier goes out of business, your staff should be aware that there is a process for contacting secondary suppliers so you are never left without stock.
5. Establish Relationships with Key Suppliers
Staff who deal with suppliers on a daily basis need to have brilliant relationship building skills. Procurement employees need to work closely with suppliers to try and keep communication consistent and amicable, even if issues arise at either end.
Suppliers can help procurement teams reach their performance goals, and they are often very knowledgeable, with expertise to share about their products. Procurement teams can learn a lot from them, like the audience, seasonality and key selling points of products; it’s worth working on these relationships.
6. Stick to Ambitious but Manageable Targets
If a team has a tough but not unattainable goal to work towards they can prioritise, measure and focus on their tasks with a clear end in mind. This helps staff members feel more motivated and gives meaning to their work.
There will also be a sense of achievement when the targets are met, bringing your team closer together and improving teamwork.
7. Efficiency Is Attainable
The creation of a brilliant supply chain depends on your company’s understanding of procurement, along with the procurement team’s estimation of the total costs associated with each supplier and their contacts.
With help from technology, outsourcing, a great team and strong relationship building skills, your procurement team should improve its efficiency and business impact.
Concrete Proves Its Versatility Is Endless
If You Want to Make Enemies, Try to Change Something: 17 Inspiring Change Quotes to Live By
- “One of the reasons so many celebrities keep going in and out of rehab is that they leave out the critical element to lasting change: God.” – Unknown
- “There is nothing more difficult to take in hand, more perilous to conduct, or more uncertain in its success than to take the lead in the introduction of a new order of things.” — Niccolo Machiavelli
- “Change has its enemies.” — Robert Kennedy
- “He who rejects change is the architect of decay.” — Harold Wilson
- “Change is not made without inconvenience, even from worse to better.” — Samuel Johnson
- “The world hates change, yet it is the only thing that has brought progress.” — Charles Kettering
- “God supplies everything you need for successful change, and when you make changes with his help, it says changed.” – Unknown
- “It is always easier to talk about change than to make it.” — Alvin Toffler
- “It must be considered that there is nothing more difficult to carry out nor more doubtful of success nor more dangerous to handle than to initiate a new order of things.” — Machiavelli
- “The path of least resistance is the path of the loser.” — H. G. Wells
- “When you feel weak in the face of change, God is omnipotent, or all-powerful. “If God is for us, who can be against us?” the Bible says. (Romans 8:31, NIV) Knowing the invincible God is on your side gives you tremendous confidence.” – Unknown
- “Paralyze resistance with persistence.” — Woody Hayes
- “Culture does not change because we desire to change it. Culture changes when the organization is transformed – the culture reflects the realities of people working together every day.” — Frances Hesselbein
- “The greatest danger in times of turbulence is not the turbulence – it is to act with yesterday’s logic – Peter Drucker
- “The rate of change is not going to slow down anytime soon. If anything, competition in most industries will probably speed up even more in the next few decades.” — John P. Kotter
- “Your success in life isn’t based on your ability to simply change. It is based on your ability to change faster than your competition, customers, and business.” — Mark Sanborn
- “If you want to make enemies, try to change something.” — Woodrow Wilson
Don’t make change harder than it has to be. Do it the right way. Ask God for help.
How Technology Has Changed Procurement in the Last 10 Years

Over the past decade business procurement has experienced rapid technological upheaval that, in the main, has made life easier for everyone involved.
The first ever Global Procurement Technology Summit was held in March 2016. It shows the emphasis procurement is now putting on understanding and utilising new technologies, and that it’s clearly a huge talking point for professionals across the world.
Looking in greater detail: which technology has been responsible and what has the effect been on procurement and buying professionals?
1. More informed decisions are being made
The digitalisation of procurement processes and integration of data-sharing across buyer behaviour, ratings and history of purchases over extended periods of time, has made for smarter and more informed decisions.
Despite the greater insight into decision-making, a study of US procurement professionals still revealed accurate forecasting to be the biggest challenge, something that’s possibly down to the rise in budget responsibilities over the last ten years.
The Coupa ‘Top 5: Constants and Change in Cloud Procurement’ report revealed that in 2003, budgets were reported as an average of $31m, compared to $100m in 2013.
2. Response times have drastically reduced
Procurement solutions are now quicker and easier than ever thanks to new marketplace technologies.
Buyers can take advantage of online purchasing possibilities, using websites like Amazon to source, purchase and arrange delivery of items.
The speed of procurement reflects the new speed in which consumerism moves ’’ the integration of digital mediums with online shopping has made the process of deliberation through to transaction much easier, a trend which has been reflected in the world of procurement.
3. Integration has brought its own problems
Technological integration has created many positives for procurement, but it’s also created challenges.
Millennials will make up 40% of the workforce by 2020, which is great for improving current procurement solutions as younger generations have higher expectations for technology and are early adapters.
However, the average age of procurement professionals in the UK is currently 44 – much older than the next generation of workers, who fully understand the capabilities of technology, and who will be easier to train and able to work with increased speed and accuracy.
The gap will close in the coming years, but procurement faces a struggle as older workers need to ensure their skills are relevant to the changing world around them.
Additionally, Hays’ ‘Procurement Salary Guide’ revealed that demand for procurement professionals has increased at all levels within the public sector, pushing salaries up. This demand is the result of a squeeze on public finances and attempts to cut costs following the slowdown in the economy.
4, Technology and the future of procurement
To conclude, technology is clearly a powerful enabler that’s here to stay. Plenty of companies are now seeing the importance of procurement technology as a means to improve their bottom lines, which was reflected in the inaugural Global Procurement Technology Summit earlier this year.
Integration of contract management, risk management and supplier lifecycle systems through investment in improved systems with added capabilities, has ensured more accurate sourcing is possible and due to the skills involved in running these systems, has driven salaries up.
Sophia Chapman is a guest contributor from Portfolio Procurement, expert recruiters in the compensation, benefit and reward sector.
The New Day: How Should I Think About My Failures?
Everyone wants to be a success. I have never met anyone who purposely set out to be a failure. Undoubtedly, this is why so much has been written on the topic “How to be a Success” and why these books are so popular.
However, The New Day daily newspaper closed just nine weeks after launching, Trinity Mirror confirms.
The New Day was a British compact daily newspaper published by Trinity Mirror, launched on 29 February 2016. It was aimed at a middle-aged female audience and was politically neutral. The editor, Alison Phillips, intended readers to get through the newspaper in under 30 minutes.
The new paper was initially available for 25p for two weeks, then rising to 50p. Two million copies of the New Day was given away on the first day, as the turquoise-branded upstart attempted to spark a revival in readership and gain ground against the mid-market Mail and Express offline.
Arrogance about their own ability to rescue a situation can prevent leaders from changing course
The New Day had no leading articles, no website, and columnists and believed it could successfully drag readers back to print? The sad truth is that it did not attract enough attention and failed to create a daily newspaper that could co-exist in the digital age, especially as tabloids and broadsheets continue to suffer a significant circulation decline.

Shareholders at Trinity Mirror’s annual meeting called the failure “demoralising”. Analysts said it was “embarrassing”.
Assume for a moment that the leaders of The New Day had no idea about the changes swamping the print media as a result of the digital revolution, and carelessly decided to invest millions into the venture without undertaking a risk assessment and also decided to ignore every indication that the paper was failing. That would have been embarrassing and demoralising.
However, the leaders decided to fail quickly and shut down the project they started.
Abandonment is a rare, difficult and a valuable management skill. The natural instinct of most people is to persist, particularly when the project is a collective commitment, as most corporate ventures are, but then it becomes even harder to hit the red “stop” button.
The New Day’s editor, Alison Phillips, said in a statement posted on Facebook that the team “tried everything we could” but were unable to reach the figures needed to make it work financially.
We dread failure. We don’t like talking about it. Some of us will internalise and rethink our failures in our heads time and time again. Others will swipe them away, moving onto the next thing immediately. In the public, we prefer sweeping our failures under the rug, silently, while nobody is watching.
While this might save our feelings momentarily, this is not the way learn and innovate.

According to Albert Savoia – ex Googler and innovation expert, most project innovations will fail.
“Most New Things Will Fail – Even If They Are Flawlessly Executed.” – Albert Savoia – Ex Googler
Does this mean you should stay away from trying new things (and failing in the process)? Certainly not. It just means you need to accept failure will inevitably be a part of the process.
In most cases, however, a combination of arrogance about personal ability to rescue the situation and blindness to the lengthening odds of success stops leaders from changing course.
The natural lifespan of most projects is finite, and the rarities are companies that survive.
The Art of “strategic Quitting” Will Become More Important as Careers Fragment and Companies Exert More Discipline
So if an idea is doomed, organisations usually treat the person who pulled the plug early on as a hero right? Not exactly, it’s complicated.
Roy Greenslade, Professor of Journalism at City University London, wrote a report in The Guardian explaining how The New Day had failed. He pinpointed the error of marketing a newspaper to people who inherently despise newspapers, and the short period of time between the announcement and launch, leaving no time to advertise the product. It was also published early in the evening thus missing out on late-night breaking news such as Leicester City F.C.’s shock win of the Premier League.
“Nothing so powerfully concentrates a man’s mind on innovation as the knowledge that the present product or service will be abandoned in the foreseeable future.” – Peter Drucker
The first thing the Bible wants to say is that all of us have failed. None is without failure. If you think you haven’t failed, two things are true of you. One is you are blind to your failures and the other is you probably haven’t taken enough risks to try enough hard things so that you would be aware of your failures.
Peter Drucker’s influence on business management is legendary. Peter realised that “systematic abandonment” a regular, unsentimental spring-clean is critical to the fostering of new business ideas.
Conclusion, every organization needs to have a regular “rummage sale” to determine which products, services, and programs are worth keeping and which ones must be abandoned.
The Nature of Good ‘Project Chemistry’
Has Nigeria Become the World’s Junk Yard of Abandoned and Failed Mega Projects worth Billions?
Dim1, N. U., Okorocha2, K. A., & Okoduwa3 V. O.
