Brexit and Christians: Did God command the UK to leave the EU?
Christians overwhelmingly voted in favour of leaving the European Union last Thursday but the aftershocks will not only impact heavily on UK economic growth, but also on any foreseeable infrastructure developments due to the uncertainty created by the Brexit vote to leave, an industry source has warned. Polling from Lord Ashcroft showed that nearly six in ten of those who identified as Christian voted for Brexit.
Although numbers have fallen, 93 per cent of Christians in the UK are white. By contrast two-thirds of British Muslims are from an Asian background. And Lord Ashcroft’s poll showed that 67 per cent of Asians and 73 per cent of black people voted to remain compared to 47 per cent of white people.”
The assumed time frame for the UK-EU divorce terms to be agreed is two years which has left many businesses anxious and investors unclear of what the future may hold.
The conclusion of a recent analysis by the Pew Research Center in the US suggests that in the UK, the proportion of the population identifying themselves as Christians was approximately 64% in 2010.
The Knock-On Effects of the Brexit Vote
All Brits must now confront the truths about the forthcoming EU DIVORCE. Don’t kid yourself. Separation always harms both parties. However, what does this mean for investment in the capital project wise? Well, the Brexit verdict will impact construction projects as follows.
Osborne Said “It Is Very Clear That the United Kingdom Is Going to Be Poorer,” on a BBC Radio 4 Programme.
1. Access to Foreign Labour
The first most important issue is access to labour. A core principle of the EU is the right of free movement, which has made immigration between member states somewhat easy and stress-free. The construction industry relies heavily on overseas workers to fill both skilled and non-skilled job roles, and a significant percentage, predominantly within the London market, come from continental Europe.
“Across the UK, Nearly 12% of the 2.1 Million Construction Workers Come from Overseas, Official Statistics Indicate Largely from the EU.”
It’s logical that with an EU DIVORCE those skilled individuals will instead travel to France, Germany, or Spain, where the right of free movement still exists.
David Thomas, chief executive of Barratt Developments Plc the UK’s largest homebuilder said, “an EU DIVORCE would lead to a shortage of construction staff, and impair the UK Construction Industries ability to build houses.”
The free movement of labor in the European market has been seen as a positive for many. However, it’s also possible that a skills shortage may result in increased investment in training and upskilling of local workers to fill the gaps. This could also result in higher wages being demanded by those workers who are in the UK labor market which individual labors would no doubt welcome, but which in turn could escalate the cost of projects.
Migrant construction workers who have arrived in the UK in the past 10 years. – Construction Industry Training Board (CITB) 2014:
Poland: 30,120
Romania: 24,842
Lithuania: 7,569
India: 7,704
Bulgaria: 5,443
Latvia: 3,830
South Africa: 1,316
Hungary: 1,448
Australia: 937
2. Investment in the Capital
Another major concern is the investment in the UK. The EU presently makes it easy for companies in different countries to do business with, and invest in, one another.
European manufacturing giants Airbus has voiced concern about investing in the independent UK. Likewise, German firm Festo has said German companies should be cautious about investing in Britain. And let’s not forget that Germany is the financial driving force of the EU.
On the other hand, Lord Bamford, the Chairman of JCB is however persuaded that an eventual EU DIVORCE could reduce the costs of administration so much so that the costs of leaving the EU will be covered.
3. Prestigious Projects
An enormous question mark hangs over prestigious projects such as a third runway for Heathrow which has now been delayed again in wake of Brexit fallout and the Hinkley Point nuclear power station in Somerset which is now “extremely unlikely”.

There are also growing suspicions about the future of less well-known operations such as the London Gateway port in Essex, operated by Dubai’s DP World, which opened in 2013 and is still only half complete.
This new outbreak of ambiguity is also likely to engulf many other scheduled construction projects in the UK.
4. EU Legislation and Regulation
A significant amount of EU legislation is now rooted in UK law and affects construction. The EU DIVORCE would not instantly result in less regulation. By way of example, the CDM regulations basically enacted EU Directive 1992/57/EEC and there is no indication that the regulations or health and safety in the construction cycle will be swept away because of the leave vote. The UK may now choose to reduce the scope of this and other dictates or, abolish them completely. However, one thing is for sure, this will not happen overnight.
5. Imports and Exports
The supply of goods and services for the construction industry is a key driver of growth in the UK. The UK is at least partly dependent on imports from the EU, particularly Germany, Italy and Sweden.
In 2014, 53% of Goods and Services Were Imported into the UK from the EU.
The degree to which these may be affected depends upon the post-Brexit model.
6. Exchange Rates
Can Sterling’s Recovery Continue with Brexit Looming? From the moment the EU leave vote was announced, the Pound Euro exchange rate has been volatile.
Pound Euro Exchange Rate Reaches 1.2150 – Half-Way Recovered to the Week’s Opening Levels
In a trade where margins are tight, there is heavy dependence on the import and export of goods and services, currency fluctuations will have a major fiscal impact on construction projects. Whereas the inclusion of exchange rate phrases in constructions contracts is always an option, it does mean companies will need to undertake an additional level of strategizing, prior to planning or otherwise undertaking construction projects in the immediate future.
7. Access to Finance
The availability of money is often a pre-requisite for construction projects. Access to money can control whether or not a specific projects can proceed from design to construction.
Currently UK small and medium enterprises have access to SME financing which will at some point no longer be available once the EU DIVORCE is complete.
Standard & Poor’s stripped Britain of its “AAA” credit rating reducing it to “AA”. Fitch Ratings also downgraded its ranking for Britain’s creditworthiness by one notch.
It is therefore clear that the UK’s connection with the EU enhanced its creditworthiness. The looming EU DIVORCE is quickly changing all that. The cost for developers of finding finance for construction projects will no doubt also increase as lenders seek to impose higher interest rates.
The results of an imminent EU DIVORCE are complex and widespread and something that the wise business should be planning for now. There will be significant insecurity for businesses in the months, if not years, resulting from the vote to leave.
This failure to convince Christians of either the economic, spiritual or cultural benefits of the EU was disastrous for the Remain campaign and has changed the face of the UK forever.
Concrete Proves Its Versatility Is Endless
The Nature of Good ‘Project Chemistry’
Racism Is Still Alive and Well in the UK, 50 Years after the Race Relations Act
Written by Denise Courtney
The truth is, we’re making slow progress, racial discrimination in construction industry is rife. Well, that was the finding of a report commissioned by the Construction Industry Training Board on the under-representation of ethnic minorities in the industry in 2014. The findings, published made for shocking reading. It stated that the construction workforce was only 1.9% black and Asian, compared with 6.4% of the working population as a whole – more than 70% fewer black and Asian workers than the UK industry average.
“There’s been some progress since 1965, no longer would signs of No Blacks, No Irish, No Dogs be allowed, but focusing on individual prejudice has avoided tackling endemic systematic racism, leaving significant inequalities in the UK and aboard.”
The survey proved that there is still much work to be done within the industry in order to attract the very best talent.
A painting contractor based in New England has been ordered to pay two former employees more than $1.5m each by a court in New Haven, Connecticut. The court ruled that the company had discriminated against the men on racial grounds.
The lawsuit, against Safety Marking alleged that Yosif Bakhit, a Sudanese-American, and Kiyada Miles, an African-American, were subject to “a pattern of abuse” for years, from racial insults and slurs to being passed over for promotions in favour of less experienced white employees.
There have been many cases both in the UK and aboard, the evidence is overwhelming, just do a search on Google, the problem is most people suffer in silence.
“Is There a Glass Ceiling Where You Work? One in Three Brits ‘admits to Being Racist’, according to poll.”
Many people get attracted to the lucrative payments that usually accompany working in the UK and US. The need to explore what is beyond their boundaries is so tempting that one will use any means and any chance they get to ensure that they secure themselves a better paying job which is mostly found in the construction industry. However, their arrival is mostly characterized by hostility from the locals making their stay unbearable. In addition, proper recruitment practices in some cases have not been put in place to ensure that ethnic minorities are treated well.
The need for a diverse workforce in the construction industry by most governments is seen as a bid to fill the gap of an aging workforce. Many organisations have already become reliant on foreign construction laborers who are hungry for opportunities to further their careers.