The Nigerian construction industry is mostly concerned with the development and provision of projects such as roads, bridges, railways, residential and commercial real estates, and the maintenance necessary for the socio-economic developments contributes immensely to the Nigerian economic growth (Bureau of Statistics, 2015). Butcher and demmers (2003) described projects as an idea which begins and ends by filling a need. However, a project fails when its idea ends without meeting the needs and expectations of its stakeholders.
Nigeria Has Become the World’s Junk – Yard of Abandoned and Failed Projects worth Billions of Naira!
Hanachor (2013), revealed that projects form part of the basis for assessing a country’s development. However, a damming report from the Abandoned Projects Audit Commission which was set up by the Ex-President Goodluck Jonathan in 2011 revealed that 11,886 federal government projects were abandoned in the past 40 years across Nigerian (Abimbola, 2012). This confirmed the assertion by Osemenan (1987) “that Nigeria has become the world’s junk –yard of abandoned and failed projects worth billions of naira”.
Abandoned projects including building and other civil engineering infrastructure development projects now litter the whole of Nigeria.
Physical projects do not only provide the means of making life more meaningful for members of the community where the projects are located, successful projects also result in empowerment and collective action towards self improvement (Hanachor, 2013).
This Issue of Abandonment Has Been Left Without Adequate Attention for Too Long, and Is Now Having a Multiplier Effect on the Construction Industry in Particular and the Nigeria’s National Economy as a Whole. (Kotngora, 1993)
PROJECT FAILURE
Project Failure might mean a different thing to different stakeholders. A project that seemed successful to one stakeholder may be a total failure to another (Toor and Ogunlana, 2008). Some stakeholders, more especially the project users and some private owners, think of failed projects as a situation where a completed building project collapsed, a situation where by a completed dam project stopped working after few days of completion, or a completed road project that broke down after few months of completion. Other experienced stakeholders, such as engineers and architects conform to the iron triangle by Atkinson (1999) which states that the most strategically important measures of project failure are “time overrun”, “cost overrun”, and “poor quality”.
Turner (1993) noted that a project fails when the project specifications are not delivered within budget and on time; the project fails to achieve its stated business purpose; the project did not meet the pre-stated objectives; the project fails to satisfy the needs of the project team and supporters; and the project fails to satisfy the need of the users and other stakeholders. Lim and Mohamed (1999) cited in Toor and Ogunlana (2009) clarified that there are two possible view points to project failure namely; the macro-level and the micro-level. They further explained that the macro view point reviews if the original objectives and concepts of the project was met. Usually the end users and the project beneficiaries are the ones looking at the project failure from the macro view point, where as the project design team, the consultants, contractors, and suppliers review projects from a micro view point focusing on time of delivery, budget, and poor quality.
In the early 1990s, the failure as well as the success of any project was determined by the project duration, monetary cost, and the performance of the project (Idrus, Sodangi, and Husin, 2011). Belout and Gauvrean (2004), also confirmed that the project management triangle based on schedule, cost, and technical performance is the most useful in determining the failure of a project. Moreover, a project is considered as an achievement of specific objectives, which involves series of activities and tasks which consume resources, are completed within specifications, and have a definite start and end time (Muns and Bjeirmi 1996, cited in Toor and Ogunlana, 2009). Reiss (1993) in his suggestion stated that a project is a human activity that achieves a clear objective against a time scale. Wright (1997) taking the view of clients, suggested that time and budget are the only two important parameters of a project which determines if a project is successful or failed. Nevertheless, many other writers such as Turner, Morris and Hough, wateridge, dewit, McCoy, Pinto and Slevin, saarinen and Ballantine all cited in Atkinson (1999), agreed that cost, time, and quality are all success as well as failure criteria of a project, and are not to be used exclusively.
FACTORS OF PROJECT FAILURE
Cookie-Davies (2002) stated the difference between the success criteria and the failure factors. He stated that failure factors are those which contributed towards the failure of a project while success criteria are the measures by which the failure of a project will be judged. The factors constituting the failure criteria are commonly referred to as the key performance indicators (KPIs).
Time and Cost Overrun
The time factor of project failure cannot be discussed without mentioning cost. This is because the time spent on construction projects has a cost attached to it. Al-Khali and Al-Ghafly, (1999); Aibinu and Jagboro, (2002) confirmed that time overrun in construction projects do not only result in cost overrun and poor quality but also result in greater disputes, abandonment and protracted litigation by the project parties. Therefore, focus on reducing the Time overrun helps to reduce resource spent on heavy litigation processes in the construction industry (Phua and Rowlinson, 2003). Most times, the time overrun of a project does not allow resultant system and benefits of the project to be taking into consideration (Atkinson, 1999). Once a project exceeds the contract time, it does not matter anymore if the project was finally abandoned or completed at the same cost and quality specified on the original contract document, the project has failed. Furthermore, Assaf and Al-Hejji, (2006) noted that time overrun means loss of owner’s revenue due to unavailability of the commercial facilities on time, and contractors may also suffers from higher over heads, material and labour costs.
Poor quality/Technical Performance
The word “Performance” has a different meaning which depends on the context it is being used and it can also be referred to as quality. Performance can be generally defined as effectiveness (doing the right thing), and efficiency (doing it right) (Idrus and Sodangi, 2010). Based on this definition of performance, at the project level, it simply means that a completed project meets fulfilled the stakeholder requirements in the business case.
CAUSES OF PROJECT FAILURE
A lot of research studies have investigated the reasons for project failures, and why projects continue to be described as failing despite improved management. Odeh and Baltaineh, 2002; Arain and Law, 2003; Abdul-Rahman et al., 2006; Sambasivan and Soon, 2007; all cited in Toor and Ogunlana, 2008, pointed out the major causes of project failures as Inadequate procurement method; poor funding and availability of resources; descripancies between design and construction; lack of project management practices; and communication lapses
The contract/procurement method
A result obtained from two construction projects which were done by the same contractor but using different procurement methods showed that rework, on the design part which occurs when the activities and materials order are different from those specified on the original contract document, makes it difficult for the project to finish on the expected time (Idrus, Sodangi, and Husin, 2011). This is as a result of non-collaboration and integration between the design team, contractor, and tier suppliers. The rework on the design portion has a huge impact on project failure leading to the time overrun. The traditional method of procurement has inadequate flexibility required to facilitate late changes to the project design once the design phase of the construction project has been concluded.
Nigerian most widely used procurement method is the traditional method of procurement (design-bid-construct) which has been confirmed to be less effective to successfully delivery of a construction project (Dim and Ezeabasili, 2015). And, the world bank country procurement assessment report (2000) cited in Anigbogu and Shwarka, (2011) reported that about 50% of projects in Nigeria are dead even before they commence because they were designed to fail.
The way the construction projects are contracted, in addition to the way the contracts are delivered, contributes to the causes of projects failure. Particularly, among the methods of project contracting is lump-sum or a fixed-price contracting method, in which the contractor agrees to deliver a construction project at a fixed price. The fixed-price contract can be low-bid or not however, once the contract cost has been agreed upon the contract award, it cannot be changed. And, contractors are expected to honor and deliver the contract agreement, failure to do so can result in a breach of contract which can result in the contractor being prosecuted.
Awarding a contract to an unqualified personnel also contributes to project failures. When a contractor places more emphasis on money and the mobilization fee after a construction project has been initiated instead of getting the right workforce and skilled professionals that will execute the project. Instead the workforce chosen will often not be base on competence and required skills rather it will be based on availability. Moreover, poor strategy and planning by contractors who have overloaded with work also contributed to one of the causes of project failure.
Poor funding/Budget Planning
A lot of public projects in the Nigerian construction industry failed as a result inadequate funding, and the difference between the national annual budget and the budget actual released. Most of the Nigerian public projects are signed even before the actual release of the national budget. The difference in budget of the contracted project and the actual budget release can get the contracted company stuck as a result of inflation of prices, scarcity of construction material at the time of the budget release and mobilization to site. Also un-planned scope of work which can be as a result of the contractor working on another contract when he is called back to mobilization to start work. Moreover, poor budget planning is a regular mistake made by some contractors by not undertaking feasibility assessments before starting the design. The construction project should be planned according to the available resources and not according to the unrealistic expectations a client has in mind.
Discrepancies Between the Design and Construction
Limited collaboration between the contractors, engineers, and the architect results in discrepancies between the project designs and construction on site, and further leads to rework. Changes on a project designs, and changing to the scope of work in the middle of construction processes on site can be dangerous, and can lead to time overrun, increase in cost, and most of all can lead to abandonment. Moreover, many cases have been seen where the designs from the architects are not buildable on site, while In some cases, most contractors are unable to adequately specify the scope of work for the construction processes on site. Therefore any default on the design by the architect can be an opportunity for the contractor to make more money which might cause the project duration to exceed the time specified on the contract document.