Despite various measures and policies put in place to prevent or minimize racial discrimination, studies have shown that although the makeup of the population in the construction industry is in the process of changing, the picture still being painted is that the industry is still dominated by white people instead of having multicultural diversity throughout.
Lewis Iwu, Director of the Fair Education Alliancec Recently Stated That ‘at Some Companies the Only Bme People Are the Ones Who Let You in the Door.’
Noticeable issues of racial discrimination which can be attested by ethnic minorities who comprise of blacks and people of Asian origin today are that most contractors and consultants are white with the stakeholders who are deemed to have stronger networks and connections despite the fact that there are equally qualified ethnic minority workers. This can be attributed to the fact that it will take a while for you to earn people’s trust which is hard, prejudice and stereotypes considered.
Strategic roles are also given to white colleagues and when there are opportunities for leadership roles, priority is given to the white counterparts despite the presence of more qualified Ethnic Minorities who are willing to avail themselves for the role. Another challenge is that even if an ethnic minority gets this position, their subordinates find it hard to take instructions from them making it hard for them to accomplish their tasks and achieve the set targets.
It is a common belief that there is power in a name and in most cases Ethnic Minorities will find themselves adopting English names just to make them seem white. Other instances of discrimination are that during submission of reports, the reports from ethnic minorities are criticized more.
Ethnic minorities have turned to the construction project management industry with the hope of building a career in construction to subsequently improve their lives but due to racial discrimination, they find themselves working in the same level for years without being promoted therefore making their lives hard. This can be attributed to a common perception that black people cannot bring anything substantial to the table and should instead be seen digging with a shovel and not in a management level, according to Kwasi Boateng who spoke to Nancy Cavill of Building.co.uk
Even with these cases being minimal today due to the policies put in place to see to it that there is equal opportunity for all; Ethnic minorities still suffer from issues of name calling which makes them isolate themselves from the rest of the workforce according to a report by the Equality and Human Rights commission.
“A State of Racism Exists Between Some of the Citizens of the United Kingdom, Studies Taken by the BBC in 2014 and 2015 Claim Racism Is on the Rise in the Uk with More than One Third Actually Admitting They Are Racially Prejudiced.”
EM workers are reported to limit their contact with those from a different cultural or religious background whenever they can with some even missing work due to stress leading to reduced productivity. A finding by Juliet Bourke of Deloitte.com found that apart from racial jokes and racist gestures, ethnic minorities are in some cases denied time off to attend to religious or cultural ceremonies. A plus here is that this group is however satisfied with the multicultural working environment. “Why not take a legal action?” One may ask. This has been in the minds of many but the fear of the repercussions makes them cower and tolerate the discriminatory treatment. Coupled with that, low status workers with limited skills fear that they will be exposed to adverse working conditions.
Due to the plight of these workers, construction management organizations have come up with strategies that will see an improved working condition for all and key among them include;
- A review of the current legislations which have been put in place to safeguard ethnic minority workers against discrimination in the construction industry. The review will help in deliberating on specific policies aimed at protecting them and to add on what has been overlooked. This involves punishing offenders who are found guilty of harassing or discriminating against members of a different religious or cultural background.
- Implementation of equal treatment of all workers despite their cultural or religious backgrounds. This will see that all the workers will get equal opportunities with regards to leadership chances without considering their backgrounds but their qualifications instead. This will ensure that proper representations of these minorities are achieved.
- Along with the policies of enhancing equal opportunities, policies that ensure that workers have freedom to attend to their various cultural and religious ceremonies have been put in place. This effort shows that their beliefs are acknowledged and appreciated which is motivation enough for them.
- The need for a common language which is understood by all has prompted some constructions organisations to come up with one which will help communicate its policies to the workers effectively without feeling that others have been left out. These organizations therefore encourage its workers to try and learn English which is one of the common international languages in a bid to support workers overcome the language barrier. This will also ensure that all the safety policies are communicated effectively and are understood by the entire workforce.
- Thees construction firms also ensure that it communicates clearly and precisely all the work procedures to ensure that all the tasks are done well and in a safe manner. This includes training and putting in place properly laid out instructions to ensure that the workers understand and know what they are supposed to do.
With these policies and strategies being put in place by companies, noticeable impacts on improved delivery and quality of the services provided by a well coordinated and multicultural population will be realized. Without these policies, poor psychological working conditions which include discrimination and harassment as well as issues of excessive workloads, low job control and long working hours will lead to a worsening mental and physical health of these workers leading to poor delivery. The government and those in leadership positions should be brought on board on these issues of racial discrimination in the construction project management industry if any significant changes are to be realized. They should take responsibility and make it an agenda and not merely regard it as an issue which human resource teams must deal with alone.
“Every Single Person Has a Unique, Inherent Worth.”
Even if industries put these policies in place, they should strictly follow them up and make deliberate efforts to create an environment that is inclusive of all the people from diverse backgrounds to curb direct and indirect workplace discrimination. Construction is part of a country’s development agenda because without it, infrastructure which is crucial will lag behind making production minimal as it is from construction that they will have roads to transport their goods and services. Companies should therefore understand that diversity is very crucial for their prosperity because it is through it that better business ideas as well as innovations will be realized. This is because a diverse team will bring in diverse perspectives to problems and customer needs will be best understood as they will be in a better position to tailor their products and services to meet those needs.
Do you believe legislative change can end systematic discrimination in Britain and aboard or is racism coded in to the DNA of the nation?
7 Astonishing Abandoned Projects” Surreal Riveted Sea Forts Once Protected the Kent Shores from German Attack”
Abandoned projects including building, engineering and infrastructure development projects litter the whole of the world.
Most of them were started to symbolise a country’s prosperity and vision but after years of abandonment, stalled development and economic crisis, some of the world’s most amazing projects have been abandoned and now have come to epitomise national struggle.
From Bangkok’s ‘Ghost Tower’ which was abandoned after the 1997 financial crisis to the Tower of David, here is a selection of some of the world’s most famous abandoned and incomplete projects in no particular order.
1. Bangkok’s ‘Ghost Tower’
On stormy days debris from this unfinished and abandoned skyscraper rains down on the streets of Bangkok
A towering waste. It’s called Bangkok’s ‘ghost tower’. This 49-storey prominent unfinished skyscraper in the Thai capital city of Bangkok was destined to be a state-of-the-art office and residential complex, but has instead become a destination for urban explorers. Planned as a high-rise condominium complex, construction of the building was halted during the 1997 Asian financial crisis when it was 80% complete.
Now the 174-meter graffiti-covered building mainly houses squatters.
2. The “Tower of David”

Torre de David (The Tower of David) named after David Brillembourg, the tower’s main investor who died in 1993 has been depicted as a haven for drug lords and assassins in the TV series Homeland, lauded as an experiment in social empowerment at the Venice Architecture Biennale and featured in countless articles and documentaries around the world. In May 2014, the tower was also featured in the BBC World News documentary, Our World.
For eight years, the Tower of David a half-built skyscraper in downtown Caracas the capital of Venezuela. was home to thousands of squatters who transformed the abandoned block into a ghetto complete with grocery shops, tattoo parlours, internet cafes and a hair salon.
Construction of the tower began in 1990 but was halted in 1994 due to the Venezuelan banking crisis. As of 2016, the building remains incomplete.
This vertical ghetto can be seen from almost every corner of this densely populated capital.
In 2014 Ernesto Villegas, the minister for the revolutionary transformation of greater Caracas, said all the tower’s residents would be relocated to “dignified homes”. “This is not an eviction, but rather a relocation,” he told reporters. Villegas said several children had fallen to their deaths from the tower, which in some places is lacking walls or windows.
The newspaper Tal Cual reported that Chinese banks were interested in buying the tower and renovating it for its original use.
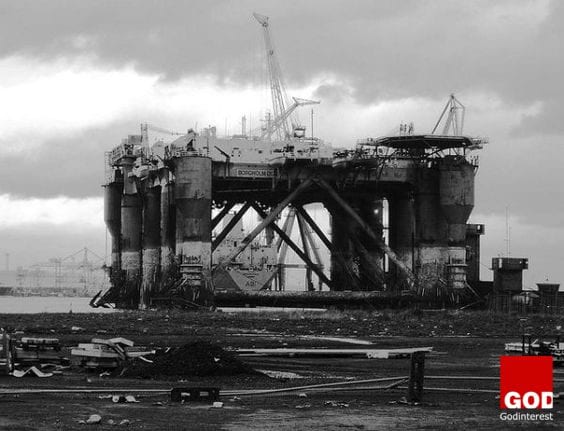
3. Mothballed Oil Rig
Oil rigs definitely fall into the mega category when it comes to size.You might think of them more as structures than machines. The rig above is a accomodation platform rather than an oil drilling rig, re-built in Belfast in the late 1990s. Mothballed as opposed to completely abandoned, the rig stands alongside the derelict area of the old Harland and Wolff shipyard.
This Patch of Wasteground Is Probably One of the Most Famous in Maritime History, Being the Construction Site of the Rms Olympic and Her Sister Ship Titanic.
Today modern redevelopment is breathing new life.
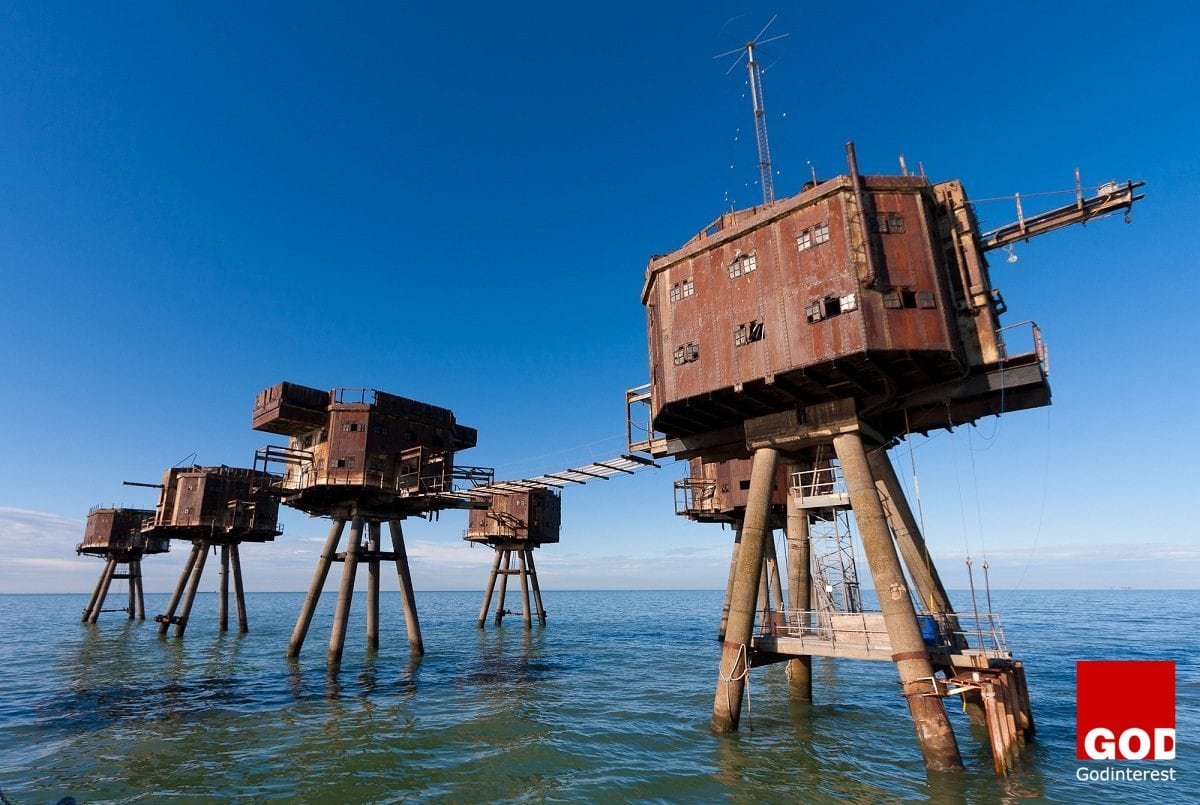
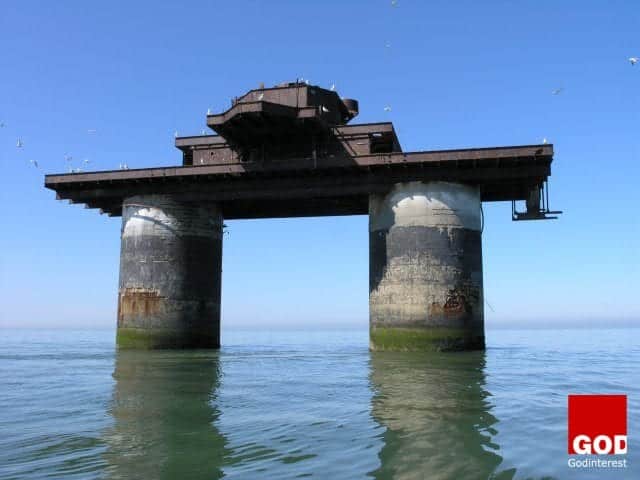
“Surreal Riveted Sea Forts Once Protected the Kent Shores from German Attack”
5. Project Babylon
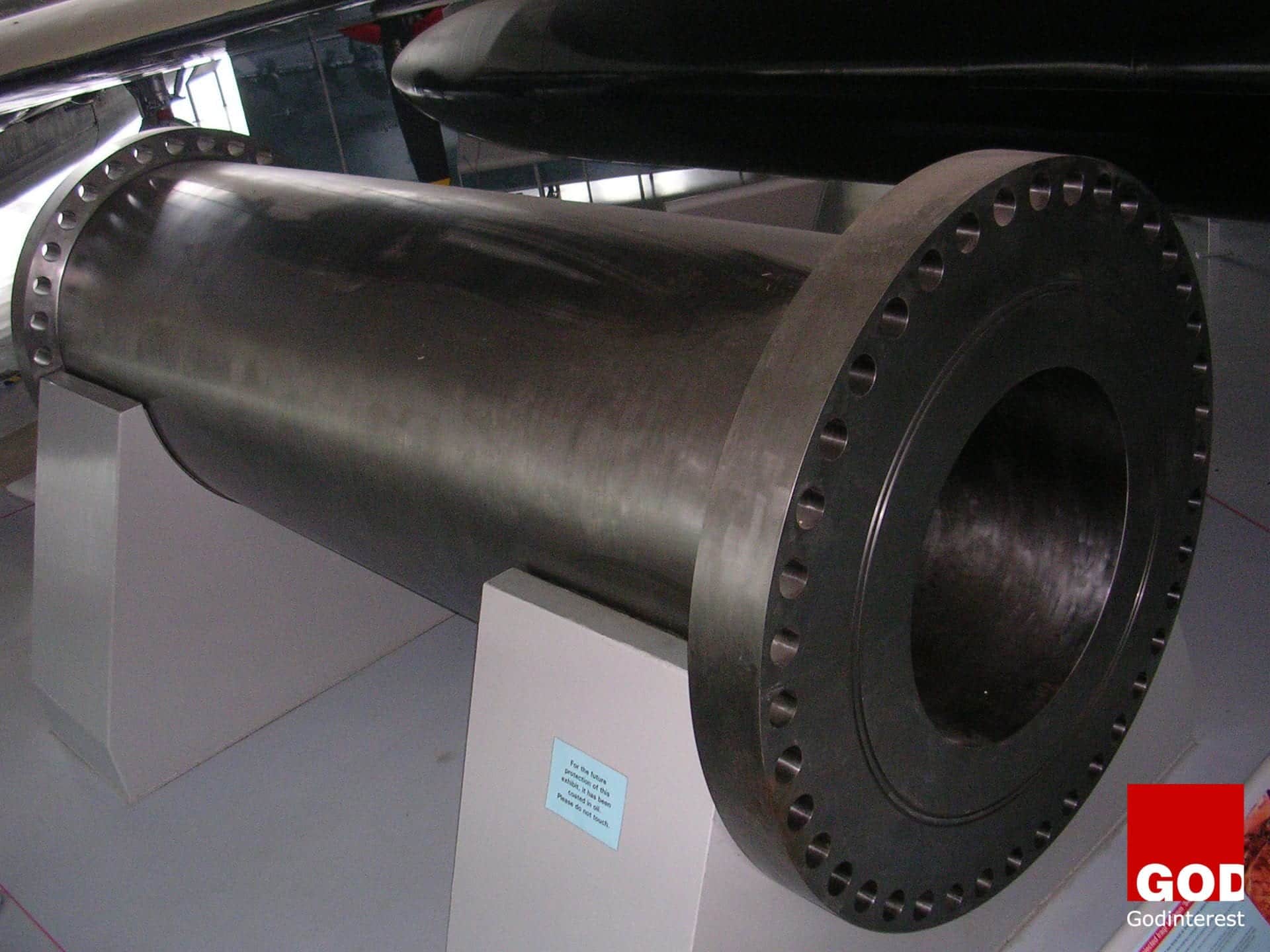
Project Babylon: The Story of Saddam’s Supergun
Project Babylon was a project with unknown objectives commissioned by the then Iraqi president Saddam Hussein to build a series of “superguns”. The Iraqi government engaged world-renowned artillery expert Gerald V. Bul whose lifetime obsession was a the construction of a “Supergun,”. The design was based on research from the 1960s Project HARP,
In early April 1990, United Kingdom customs officers confiscated several pieces of the second Big Babylon barrel, which were supposedly disguised as “petrochemical pressure vessels”. Components, such as slide bearings for Big Babylon, were seized at their manufacturers’ sites in Spain and Switzerland. After the Gulf War in 1991, Iraq confirmed the existence of Project Babylon, and permitted U.N. inspectors to destroy the hardware. A section seized by UK customs officers is on display at The Royal Artillery Museum, Woolwich, London.