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
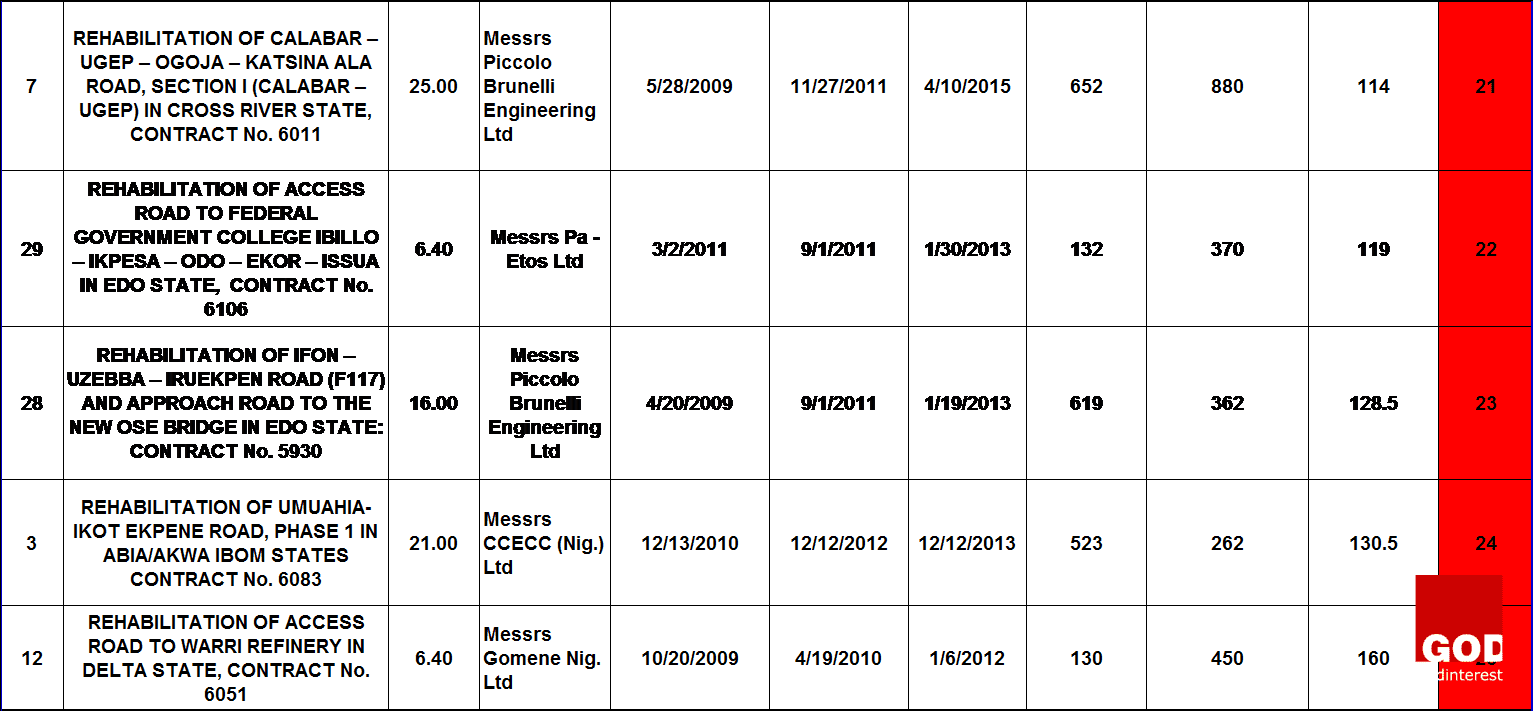
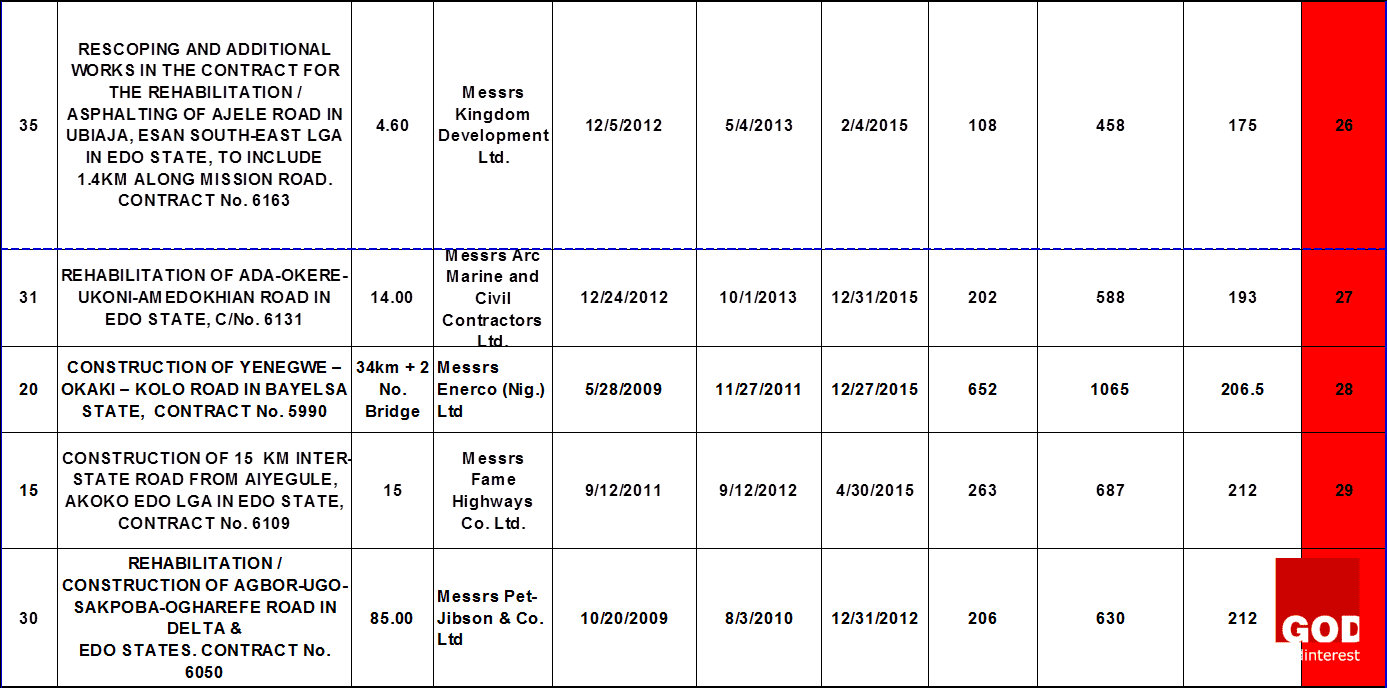
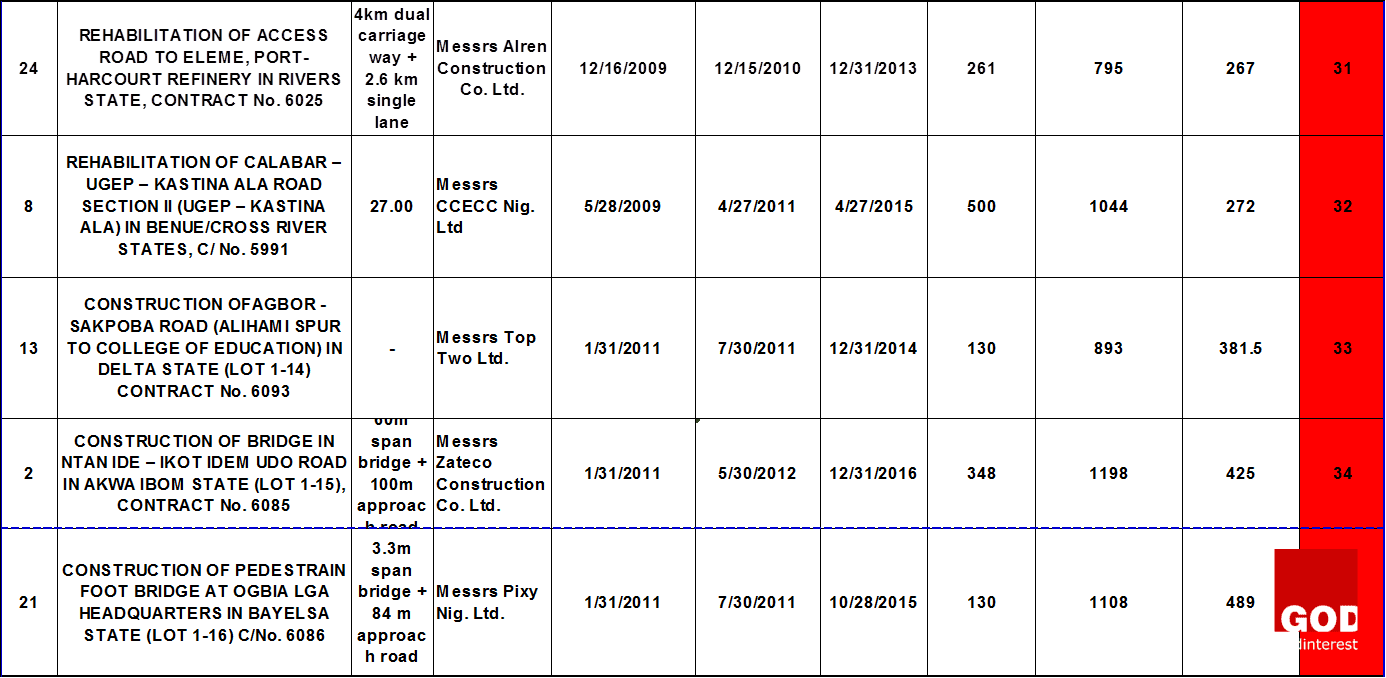
This research starts with a general reasoning or theory which says that the major cases of project failure in the Nigerian construction industry are defined based on time overrun and cost overrun. The findings from the data analysis will help on the decision to accept the theory or not. The research data was collected from the progress report for the month ending of October, 2015 published by the Nigeria of Federal Ministry of works on thirty-nine on-going highway construction projects at the South-South geopolitical zone. The table 1 below shows the information on the data collected which comprises of the project title, contract Number, project description, the contractor that was awarded the projects, the date of project commencement, date of completion and the extended date if any. The scheduled time for each project was specified as follows: project commencement date labeled as “a”, project completion date labeled as “b”, and the extended date labeled as “c”.

DATA ANALYSIS
The data analysis was done with the use of Microsoft excel. The analysis started by obtaining the number of days between the date of commencement of each project and the date of completion to show the duration of each highway project. And, the number of days between the project completion date and the extension date showed the time-overrun. The project duration and the extended days were obtained with the use of NETWORKDAYS function in Microsoft Excel which calculates the number of working days between two dates excluding weekends and any dates identified as holidays.