The BasÃlica i Temple Expiatori de la Sagrada FamÃlia is a large Roman Catholic church in Barcelona, designed by Spanish architect Antoni Gaudà (1852–1926). Although incomplete, the church is a World Heritage Site and has been visited by the Pope. Inspired by GaudÃ’s vision, and funded almost exclusively by the millions of tourists who flock to it every year, today, the Sagrada FamÃlia is more than halfway done, with a estimated completion date of 2026. The lead architect is confident that it will be finished “ within the next century.
Has Nigeria Become the World’s Junk Yard of Abandoned and Failed Mega Projects worth Billions?
Dim1, N. U., Okorocha2, K. A., & Okoduwa3 V. O.
The Nigerian construction industry is mostly concerned with the development and provision of projects such as roads, bridges, railways, residential and commercial real estates, and the maintenance necessary for the socio-economic developments contributes immensely to the Nigerian economic growth (Bureau of Statistics, 2015). Butcher and demmers (2003) described projects as an idea which begins and ends by filling a need. However, a project fails when its idea ends without meeting the needs and expectations of its stakeholders.
Nigeria Has Become the World’s Junk – Yard of Abandoned and Failed Projects worth Billions of Naira!
Hanachor (2013), revealed that projects form part of the basis for assessing a country’s development. However, a damming report from the Abandoned Projects Audit Commission which was set up by the Ex-President Goodluck Jonathan in 2011 revealed that 11,886 federal government projects were abandoned in the past 40 years across Nigerian (Abimbola, 2012). This confirmed the assertion by Osemenan (1987) “that Nigeria has become the world’s junk –yard of abandoned and failed projects worth billions of naira”.
Abandoned projects including building and other civil engineering infrastructure development projects now litter the whole of Nigeria.
Physical projects do not only provide the means of making life more meaningful for members of the community where the projects are located, successful projects also result in empowerment and collective action towards self improvement (Hanachor, 2013).
This Issue of Abandonment Has Been Left Without Adequate Attention for Too Long, and Is Now Having a Multiplier Effect on the Construction Industry in Particular and the Nigeria’s National Economy as a Whole. (Kotngora, 1993)
PROJECT FAILURE
Project Failure might mean a different thing to different stakeholders. A project that seemed successful to one stakeholder may be a total failure to another (Toor and Ogunlana, 2008). Some stakeholders, more especially the project users and some private owners, think of failed projects as a situation where a completed building project collapsed, a situation where by a completed dam project stopped working after few days of completion, or a completed road project that broke down after few months of completion. Other experienced stakeholders, such as engineers and architects conform to the iron triangle by Atkinson (1999) which states that the most strategically important measures of project failure are “time overrun”, “cost overrun”, and “poor quality”.
Turner (1993) noted that a project fails when the project specifications are not delivered within budget and on time; the project fails to achieve its stated business purpose; the project did not meet the pre-stated objectives; the project fails to satisfy the needs of the project team and supporters; and the project fails to satisfy the need of the users and other stakeholders. Lim and Mohamed (1999) cited in Toor and Ogunlana (2009) clarified that there are two possible view points to project failure namely; the macro-level and the micro-level. They further explained that the macro view point reviews if the original objectives and concepts of the project was met. Usually the end users and the project beneficiaries are the ones looking at the project failure from the macro view point, where as the project design team, the consultants, contractors, and suppliers review projects from a micro view point focusing on time of delivery, budget, and poor quality.
In the early 1990s, the failure as well as the success of any project was determined by the project duration, monetary cost, and the performance of the project (Idrus, Sodangi, and Husin, 2011). Belout and Gauvrean (2004), also confirmed that the project management triangle based on schedule, cost, and technical performance is the most useful in determining the failure of a project. Moreover, a project is considered as an achievement of specific objectives, which involves series of activities and tasks which consume resources, are completed within specifications, and have a definite start and end time (Muns and Bjeirmi 1996, cited in Toor and Ogunlana, 2009). Reiss (1993) in his suggestion stated that a project is a human activity that achieves a clear objective against a time scale. Wright (1997) taking the view of clients, suggested that time and budget are the only two important parameters of a project which determines if a project is successful or failed. Nevertheless, many other writers such as Turner, Morris and Hough, wateridge, dewit, McCoy, Pinto and Slevin, saarinen and Ballantine all cited in Atkinson (1999), agreed that cost, time, and quality are all success as well as failure criteria of a project, and are not to be used exclusively.
FACTORS OF PROJECT FAILURE
Cookie-Davies (2002) stated the difference between the success criteria and the failure factors. He stated that failure factors are those which contributed towards the failure of a project while success criteria are the measures by which the failure of a project will be judged. The factors constituting the failure criteria are commonly referred to as the key performance indicators (KPIs).
Time and Cost Overrun
The time factor of project failure cannot be discussed without mentioning cost. This is because the time spent on construction projects has a cost attached to it. Al-Khali and Al-Ghafly, (1999); Aibinu and Jagboro, (2002) confirmed that time overrun in construction projects do not only result in cost overrun and poor quality but also result in greater disputes, abandonment and protracted litigation by the project parties. Therefore, focus on reducing the Time overrun helps to reduce resource spent on heavy litigation processes in the construction industry (Phua and Rowlinson, 2003). Most times, the time overrun of a project does not allow resultant system and benefits of the project to be taking into consideration (Atkinson, 1999). Once a project exceeds the contract time, it does not matter anymore if the project was finally abandoned or completed at the same cost and quality specified on the original contract document, the project has failed. Furthermore, Assaf and Al-Hejji, (2006) noted that time overrun means loss of owner’s revenue due to unavailability of the commercial facilities on time, and contractors may also suffers from higher over heads, material and labour costs.
Poor quality/Technical Performance
The word “Performance” has a different meaning which depends on the context it is being used and it can also be referred to as quality. Performance can be generally defined as effectiveness (doing the right thing), and efficiency (doing it right) (Idrus and Sodangi, 2010). Based on this definition of performance, at the project level, it simply means that a completed project meets fulfilled the stakeholder requirements in the business case.
CAUSES OF PROJECT FAILURE
A lot of research studies have investigated the reasons for project failures, and why projects continue to be described as failing despite improved management. Odeh and Baltaineh, 2002; Arain and Law, 2003; Abdul-Rahman et al., 2006; Sambasivan and Soon, 2007; all cited in Toor and Ogunlana, 2008, pointed out the major causes of project failures as Inadequate procurement method; poor funding and availability of resources; descripancies between design and construction; lack of project management practices; and communication lapses
The contract/procurement method
A result obtained from two construction projects which were done by the same contractor but using different procurement methods showed that rework, on the design part which occurs when the activities and materials order are different from those specified on the original contract document, makes it difficult for the project to finish on the expected time (Idrus, Sodangi, and Husin, 2011). This is as a result of non-collaboration and integration between the design team, contractor, and tier suppliers. The rework on the design portion has a huge impact on project failure leading to the time overrun. The traditional method of procurement has inadequate flexibility required to facilitate late changes to the project design once the design phase of the construction project has been concluded.
Nigerian most widely used procurement method is the traditional method of procurement (design-bid-construct) which has been confirmed to be less effective to successfully delivery of a construction project (Dim and Ezeabasili, 2015). And, the world bank country procurement assessment report (2000) cited in Anigbogu and Shwarka, (2011) reported that about 50% of projects in Nigeria are dead even before they commence because they were designed to fail.
The way the construction projects are contracted, in addition to the way the contracts are delivered, contributes to the causes of projects failure. Particularly, among the methods of project contracting is lump-sum or a fixed-price contracting method, in which the contractor agrees to deliver a construction project at a fixed price. The fixed-price contract can be low-bid or not however, once the contract cost has been agreed upon the contract award, it cannot be changed. And, contractors are expected to honor and deliver the contract agreement, failure to do so can result in a breach of contract which can result in the contractor being prosecuted.
Awarding a contract to an unqualified personnel also contributes to project failures. When a contractor places more emphasis on money and the mobilization fee after a construction project has been initiated instead of getting the right workforce and skilled professionals that will execute the project. Instead the workforce chosen will often not be base on competence and required skills rather it will be based on availability. Moreover, poor strategy and planning by contractors who have overloaded with work also contributed to one of the causes of project failure.
Poor funding/Budget Planning