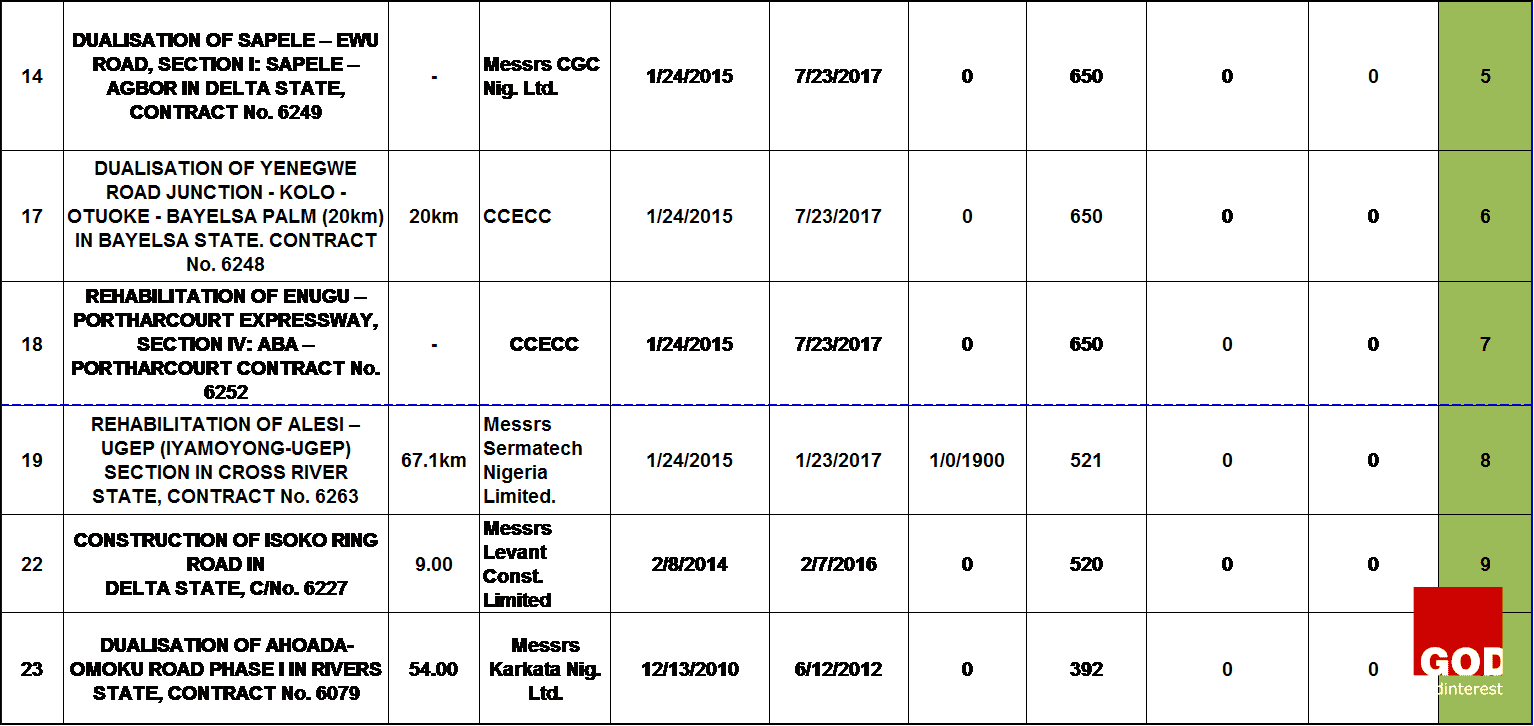
The standard deviation between the specified project duration for each highway projects and the extended days was calculated to obtain the extent to which each highway project contract failed on its time of delivery. This was denoted as the degree of failure. The table 1 above showed the projects ranking which was done based on the degree of failure of all the highway projects. The highway projects that were ranked from one to sixteen have low degree of failure and are represented with green color, while the rest are those with high degree of failure and are represented with red color.
FINDINGS
The findings made showed that the successfully completed highway projects have no extended days or time overrun, and the successful on-going highway projects are still on schedule and have no extended days unlike the on-going highway projects that have already failed as a result of the extended dates. Other projects have been abandoned because they have exceeded the delivery date as specified on the contract document, and have no extended date of completion. Thus, no work is going on.
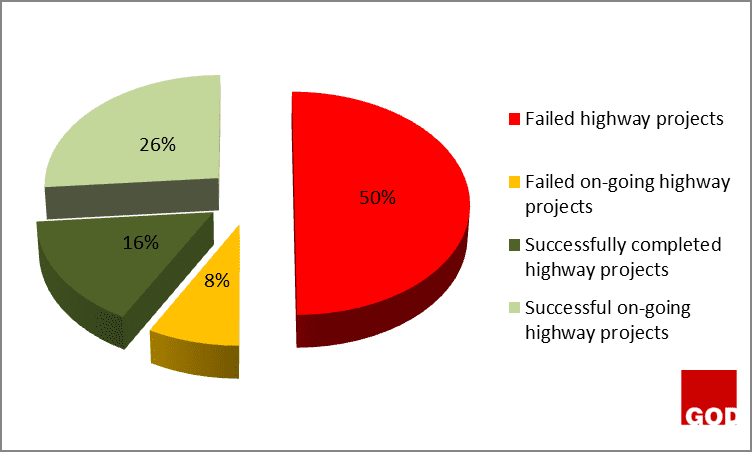
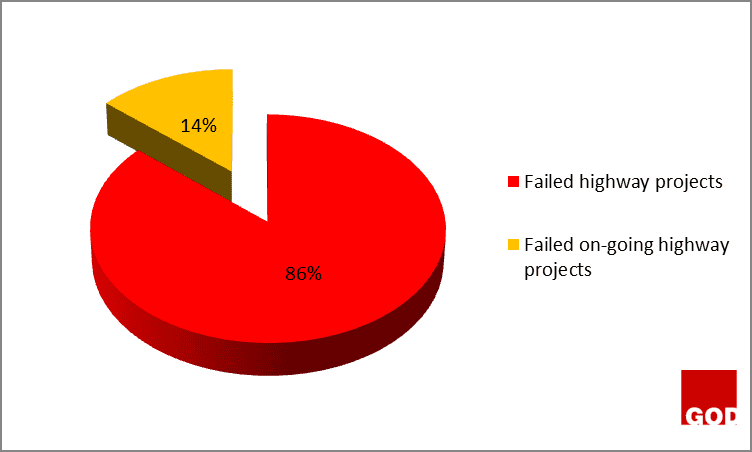
Figure 2 above showed that 14% of highway projects are still on-going projects because they have not exceeded the original date of completion as specified on the contract document. However, they are heading towards failure because they have been given an extended date of completion which can be as a result of some critical activities running behind schedule, causing delay on the critical path network of the projects. Moreover, the other 86% completely failed because they have exceeded their completion date specified on the contract document.
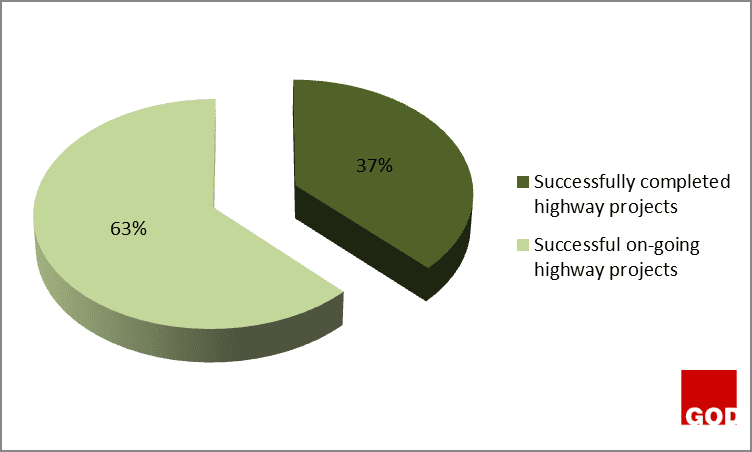
The figure 3 above showed that 63% of the successful highway projects are still on-going because they have not exceed their completion dates, and they are not yet completed. However, those on-going highway projects might end up as failed projects as a result of poor funding, discrepancy between the design and the construction on site, and conflict between the construction parties or stakeholders.
“Say what you will do, and do what you said” or “Say as you will do it, and do it as you said”
CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION
The idea of knowing what a failed project is, the factors and the causes is very important in project management. Success in project management can neither be achieved nor measured without the knowledge of project failure, its factors, and causes in the Nigerian construction industries. This work has shown that project failure is as a result of exceeded time of delivery, cost overrun, and poor quality. However, the analysis was only done based on exceeded time of project delivery because of the nature of the data collected.
This work suggested a few approaches to help reduce the number of failed projects in the Nigerian construction industry if properly implemented. Firstly, Having good collaboration between the project stakeholders involved in a construction project at the early stage of project conception is most important in order to accomplish the project objectives, and deliver the project on time, within budget, and quality specified on the original contract document (Othman, 2006).
Secondly, Adopting the ISO 9000 technique which is used for quality management will also help in achieving a successful project delivery. This technique states “ say what you will do, and do what you said” or “say as you will do it, and do it as you said”. This technique is not an indication of high quality but it promotes control and consistency which leads to specialization, and improved productivity and quality. Also, adopting the principles of lean construction will help to reduce waste within the construction and stream-line activities in order to improve the on-time delivery of projects.
Thirdly, Learning from the precedent failed projects, how those projects failed, and the reason for their failures. This will help the project manager to plan and mitigate the risks of project failures in the future. And, finally, more seminars and workshops will help to educate and enlighten clients (the federal government representatives), users, contractors, engineers, and architects on what is project failure, the factors that contributes to abundant failed projects, and their causes.
REFERENCE
Abimbola, A. (Novermber 24, 2012). About 12,000 Federal Projects Abandoned across Nigeria. Premium times (November 16, 2015). Retrieved from www. Premium timesng.com/news/108450-about-12000-federal-projects-abandoned-across-nigeria.html.
Al-Khali, M.I and Al-Ghafly, M.A. (1999). Important Causes of Delays in Public Utility Projects in Saudi Arabia. Construction management and Economics, 17, 647-655
Aibinu, A.A and Jagboro, G.O. (2002). The Effects of Construction Delays on Project Delivery in Nigeria Construction Industry. International journal of Project management, 20(8), 593- 599.
Anigbogu, N. and Shwarka, M. (2011). Evaluation of Impact of the Public Procurement Reform Program on Combating Corruption Practices in Public Building Project Delivery in Nigeria. Environtech Journal, 1(2). 43-51.