A lot of public projects in the Nigerian construction industry failed as a result inadequate funding, and the difference between the national annual budget and the budget actual released. Most of the Nigerian public projects are signed even before the actual release of the national budget. The difference in budget of the contracted project and the actual budget release can get the contracted company stuck as a result of inflation of prices, scarcity of construction material at the time of the budget release and mobilization to site. Also un-planned scope of work which can be as a result of the contractor working on another contract when he is called back to mobilization to start work. Moreover, poor budget planning is a regular mistake made by some contractors by not undertaking feasibility assessments before starting the design. The construction project should be planned according to the available resources and not according to the unrealistic expectations a client has in mind.
Discrepancies Between the Design and Construction
Limited collaboration between the contractors, engineers, and the architect results in discrepancies between the project designs and construction on site, and further leads to rework. Changes on a project designs, and changing to the scope of work in the middle of construction processes on site can be dangerous, and can lead to time overrun, increase in cost, and most of all can lead to abandonment. Moreover, many cases have been seen where the designs from the architects are not buildable on site, while In some cases, most contractors are unable to adequately specify the scope of work for the construction processes on site. Therefore any default on the design by the architect can be an opportunity for the contractor to make more money which might cause the project duration to exceed the time specified on the contract document.
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
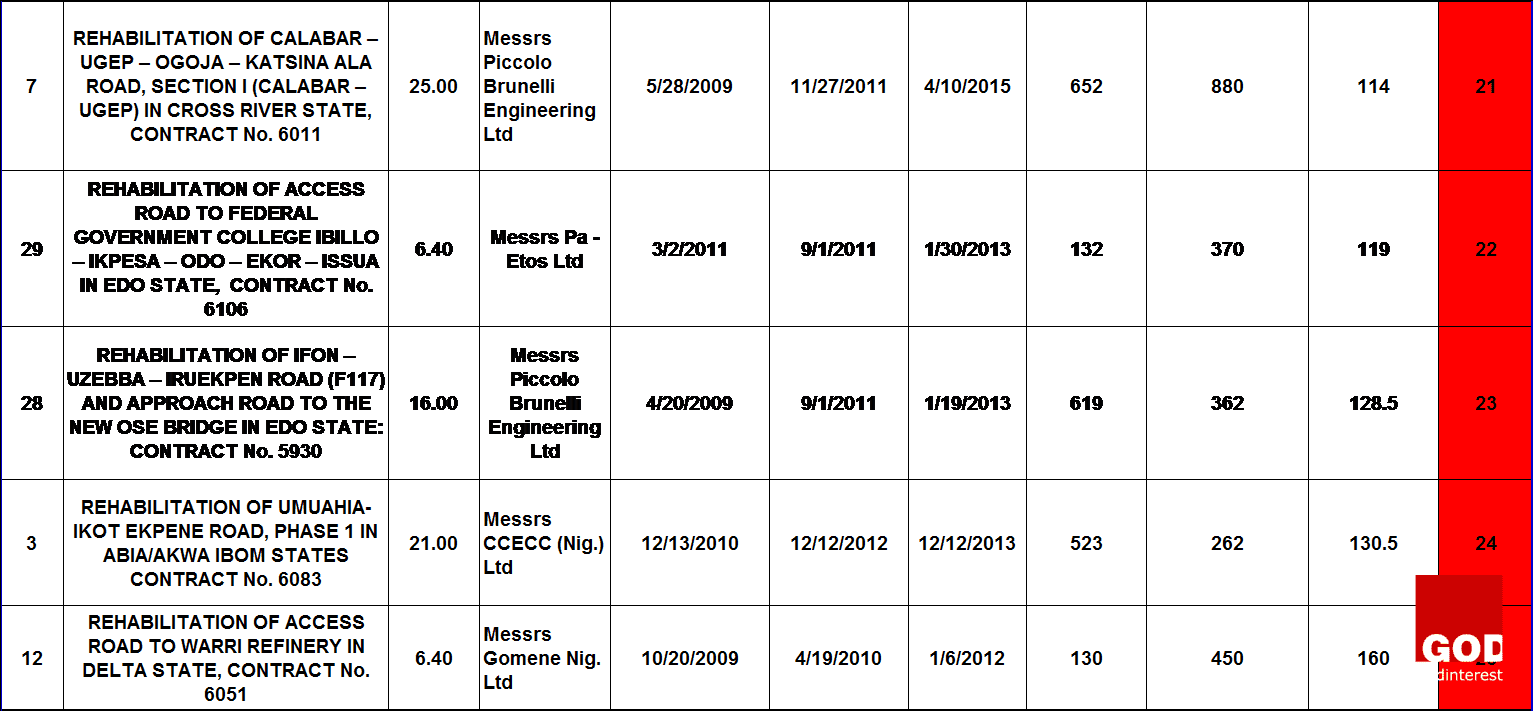
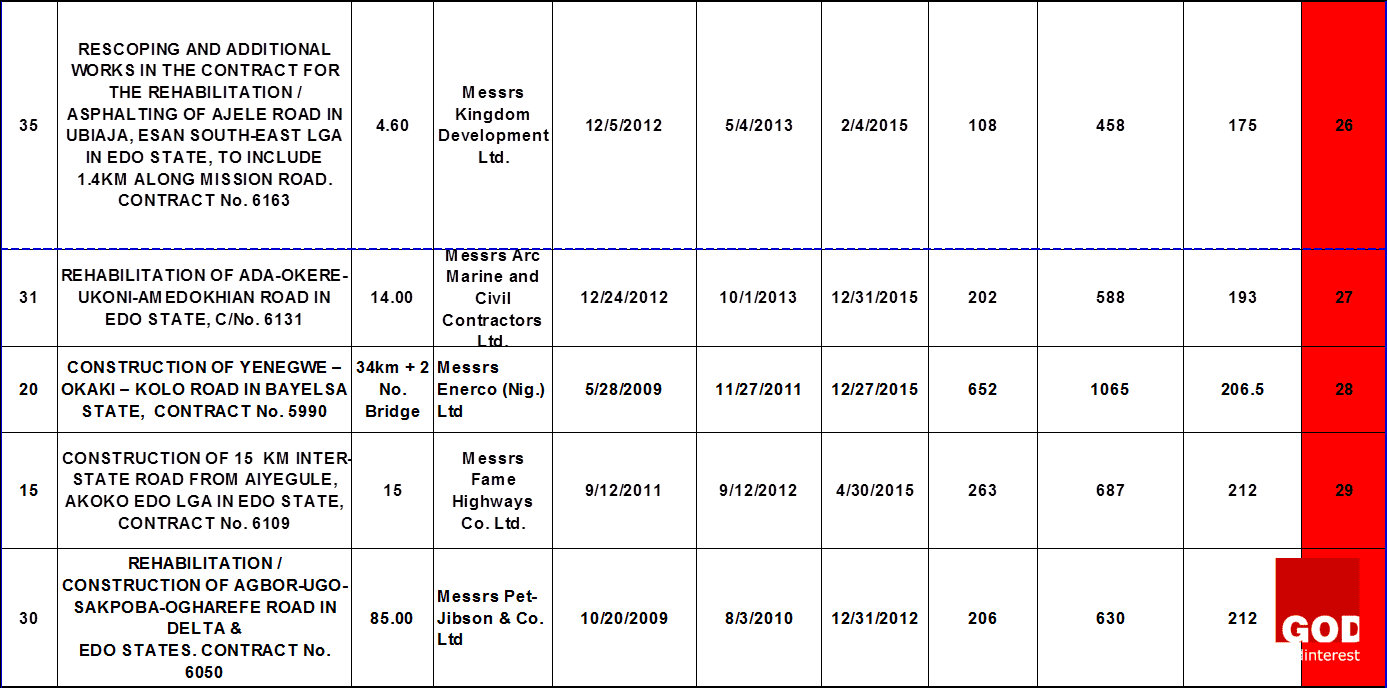
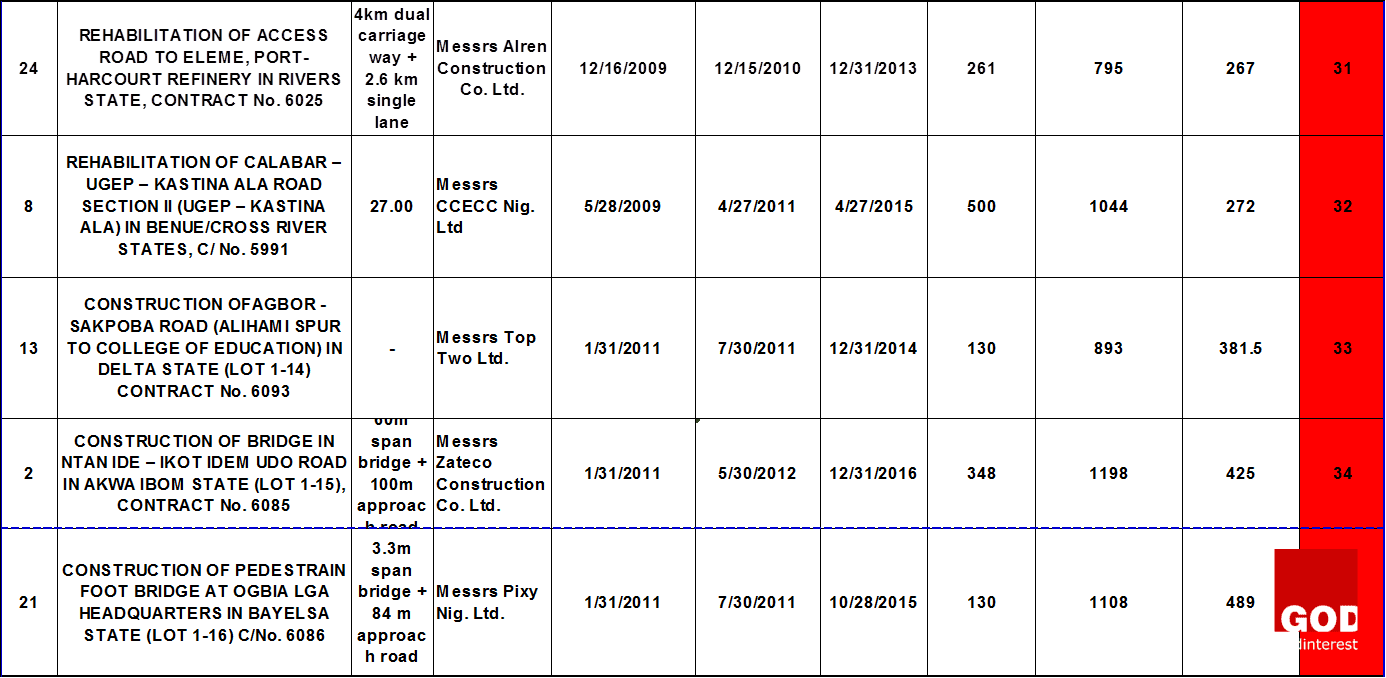
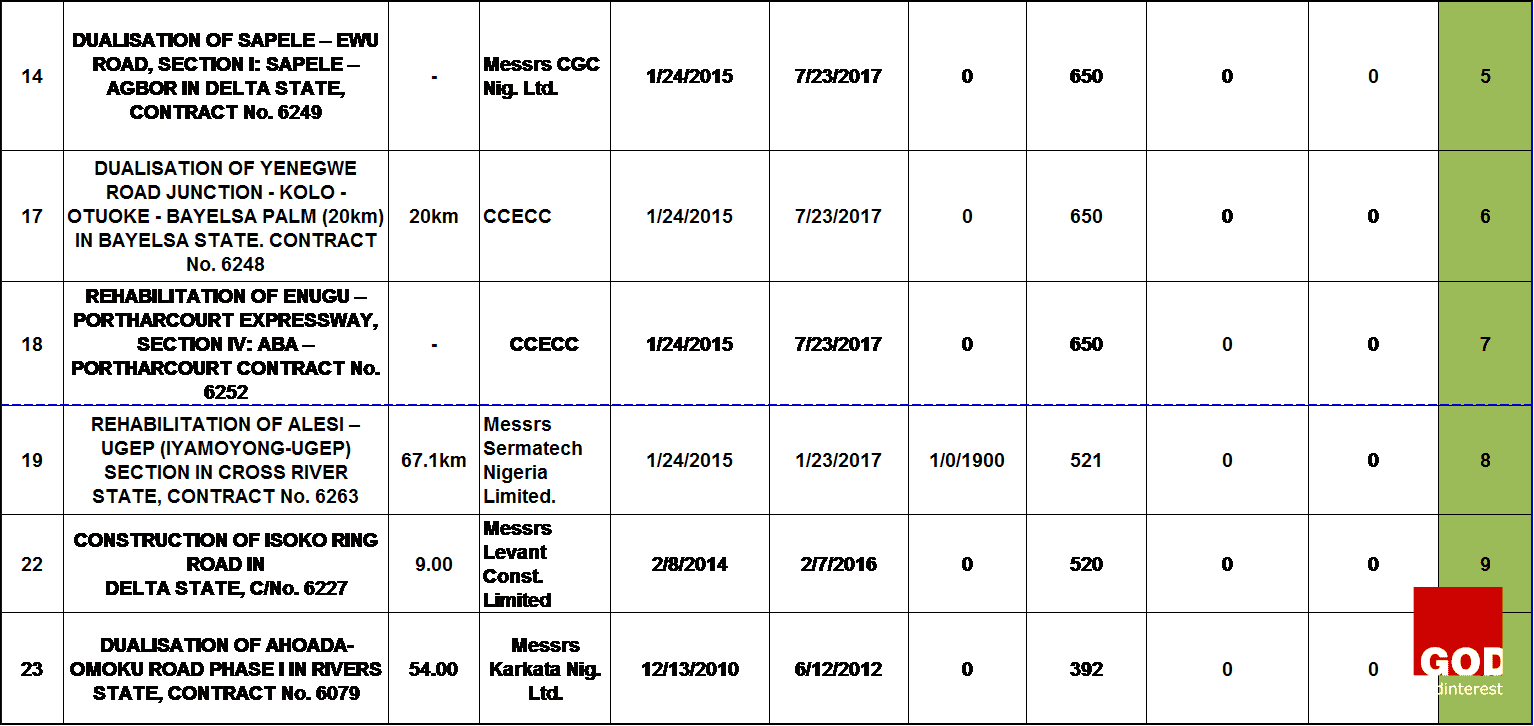
This research starts with a general reasoning or theory which says that the major cases of project failure in the Nigerian construction industry are defined based on time overrun and cost overrun. The findings from the data analysis will help on the decision to accept the theory or not. The research data was collected from the progress report for the month ending of October, 2015 published by the Nigeria of Federal Ministry of works on thirty-nine on-going highway construction projects at the South-South geopolitical zone. The table 1 below shows the information on the data collected which comprises of the project title, contract Number, project description, the contractor that was awarded the projects, the date of project commencement, date of completion and the extended date if any. The scheduled time for each project was specified as follows: project commencement date labeled as “a”, project completion date labeled as “b”, and the extended date labeled as “c”.

DATA ANALYSIS
The data analysis was done with the use of Microsoft excel. The analysis started by obtaining the number of days between the date of commencement of each project and the date of completion to show the duration of each highway project. And, the number of days between the project completion date and the extension date showed the time-overrun. The project duration and the extended days were obtained with the use of NETWORKDAYS function in Microsoft Excel which calculates the number of working days between two dates excluding weekends and any dates identified as holidays.
The standard deviation between the specified project duration for each highway projects and the extended days was calculated to obtain the extent to which each highway project contract failed on its time of delivery. This was denoted as the degree of failure. The table 1 above showed the projects ranking which was done based on the degree of failure of all the highway projects. The highway projects that were ranked from one to sixteen have low degree of failure and are represented with green color, while the rest are those with high degree of failure and are represented with red color.
FINDINGS
The findings made showed that the successfully completed highway projects have no extended days or time overrun, and the successful on-going highway projects are still on schedule and have no extended days unlike the on-going highway projects that have already failed as a result of the extended dates. Other projects have been abandoned because they have exceeded the delivery date as specified on the contract document, and have no extended date of completion. Thus, no work is going on.
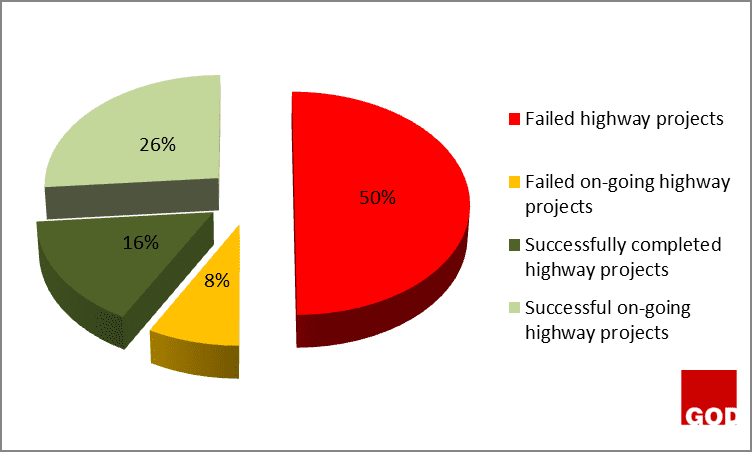
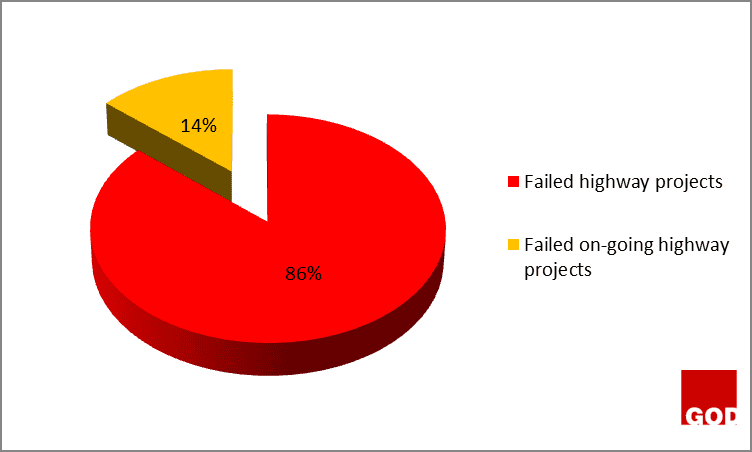
Figure 2 above showed that 14% of highway projects are still on-going projects because they have not exceeded the original date of completion as specified on the contract document. However, they are heading towards failure because they have been given an extended date of completion which can be as a result of some critical activities running behind schedule, causing delay on the critical path network of the projects. Moreover, the other 86% completely failed because they have exceeded their completion date specified on the contract document.
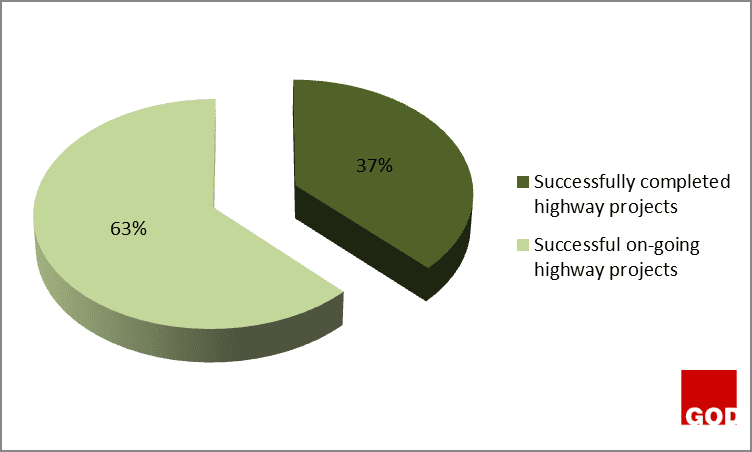
The figure 3 above showed that 63% of the successful highway projects are still on-going because they have not exceed their completion dates, and they are not yet completed. However, those on-going highway projects might end up as failed projects as a result of poor funding, discrepancy between the design and the construction on site, and conflict between the construction parties or stakeholders.
“Say what you will do, and do what you said” or “Say as you will do it, and do it as you said”
CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION
The idea of knowing what a failed project is, the factors and the causes is very important in project management. Success in project management can neither be achieved nor measured without the knowledge of project failure, its factors, and causes in the Nigerian construction industries. This work has shown that project failure is as a result of exceeded time of delivery, cost overrun, and poor quality. However, the analysis was only done based on exceeded time of project delivery because of the nature of the data collected.
This work suggested a few approaches to help reduce the number of failed projects in the Nigerian construction industry if properly implemented. Firstly, Having good collaboration between the project stakeholders involved in a construction project at the early stage of project conception is most important in order to accomplish the project objectives, and deliver the project on time, within budget, and quality specified on the original contract document (Othman, 2006).
Secondly, Adopting the ISO 9000 technique which is used for quality management will also help in achieving a successful project delivery. This technique states “ say what you will do, and do what you said” or “say as you will do it, and do it as you said”. This technique is not an indication of high quality but it promotes control and consistency which leads to specialization, and improved productivity and quality. Also, adopting the principles of lean construction will help to reduce waste within the construction and stream-line activities in order to improve the on-time delivery of projects.
Thirdly, Learning from the precedent failed projects, how those projects failed, and the reason for their failures. This will help the project manager to plan and mitigate the risks of project failures in the future. And, finally, more seminars and workshops will help to educate and enlighten clients (the federal government representatives), users, contractors, engineers, and architects on what is project failure, the factors that contributes to abundant failed projects, and their causes.
REFERENCE
Abimbola, A. (Novermber 24, 2012). About 12,000 Federal Projects Abandoned across Nigeria. Premium times (November 16, 2015). Retrieved from www. Premium timesng.com/news/108450-about-12000-federal-projects-abandoned-across-nigeria.html.
Al-Khali, M.I and Al-Ghafly, M.A. (1999). Important Causes of Delays in Public Utility Projects in Saudi Arabia. Construction management and Economics, 17, 647-655
Aibinu, A.A and Jagboro, G.O. (2002). The Effects of Construction Delays on Project Delivery in Nigeria Construction Industry. International journal of Project management, 20(8), 593- 599.