Assaf, S. and Al-Hajji, S. (2006). Causes of Delays in large Construction Projects. International Journal of Project Management, 24, 349-357.
Atkinson , R. (1999). Project management: Cost, time, and quality, two best guesses and a Phenomenon, it’s time to accept other success criteria. International Journal of project Management, 17(6), 337-342.
Belout, A and Gauvrean, C. (2004). Factors Influencing the Project Success: The impact of human resource management. International Journal of project Management, 22, Pp. 1-11.
Butcher, N. and Demmers, L. (2003). Cost Estiumating Simplified. Retrieved from www.librisdesign.org.
Cookie-Davies, T. (2002). The Real Success Factors on Projects. International Journal of Project management, 20(3), 185-190.
Dim, N.U. and Ezeabasili, A.C.C (2015). Strategic Supply Chain Framework as an Effective Approach to Procurement of Public Construction Projects in Nigeria. International Journal of Management and Susutainability, 4(7), 163-172.
Hanachor, M. E. (2012). Community Development Projects Abandonment in Nigeria: Causes and Effects. Journal of Education and Practice, 3(6), 33-36.
Idrus, A., Sodangi, M., and Husin, M., H. (2011). Prioritizing project performance criteria within client perspective. Research Journal of Applied Science, Engineering and Technology, 3(10), 1142-1151.
Idrus, A. and Sodangi, M. (2010). Framework for evaluating quality performance of contractors in Nigeria. International Journal of Civil Environment and Engineering. 10(1), 34-39.
National Bureau of Statistics (January, 2015). Nigerian Construction Sector Summary Report: 2010-2012.
Kotangora, O. O. (1993). Project abandonment, Nigerian Tribune.
Osemenan, I. (1987). Project Abandonment. New Watch Magazine, Vol. 1, pp. 15.
Othman, M.,R. (2006). Forging main and sub-contractor relationship for successful projects. Retrieved from http://rakanl.jkr.gov.my/csfj/editor/files/file/projek/lessonslearned/MAIN&SUB_2.pdf
Phua, F.T.T and Rowlinson, S. (2003). Cultural Differences as an Explanatory Variable for Adversarial Attitude in the Construction Industry: The case of HongKong. Construction Management and Economics, 21, 777-785.
Reiss, B. (1993). Project Management Demystified. London: E and FN Spon Publishers.
Toor, S. R. and Ogunlana, S. O. (2008).Problems causing Delay in Major Construction Projects in Thailand. Construction management and Economics, 26, 395-408.
Toor, S. R. and Ogunlana, S. O. (2008). Critical COMs of Success in Large-Scale Construction Projects: Evidence from Thailand constructuction industry. International Journal of Project management, 26(4), 420-430.
Toor, S. R. and Ogunlana, S. O. (2009).Beyound the “Iron Triangle”: Stakeholder perception of key performance indicators (KPIs) for large-scale public sector development projects. International Journal of Project management, doi: 10.1016/j.ijproman.2009.05.005.
Toor, R. and Ogunlana, S. (2009). Construction Innovation: Information, process, management. 9(2), PP. 149-167.
Turner, J. R. (1993). The Handbook of project-Based Management: Improving the process for achieving strategic objective. London, McGraw-Hill.
Wright, J., N. (1997). Time and Budget: The twin imperatives of a project Sponsor. International Journal of Project Management, 15(3), 181-186.
Professor Pavel Matousek – Laser Man

Professor Pavel Matousek, a Science and Technology Facilities Council (STFC) Senior Fellow and Chief Scientific Officer of Cobalt Light Systems Ltd, has pioneered revolutionary techniques for analysing the chemical composition of materials and co-founded a highly successful spin-out company. He has helped develop and commercialize award-winning laser technologies that detect liquid explosives at airports, rapidly check the quality of pharmaceutical products, and that may one day non-invasively diagnose breast cancer. Pavel states:
“I Am Very Excited about What I Do and Driven to Answer Questions in Front of Me, Unravel Complex Problems and Deliver Something Useful to Society.”
STFC science writer James Doherty meets the Laser Man.
Pavel, what first got you interested in physics?
I became fascinated by the stars and Universe while growing up in the Czech Republic. I joined an astronomy society at secondary school and it became clear I wanted to study physics. I got very interested in laser physics during my MSc at the Czech Technical University in Prague. It is a very dynamic field.
When did you arrive at Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (RAL)?
I joined as a research associate in 1991, and went on to complete my PhD in ultra-fast Raman Spectroscopy at RAL, awarded by the Czech Technical University. I’ve been here almost 25 years to the day.
So what is Raman Spectroscopy?
It is a technique that involves shining a laser beam at the surface of a material, and then observing the colour of light scattered from the point of illumination. This typically provides information about the chemical composition of the material’s surface. C.V. Raman observed the effect in 1928 and subsequently won a Nobel Prize.
You pioneered a technique called Spatially Offset Raman Spectroscopy (SORS): What is it and how does it differ from normal Raman Spectroscopy?
“We couldn’t have developed the SORS technique without the instrumentation and long term research continuity available at the Central Laser Facility at RAL”
SORS is a technique that we stumbled across in the Ultrafast Spectroscopy Laboratory (ULTRA) by chance. We had assumed that photons could only be detected at the illumination point but we were wrong. Some photons migrate sideways through the material then emerge adjacent to the illumination point. As these photons have interacted with molecules deeper inside the medium, they provide information about internal chemical make-up: SORS probes deeper into the material. And the further you move from the illumination point, the deeper you see into the medium. The process
involves large photon migration distances, often extending to several centimetres or more. This came as a big surprise.
“SORS involves probing at one location and detecting at another. Our minds, and those of others, were constrained by our perception of how the Raman Spectroscopy process worked but once we made this serendipitous discovery, we quickly realised it had potential major applications.”
What kind of applications?
“The Range of Potential Applications for Sors Is Staggering.”
We immediately realised SORS could determine the chemical make-up of substances by non-destructive means. This could have applications in bio-medicine, chemistry, security, forensics, heritage, and beyond. But we first focused on pharmaceuticals, and developed novel ways for analysing the chemical make-up of manufactured drugs.
We swiftly filed 8 patents, which became the basis of our company Cobalt Light Systems.
Cobalt Light Systems is perhaps best known for its airport security scanners. Can you describe how these work and their impact to passenger travel?
Security scanners represent the second generation of technology developed by Cobalt. To date there are around 400 operational units in 70 airports across Europe and Asia. They are used to scan traveller essentials, such as medicines or baby milk, and compare their chemical make-up to a database of potentially explosive substances. Suspicious substances are automatically identified and flagged. For example, the technology avoids passengers having to drink liquids (e.g. baby milk) in front security officer to prove they are not dangerous, which is clearly safer and more hygienic. It has also contributed to new legislation, and is expected to lead to a relaxation of the complete ban of taking liquids on board a plane in the future.
The scanners are currently the size of a microwave oven but right now we are launching a SORS handheld device. This should have further applications for first responder teams called to spillages of unknown substances and fire fighters attending chemical fires.
Pavel Matousek Pioneered a Technique Called Spatially Offset Raman Spectroscopy (SORS)
How did STFC help with this process?
First off, we used instrumentation at STFC’s Central Laser Facility to demonstrate the basic capability to detect the SORS subsurface signal. Once we made the discovery in 2004, we worked closely with STFC’s Technology Transfer Office SIL (formerly CLIK) and Business and Innovations (BID) to develop, optimise and protect our ideas. There was a complex path to navigate from discovery, to optimising SORS, building a prototype, and ultimately to securing investment in 2008. BID/SIL coordinated the company at all levels and provided the support necessary to achieve this goal.
“My story illustrates the national and international importance of STFC. If its determination to deliver impact on science was absent, the chain from a fundamental discovery to Cobalt Light Systems’ product would have been broken. STFC responded appropriately at every stage. And this is just one example of how STFC contributes to the UK’s know-how economy.”
What are you working on currently?
I’m focused on developing novel non-invasive medical screening techniques, including diagnosing bone disease such as osteoporosis (jointly with STFC’s Prof Tony Parker and University College London’s Prof Allen Goodship), and I’m working with Professor Nicolas Stone of Exeter University on non-invasive breast cancer screening.
In addition, I’m collaborating with Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche in Italy to apply the SORS technology to objects of art on microscales. For example, we can scan different layers of paint to determine compositional information essential in restoration and preservation of artefacts.
How will the medical applications benefit patients?
Patient benefit could be enormous. Current diagnosis techniques for osteoporosis are around 60-70% accurate as they sense only mineral content. SORS on the other hand has a high specificity for mineral and collagen content – both of which determine bone strength – and so holds considerable promise for providing improved diagnostic accuracy. SORS could also be used to classify breast or prostate tumours as malignant or benign without needle biopsy. This would reduce patient stress and save medical provider costs.
However, medical problems are challenging as the human body is complex and variable. These applications are probably still 7-10 years away.
Why do you do this research?
This is where my passion and interest lies – I’m very excited about what I do.
“As You Push the Boundaries of Technology and Make New Discoveries, the End Goal Always Changes. This Is the Nice Thing about Science.”
33 of the Most Inspirational Leadership Quotes for You to Live By
We’ve all seen quotes designed to motivate or inspire us. Well, according to a new study, people who post these ‘inspirational’ quotes also have lower levels of intelligence. However, Godinterest disagrees, and see’s some quotes as universal nuggets of wisdom. You know the ones – those quotes that give you “Aha!” moments of inspiration or meaningful insights into your personal and professional lives. These are the ones you want to print out and place on your fridge so you’ll see them every day.
This collection of inspirational quotes features some of the all-time classics you may know, as well as some lesser-known ones you’ll love too. If you have any quotes you would have added, feel free to share in the comments section!
- “The reason most people never reach their goals is that they don’t define them, or ever seriously consider them as believable or achievable.” – Denis Watley
- “Our goals can only be reached through a vehicle of a plan, in which we must fervently believe, and upon which we must vigorously act. There is no other route to success.” – Stephen A. Brennan
- “Without goals, and plans to reach them, you are like a ship that has set sail with no destination.” – Fitzhugh Dodson
- “Goals are dreams with deadlines.” – Diana Scharf Hunt
- “You must have long-term goals to keep you from being frustrated by short-term failures.” – Charles C. Noble
- “Crystallize your goals. Make a plan for achieving them and set yourself a deadline. Then, with supreme confidence, determination, and disregard for obstacles and other people’s criticisms, carry out your plan.” – Paul Meyer
- “The tragedy of life doesn’t lie in not reaching your goal. The tragedy lies in having no goals to reach.” – Benjamin Mays
- “Progress has little to do with speed, but much to do with direction.” – Unknown
- “The world makes way for the man who knows where he is going.” – Ralph Waldo Emerson
- “Goals help focus you on areas in both your personal and professional life that are important and meaningful, rather than being guided by what other people want you to be, do, or accomplish.” – Catherine Pulsifer
- “What you get by achieving your goals is not as important as what you become by achieving your goals.” – Zig Ziglar
- “It doesn’t matter where you are coming from. All that matters is where you are going.” – Brian Tracy
- “The true measure of a man is not how he behaves in moments of comfort and convenience but how he stands at times of controversy and challenges.” – Martin Luther King Jr.
- “It’s not the load that breaks you down, it’s the way you carry it.” – Horne, Lena
- “Difficulties are meant to rouse, not discourage. The human spirit is to grow strong by conflict.” – William E. Channing
- “Nothing is particularly hard if you divide it into small jobs.” – Henry Ford
- “It’s not whether you get knocked down. It’s whether you get up again.” – Vince Lombardi
- “You must do the thing you think you cannot do.” E- Eleanor Roosevelt
- “Motivation is what gets you started. Habit is what keeps you going.” – Jim Ryun
- “Strong lives are motivated by dynamic purposes.” – Kenneth Hildebrand
- “People who are unable to motivate themselves must be content with mediocrity, no matter how impressive their other talents.” – Andrew Carnegie
- “Be miserable. Or motivate yourself. Whatever has to be done, it’s always your choice.” – Wayne Dyer
- “The surest way not to fail is to be determined to succeed.” – Richard B. Sheridan
- “A determined person will do more with a pen and paper than a lazy person will accomplish with a personal computer.” – Catherine Pulsifer
- “There is no chance, no destiny, no fate, that can hinder or control the firm resolve of a determined soul.” – Ella Wheeler Wilcox
- “It was courage, faith, endurance and a dogged determination to surmount all obstacles that built this bridge.” – John J. Watson
- “Failure will never overtake me if my determination to succeed is strong enough.” – Og Mandino
- “You’ve got to get up every morning with determination if you’re going to go to bed with satisfaction.” – George Lorimer
- “We will either find a way or make one!” – Hannibal
- “That some achieve great success, is proof to all that others can achieve it as well.” – Unknown
- “Do not let what you cannot do interfere with what you can do.” – John Wooden
- “Success seems to be largely a matter of hanging on after others have let go.” – William Feather
- “Success is the sum of small efforts, repeated day in and day out.” – Robert Collier
10 Proposed Infrastructure Projects for London to Retain Its World Class Status
London hasen’t reached the density of Hong Kong, but it’s certainly heading that way as the cities population continues to expand. The “London Infrastructure Plan 2050″ aims to tackle the problem and outlines the spending needed for the capital to remain one of the world’s leading cities.
London Mayor Boris Johnson Has Said £1.3tn of Investment Is Needed over the next 35 Years in Order for London to Retain Its World Class Status
“This plan is a real wake up call to the stark needs that face London over the next half century. Infrastructure underpins everything we do and we all use it every day. Without a long-term plan for investment and the political will to implement it this city will falter.”
London School of Economics Professor Tony Travers Said: “the London Infrastructure Plan Is a Necessary Step Towards Understanding the Needs of the ‘10 Million City’ Which London Will Soon Become.
Transport is the biggest focus of the “London Infrastructure Plan 2050” as the population hit 8.5 million in 2014 the largest it has been since 1939. By 2050 it is predicted to exceed 11 million, growing at a rate of 41,000 a year.
Some infrastructure project proposals are already in development, others may not be approved at all, however, these are some transport developments suggested for London by 2050.
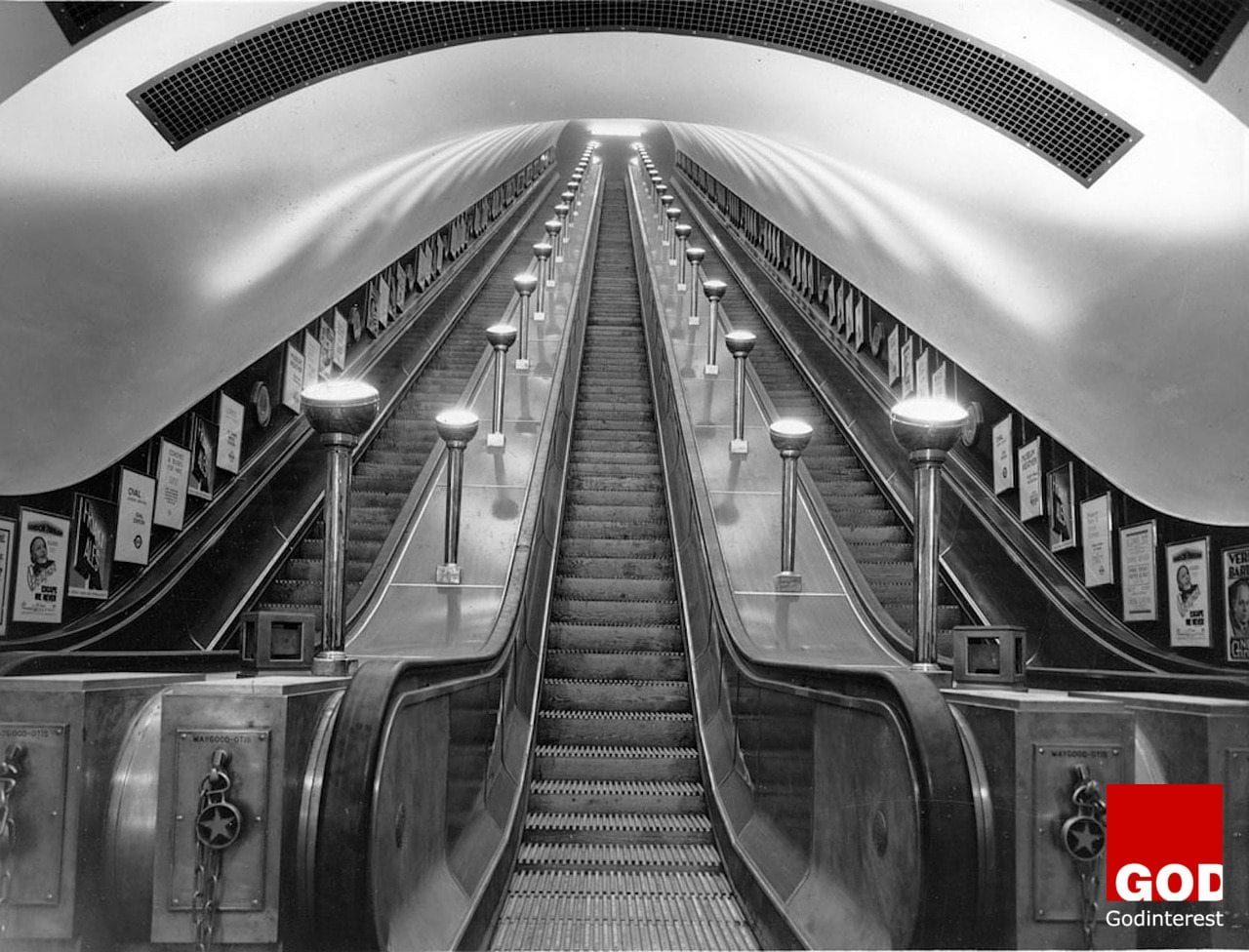
1. Air con on the Tube, £900m
It was find in the beginning, in fact, conditions were so pleasant in 1906 that the city proclaimed the underground ‘The coolest place in hot weather’. But that was before deep lines and millions of passengers.
Better Late than Never, London’s Tube Is Getting Air-con
In summer, temperatures on parts of the London Underground can become very uncomfortable due to its deep and poorly ventilated tube tunnels: temperatures as high as 116 °F were reported in the 2006 heat wave. New Tube trains, which allow better access for customers, are being rolled out on the Circle line as part of the introduction of 53 new trains on both the Hammersmith & City and Circle lines. By the end of 2016 there will be a total of 191 walk-through, air-conditioned trains covering 40% of the Tube network running on the District,Circle, Metropolitan and Hammersmith & City lines.
2. Inner orbital tolled tunnel, £15bn-25bn
Mayor sets out plan for 22-mile ring-road tunnel under London, which is considered by many to be one of the most ambitious infrastructure scheme ever proposed in the city.
The tunnel will cost an estimated £30 billion to construct and will remove tens of thousands of cars from the crowded streets of London and avert traffic gridlock. With subterranean dual carriageways linking key routes, from the A40 Westway to the A12 in the east, and the A1 route north to the A2 running south.
London Major Boris Johnson, who commissioned work to develop the idea, believes it could dramatically improve quality of life for residents. He said: “I would love the views of Evening Standard readers on this. There are big arguments in favour. There are obviously arguments against.”
Transport for London is working on the concept.
3. Northern Line extension, £1bn
Works commenced on London Underground’s £1bn Northern Line extensionfrom Kennington to Battersea via Nine Elms in the UK in 2015.
Tunnelling work is scheduled to start in early 2017 and will take six months to complete, while the project is expected to be completed in 2020.
The project will reduce journey times to the West End and the city to less than 15min.
4. Cycle Super Highways, £2bn- £4bn
London’s New Superhighway Linking East and West London Will Open on 30 April, Says the Capital’s Mayor Boris Johnson
The route, which links Barking, Canary Wharf and Tower Hill to Westminster, will open less than a week before his term is set to end.
Chris Boardman, the former Olympic champion and policy advisor to British Cycling, said: “This YouGov poll shows us, yet again, that the vast majority of the public want to see more cycle tracks on main roads.
“If this kind of evidence isn’t enough to give politicians and transport authorities the confidence to act, I don’t know what is.”
Last month, Boris Johnson pressed ahead with plans for three cycle superhighways.
5. Bakerloo and Overground extensions, £2.5bn-3.5bn
The extension of the Bakerloo line could help regenerate South East London from Old Kent Road to Catford, improve routes into London and relieve congestion on the main rail services into London Bridge.
6. Crossrail 2 and 3, £23bn- £30bn
TRANSPORT chiefs say it is “full steam ahead” for Crossrail 2 after the Government made an £80million pledge towards the project – but it will be months before passengers find out if a station will be built at Balham or Tooting.
Construction work is due to begin on the rail link in the early 2020s, which would enable the service to be operational by 2033.
7. New Stations, £500m and 24/7 Night Tube service
New stations at Cricklewood, Beam Park in Rainham and Thames Wharf could be built to support redevelopment in these areas. It has also been claimed that night services on the Piccadilly, Central, and Northern Lines are then due to start in September, with all major lines being served by the weekend night tube by September 23.
8. Another channel tunnel, £1bn
The “London Infrastructure Plan 2050″ suggests an additional cross-channel rail tunnel would provide high speed links from the UK to the rest of Europe for passengers and freight.
9. 13 new crossings in London, £1-2bn
The vision for east London includes 13 proposed new river crossings include Gallions-Thamesmead, Belvedere-Rainham, Woolwich- Royal Docks to replace the Woolwich Ferry, as well as the Silvertown tunnel.
Boris Johnson states “By creating more links between the north and south of the river, we won’t just improve day-to-day travelling across the capital, we’ll unlock areas for development and create thousands of jobs and homes.
- Rotherhithe to Canary Wharf: Pedestrian and cycle bridge (feasibility).
- North Greenwich to the Isle of Dogs: a passenger ferry linking North Greenwich and the Isle of Dogs (Blackwall) (conceptual).
- Silvertown tunnel: Twin bore tunnel connecting Silvertown on the north side to the Blackwall Tunnel Approach on the south side (preparation).
- Charlton: a passenger ferry crossing linking the Royal Docks and Charlton Riverside (conceptual).
- Crossrail: New rail line linking Woolwich with Custom House and onward to Canary Wharf, central London and Heathrow Airport (construction).
- Gallions Reach: Multi-modal crossing linking Thamesmead with Beckton along a safeguarded alignment (consultation).
- Belvedere: Multi-modal crossing connecting Belvedere with Rainham (consultation)
- Barking Riverside to Thamesmead: London Overground tunnel extension from Barking Riverside to Thamesmead (conceptual).
- Lower Thames Crossing: New road crossing linking Essex and Kent (progressing).
- Diamond Jubilee: Pedestrian and cycle bridge linking Fulham with Battersea (planning permission granted).
- Crossrail 2: New railway line connecting Hertfordshire and Surrey via central London and providing a new cross river link between Victoria and Clapham Junction (consultation).
- Vauxhall, Nine Elms and Battersea: Pedestrian and cycle bridge (feasibility).
- Garden Bridge: New pedestrian crossing linking the South Bank to Temple station (planning permission granted).
10. Thames Estuary airport, 18bn-25bn
A new Thames Estuary Airport has been proposed at various times since the 1940s. Economic considerations have ruled out a new coastal airport, while political considerations have ruled out a new inland airport, leaving planners with an as-yet-unresolved dilemma.
‘Bizarre proposal’ states Rehman Chisthti, MP for Gillingham and Rainham “The airport in the estuary was not the right thing do so we all worked together to oppose it. It’s really good news and we’re really pleased that common sense has prevailed.”
However,Boris Johnson refloats idea of Thames Estuary airport 18 months after it was rejected by Airports Commission. Mr Johnson believes a hub in the east of the capital would offer around double the number of long haul and domestic routes served by Heathrow while exposing 95 per cent fewer people to significant aircraft noise.
‘Grain isn’t the answer’ states Rodney Chamber, Leader of Medway Council “We have said all along that it should never have even been considered as it would have resulted in the mass destruction of habitat and wildlife that could never be replaced.”
How to Cope with a Mis-Sold Job
Everyone knows a story about a smart and talented professional who has lost his or her passion for a role, who no longer looks forward to going to the office yet remains stuck without a visible way out. Getting on the career ladder is a great thing, you start off at the bottom and work your way up, but sometimes you can get stuck and do not even realize it.
“One in Five Employees Claim They Were Mis-sold Opportunities When They Joined Their Organisation – Kelly Global Workforce Index (Kgwi).”
Commenting on the findings, Debbie Pettingill, Director, Kelly Services UK and Ireland said
“Employee retention will become an increasing challenge for employers as we move out of the recession. As we move into a more candidate driven market, this trend is likely to accelerate. Our findings indicate that this problem is being exacerbated by the misrepresentation of job role or company culture at the interview stage, leading to the dissatisfaction of new hires.”
Most of us know what we are trying to escape a “mis-sold” job resulting in a narrowly defined career, inauthentic or unstimulating work, numbing corporate politics, and perhaps blackmail including direct threats of being used as a scapegoat. A job where you are both overlooked and underappreciated. One may ring true for some of you.
“Fewer than Half of Uk Employees Are Happy with the Way Their Careers Are Progressing According to New British Research.”
Why Would A Company or Person Block Your Move?
Well, this could be because of his or her personal insecurity i.e. as the team works well, why rock the boat? Comfort zone: sometimes the team gets too comfortable? Golden child syndrome: you’re working your butt off and your sponsor or other senior is reaping the recognition from your amazing deliverables?
Working a job you don’t like can leave you feeling stuck, forgotten by God, and asking yourself questions like:
Why hasn’t God opened another door for me yet?
Why is God not moving?
Why would God leave me here in this job I hate?
But the truth is God has not left you. He’s not holding back on you. When you feel God is silent, that’s exactly when He’s moving! Your situation does not change God. He still loves you and is with you no matter what.
Instead of looking at our situation from a perspective of fear and worry, we need to look at it through faith and hope.
What Can You Do About it?
Don’t fret, you can handover your work or completely leave the organisation and still stay sane. You might worry that announcing your intentions will cause your company grief, but ultimately you have to do what’s best for you no matter what!
Think and pray long and hard about how you’re going to drop this bombshell as you will need to give notice. A sound method is required to overcome the assault and possible backlash – including of course more prayer and fasting.
So how are you going to approach it? What’s your reasoning going to be? How are you going to get them to understand exactly why you’re doing this? What do you need to do in order to prepare for the big day?
Easy, you’re going to read this guide.
Strategy 1 – Remote Working Arrangement
This could be a great approach if 80% of your work can be undertaken remotely. However, while there is a very logical argument to be made in favor of working from home, many people equate remote work to a lack of productivity and laziness. These people do not realize that the switch from an office to working from home can actually lead to significant increases in productivity.
Strategy 2 – What’s in It for Me?
What’s in it for me? That question sounds a little selfish, doesn’t it? Maybe you aren’t being compensated fairly, or you’re not happy with the effort vs return. When you know your client and team needs you and you’re willing to stay for a price, don’t mess around. Give them the real number or offer that will make it worth your while to stick it out for awhile.
Strategy 3 – The Budget Cut
The re-structuring. The downsizing. The dreaded budget cut. Whatever name you want to give it, this can be terrifying for a lot of professionals. However, if you’re already thinking about leaving, so maybe it doesn’t have to be such a scary thing. In fact, maybe it can be extremely positive for both parties.
Strategy 4 – The Ease Out
Still feeling weary about leaving the organization. Propose easing yourself out of the post. Pick a time frame, maybe four weeks or so, and come up with a plan for slowly taking yourself out of the position. This also allows you some time to slowly ramp down your time commitment.
Strategy 5 – Burning Bridges in the Industry
“Sometimes it’s about networking and being nice to people and not burning any bridges – but remembering to draw line where you must.”
There’s no harm in an early exit from a job you never plan to mention again or an interim role where you have clearly agreed on a start and finish date. But if your manager is well connected to your industry you should try to leave on a good note. Why? Because it’s a small world and the next hiring manager may put in a call to his or her former colleague (a.k.a., your new manager) to get the unofficial scoop. It happens, so if you’re going to leave anyway then try to fulfill your end of the deal.
Strategy 6 – Get Moving Fast
Imagine, for example, that you were hired to help the company manage multiple programmes and projects across the globe, but a recent change in leadership means all efforts moving forward will be focused locally.
If you’re spending your days just trying to find ways to be productive or are undertaking a role you never signed up for, you have every right to pursue new opportunities. Of course, the first course of action should normally be to discuss this with your manager to see if there are other roles you can take on. But if you know that this isn’t going to happen in the new world, get moving fast.
Strategy 7 – Your Dream Job Awaits
“When you’re being interviewed, always treat the interview as a 50-50 thing,” says Andy Dallas, a director at Robert Half International, recruitment consultants. “Ask what you can expect to be doing in your first week, month and three months. Ask what a successful year looks like.”
Dream jobs don’t come every day. So, if you have a chance at yours, take it quickly and congratulate yourself for being strong enough to leave when you were unhappy.
Strategy 8 – Remeber to Be Patient
We will not always be in a job we desire. Maybe you are fresh out of school and are working a job that has nothing to do with the degree you just earned. Maybe you are in a situation where you are working at a job where you are overqualified, overworked, and fed up. Maybe, for the most part, you love your job but get discouraged by the mundane tasks that take up time from doing the aspects of your job you love most.
“Humble yourselves before the Lord, and he will exalt you.” – James 4:10 NIV
Here’s the thing: God will still use this season to grow, develop, and prepare you. Any season that humbles us is preparing us for what God has next.
Any thoughts to share?
15 Shocking Project Management Statistics
The project management landscape is changing with an increased emphasis on productivity, reporting, and information technology. A number of studies have been completed that look into the success and failure rates of projects.
Below are 15 shocking statistics that reveal how project management has changed and is performing across various industries over the last 5 years.
- There is projected to be 15.7 million new project management roles to be added globally across seven project-intensive industries by 2020 reaching an economic impact of over $18 trillion, across seven project-intensive industries including Manufacturing, Finance & Insurance, Information Services, Utilities, Business Services, Oil & Gas and Construction (Project Management Institute)
- 75% of IT executives believe their projects are “doomed from the start. (Geneca)
- The healthcare industry is projected to increase project management roles by 30%, a higher growth rate than any current project intensive industry between 2010 and 2020. (Project Management Institute)
- A third of all projects were successfully completed on time and on budget over the past year. (Standish Group)
- 80% of “high-performing” projects are led by a certified project manager. (PricewaterhouseCoopers, Insights and Trends: Current Programme and Project Management Practices 2012)
- One in six IT projects have an average cost overrun of 200%. (Harvard Business Review 2004)
- 44% of project managers use no software, even though PWC found that the use of commercially available PM software increases performance and satisfaction. (Pricewaterhouse Coopers)
- More than 90% of organizations perform some type of project postmortem or closeout retrospective. (The Standish Group: CHAOS Research Report 2013)
- On average, it takes 7 years in the profession to go from entry-level to managing large, complex projects. (ESI International: Annual Salary Survey 2013)
- The average large IT project runs 45% over budget, 7% over time, and delivers 56% less value than expected. (Project Management Institute: Pulse of the Profession 2015)
- Only 64% of projects meet their goals. (Project Management Institute: Pulse of the Profession 2015)
- 60% of companies don’t measure ROI on projects. (KPMG New Zealand: Project Management Survey 2010)
- The United States economy loses $50-$150 billion per year due to failed IT projects. (Gallup Business Review)
- In just a 12 month period 49% of organizations had suffered a recent project failure. In the same period only 2% of organizations reported that all of their projects achieved the desired benefits. 86% of organizations reported a shortfall of at least 25% of targeted benefits across their portfolio of projects and many organizations failed to measure benefits so they are unaware of their true status in terms of benefits realization. (KPMG – Global IT Project Management Survey 2005)
- According to an IBM study, only 40% of projects meet schedule, budget and quality goals. (Harvard Business Review 2004)
If you have any other project management statistics please share them with us.
Fighting Gender Discrimination in The High-Tech World
New research suggests that tech-savvy women might face gender discrimination in jobs at high-tech firms, partly due to mismanaged projects.
It shows gender discrimination is still as prevalent in the UK as it was 20 years ago, and comes as International Women’s Day will be celebrated this week on March 8, for the 103rd year.
The book “The Recruitment, Retention and Advancement of Technical Women: Breaking Barriers to Cultural Change in Corporations” by the Anita Borg Institute for Women and Technology, a Palo Alto-based nonprofit organization focusing on the role of women at high-tech firms.
“More than a Quarter of Women Have Experienced Some Form of Gender Discrimination in the Workplace, a New Study Shows.”
Tech firms typically rely on a “hero mindset” to save poorly organised runaway coding projects. As a result, employees with family responsibilities (generally considered to be women) are left out, the report said.
The Research Also Suggests out of 1,500 Office Workers in the Uk, 26% of Women Felt That Having Children Held Them Back in Their Career
The research also suggests that there is evidence of bias against women in recruitment and job assignment in places where high-tech corporate cultures thrive on this “hero mindset” that “rewards a ‘last minute’ crunch where 24/7 work becomes necessary to ‘save’ a project.” However, these environments fail to acknowledge family responsibilities and flexibility needs, the report said.
This fly-by-the-seat-of-your-pants workday culture represents a pattern that’s grown mainly because an organization poorly defines project management and requirements.
For example, Silicon Valley’s sometimes frantic fire-fighting pace and in-your-face communication style produces many technical cultures that often “leave women feeling isolated and crushed,” notes the report.
The study also reflects what 59 senior business and tech managers — both men and women from companies like Cisco, Facebook, Goldman Sachs, Google, HP, IBM, Intel, Microsoft and Symantec — shared during a closed forum organized by the Anita Borg Institute. According to the report, it’s common in the high-tech world to find the modern equivalent of the “good old boys network” that tends to hire “people who are like them.”
Technical women these days are “still a rarity,” said Dr. Carolyn Simard, author of the report. She added that in the United States, women earn just 18 percent of computer science degrees in college. That figure is sharply down from the 37 percent observed in 1985. Yet technical demand is still expected to grow as much as 32 percent by 2018.
The Institute published a second report titled “Senior Technical Women: A Profile of Success,” which surveyed approximately 1,800 participants from seven unidentified high-tech firms in Silicon Valley.
It found that women now hold about four percent of the senior-level technical positions at high-tech firms and an estimated one-quarter of all tech jobs. On higher levels, women are more likely to end up in a managerial position compared to men (36.9 percent of women compared to 19 percent of men), who are more likely to hold “individual contributor positions” in technical coding jobs.
The second study also found that men and women in technical jobs value most of the same attributes for success, such as being analytical, questioning, risk-taking, collaborative, entrepreneurial, assertive, working long hours and being sociable.
Far more often than men, women generally have “primary responsibility for the household,” the study showed. However, senior-level tech women are much more likely to have a partner who holds primary responsibility for the household and children (23.5 percent of partnered senior women) compared to entry or mid-level women (13.4 percent). Senior-level tech women are also more likely than their male counterparts to forego a partner and children because they believe they might hinder their careers.
To improve work-life balance and stop any perceived gender bias against women in the high-tech world, the Anita Borg Institute is pushing a few ideas that will generate debate and controversy.
“The Equality Act 2010 Makes It Unlawful for an Employer to Discriminate Against Employees Because of Their Gender.”
One recommendation suggests that because there is evidence that women are eliminated in the hiring process at the resume review level, companies might consider “that all women candidates should at least get an interview.”
With backing from firms like HP, Google, Facebook, Intel and Intuit, the Anita Borg Institute even suggested that it might be possible to create a software tool designed to weed out any unconscious bias against hiring or promoting women in the tech world.
This “software tool for detecting bias” was proposed at the Institute’s forum. It can use language recognition to zero in on everything from performance evaluations to letters of recommendation that exhibit gender bias. An online tool like this can be found at Harvard’s Project Implicit.
“We envision building on such research to create a system where specific language can be fed and analyzed for the existence of bias,” the report said. “Using machine learning and text analysis methods would help organizations and individuals address the existence of bias before the damaging language is formally used in recommendations or evaluations.”
Additionally, the software would be a “high-impact diagnostic tool for calibrating organizations with regard to hiring and promotion decisions.”
35 Powerful Quotes That Will Inspire You to Be Successful
Being a both a Christian and a leader can be an emotional ride, with ups, downs, joy, and disappointment. Words have power and these inspiring and motivating quotes are guaranteed to challenge the way you think and perhaps even change the way you live.
We hope they resonate with you as much as they have with us. Sometimes a little piece of advice or wisdom from a brilliant mind can help you motor through even the most difficult of times.
- I’ve learned that people will forget what you said, people will forget what you did, but people will never forget how you made them feel. ’- Maya Angelou
- It’s not the load that breaks you down, it’s the way you carry it. ’- Lou Holtz
- What happened, happened, and it wouldn’t have happened any other way. Lewis Carroll
- Choose a job that you like, and you will never have to work a day in your life. ’- Confucius
- Fools give full vent to their rage, but the wise bring calm in the end. ’- Proverbs 29:11
- Perfection is not attainable, but if we chase perfection we can catch excellence. —Vince Lombardi
- Whatever the mind can conceive and believe, the mind can achieve. ’- Napoleon Hill
- Keep away from people who try to belittle your ambitions. Small people always do that, but the really great make you feel that you, too, can become great. ’- Mark Twain
- The function of leadership is to produce more leaders, not more followers. ’- Ralph Nader
- As iron sharpens iron, so one person sharpens another. ’- Proverbs 27:17
- If you cannot do great things, do small things in a great way. ’- Napoleon Hill
- What is not started will never get finished. ’- Johann Wolfgang von Goethe
- When you cease to dream, you cease to live. ’- Malcolm Forbes
- Build your own dreams, or someone else will hire you to build theirs. ’- Farrah Gray
- Your most unhappy customers are your greatest source of learning. ’- Unknown
- Winners never quit, and quitters never win. ’- Vince Lombardi
- Your time is limited, so don’t waste it living someone else’s life. ’- Unknown
- Life is 10% what happens to me and 90% of how I react to it. —Charles Swindoll
- The price of success is hard work, dedication to the job at hand and the determination that whether we win or lose, we have applied the best of ourselves to the task at hand. ’- Vince Lombardi
- Speak your mind, even if your voice shakes. ’- Maggie Kuhn
- It takes 20 years to build a reputation and five minutes to ruin it. If you think about that, you’ll do things differently. ’- Warren Buffett
- Remember no one can make you feel inferior without your consent. —Eleanor Roosevelt
- When someone tells me “no,” it doesn’t mean I can’t do it, it simply means I can’t do it with them. ’- Karen E. Quinones Miller
- If you want to lift yourself up, lift up someone else. —Booker T. Washington
- You can’t build a reputation on what you are going to do. ’- Henry Ford
- A person who never made a mistake never tried anything new. ’- Unknown
- I am not a product of my circumstances. I am a product of my decisions. —Stephen Covey
- Logic will get you from A to B. Imagination will take you everywhere. ’- Unknown
- Remember that not getting what you want is sometimes a wonderful stroke of luck. ’- Unknown
- I can’t change the direction of the wind, but I can adjust my sails to always reach my destination. —Jimmy Dean
- If you’re offered a seat on a rocket ship, don’t ask what seat! Just get on. —Sheryl Sandberg. — Proverbs 15:1
- A gentle answer turns away wrath, but a harsh word stirs up anger
- Everything you’ve ever wanted is on the other side of fear. —George Addair
- The most difficult thing is the decision to act, the rest is merely tenacity. —Amelia Earhart
- A good name is more desirable than great riches; to be esteemed is better than silver or gold. — Proverbs 22:1
Bookmark this page and come back to it when you need some inspiration and motivation.