Anigbogu, N. and Shwarka, M. (2011). Evaluation of Impact of the Public Procurement Reform Program on Combating Corruption Practices in Public Building Project Delivery in Nigeria. Environtech Journal, 1(2). 43-51.
Assaf, S. and Al-Hajji, S. (2006). Causes of Delays in large Construction Projects. International Journal of Project Management, 24, 349-357.
Atkinson , R. (1999). Project management: Cost, time, and quality, two best guesses and a Phenomenon, it’s time to accept other success criteria. International Journal of project Management, 17(6), 337-342.
Belout, A and Gauvrean, C. (2004). Factors Influencing the Project Success: The impact of human resource management. International Journal of project Management, 22, Pp. 1-11.
Butcher, N. and Demmers, L. (2003). Cost Estiumating Simplified. Retrieved from www.librisdesign.org.
Cookie-Davies, T. (2002). The Real Success Factors on Projects. International Journal of Project management, 20(3), 185-190.
Dim, N.U. and Ezeabasili, A.C.C (2015). Strategic Supply Chain Framework as an Effective Approach to Procurement of Public Construction Projects in Nigeria. International Journal of Management and Susutainability, 4(7), 163-172.
Hanachor, M. E. (2012). Community Development Projects Abandonment in Nigeria: Causes and Effects. Journal of Education and Practice, 3(6), 33-36.
Idrus, A., Sodangi, M., and Husin, M., H. (2011). Prioritizing project performance criteria within client perspective. Research Journal of Applied Science, Engineering and Technology, 3(10), 1142-1151.
Idrus, A. and Sodangi, M. (2010). Framework for evaluating quality performance of contractors in Nigeria. International Journal of Civil Environment and Engineering. 10(1), 34-39.
National Bureau of Statistics (January, 2015). Nigerian Construction Sector Summary Report: 2010-2012.
Kotangora, O. O. (1993). Project abandonment, Nigerian Tribune.
Osemenan, I. (1987). Project Abandonment. New Watch Magazine, Vol. 1, pp. 15.
Othman, M.,R. (2006). Forging main and sub-contractor relationship for successful projects. Retrieved from http://rakanl.jkr.gov.my/csfj/editor/files/file/projek/lessonslearned/MAIN&SUB_2.pdf
Phua, F.T.T and Rowlinson, S. (2003). Cultural Differences as an Explanatory Variable for Adversarial Attitude in the Construction Industry: The case of HongKong. Construction Management and Economics, 21, 777-785.
Reiss, B. (1993). Project Management Demystified. London: E and FN Spon Publishers.
Toor, S. R. and Ogunlana, S. O. (2008).Problems causing Delay in Major Construction Projects in Thailand. Construction management and Economics, 26, 395-408.
Toor, S. R. and Ogunlana, S. O. (2008). Critical COMs of Success in Large-Scale Construction Projects: Evidence from Thailand constructuction industry. International Journal of Project management, 26(4), 420-430.
Toor, S. R. and Ogunlana, S. O. (2009).Beyound the “Iron Triangle”: Stakeholder perception of key performance indicators (KPIs) for large-scale public sector development projects. International Journal of Project management, doi: 10.1016/j.ijproman.2009.05.005.
Toor, R. and Ogunlana, S. (2009). Construction Innovation: Information, process, management. 9(2), PP. 149-167.
Turner, J. R. (1993). The Handbook of project-Based Management: Improving the process for achieving strategic objective. London, McGraw-Hill.
Wright, J., N. (1997). Time and Budget: The twin imperatives of a project Sponsor. International Journal of Project Management, 15(3), 181-186.
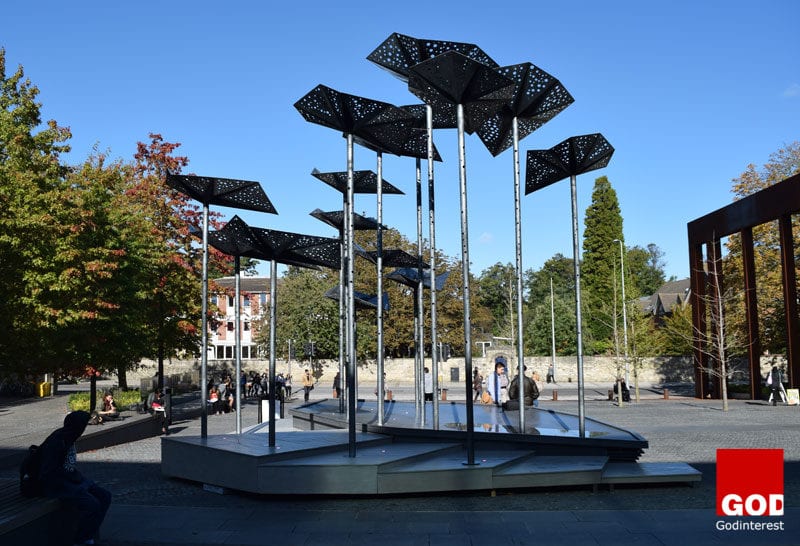
Bridge House, Croydon, Is Prefab Really Prefabulous?
Prefabricated homes have been available for years and date back at least a century. The Sears Roebuck index made and offered prefab homes to the public as early as 1908, and Prefab was later explored by famous twentieth-century architects, such as, Walter Gropius, Le Corbusier, Marcel Breuer, Frank Lloyd Wright, who saw the method as a likely solution to the dilemma of housing in modern society. Interest in Prefab grew in the first half of the twentieth-century, with the outburst of manufacturing expertise and the creation of the assembly line.
Historically the mention of prefabricated houses invokes memories of housing built to cover in the temporary a deficiency of housing in the UK following the World Wars.
The Government promised ‘homes fit for heroes’, however, negative public attitudes surfaced towards prefabricated housing because of substandard building materials used and poor workmanship.
A staggering 1 million of these homes were built during the 20th century and more than half a century on, many are still standing despite no foundations. A few are listed while others have been demolished.
Today people remember the shabby mobile classrooms as in, bitter cold in winter and like an oven in summer. Therefore, memories have rendered the concept of prefabricated houses an unattractive idea. Talk about the term prefabricated housing to an architect, and their eyes will beam with visions of fascinating contemporary homes. However, talk to the ordinary person on the street and people immediately think that we are going down the same path, a pretty hard image to shake off. The very factors that are presented as positive advantages of prefabricated homes became liabilities in the eyes of homeowners who wanted a durable appreciating asset.
An example can be found by looking at the prefabricated houses on Catford estate built by German and Italian prisoners of war in 1946.

‘They were not built to last and need regular maintenance. They are just large sheds really and taking up a lot of space. They should really be demolished.’ (Drake 2008)
Over the ten years, Lewisham Council has tried to develop the site many times and a review found none of the dwellings met Decent Homes Standard.
So why do more and more developers choose prefabricated construction?
First and foremost – Speed. “It may take a bit longer in terms of design, preparation and planning but site based activities are taking up to 30% less time and allowing homes to reach the market sooner. Other reasons cited include, in order of preference:
- Design Quality
- Cost
- Previous Experience
- Funding
Source: Design and Modern Methods of Construction. The Housing Corporation and CABE 2004″
Bridge House (Example)
Croydon Vision 2020 is a regeneration programme by the London Borough of Croydon for the centre of Croydon in South London. The Old Town Masterplan focused on the area between the High Street and Roman Way, one of the oldest areas of Croydon.
Formerly the site of a telephone exchange, Bridge House is a £20 million development that has provided 27 private and 48 affordable apartments, above ground and mezzanine retail spaces.
The block wraps around an existing multi-storey car park and offers the opportunity for cafs and shops to open onto the new square. A mix of green and brown roofs, to support biodiversity, form part of a series of environmental measures and the scheme is to be of modular construction.
The Croydon chose the modular approach principally because of the speed of construction offered. The project began on site in the spring of 2006 and the 75 flats were stated to have been erected in approximately 26 days, vastly outperforming the time taken by traditional construction.
Client: Howard Holdings plc
Architect: AWW
Structures: Walsh Associates
Principal Supplier: MC First
15 Shocking Project Management Statistics
The project management landscape is changing with an increased emphasis on productivity, reporting, and information technology. A number of studies have been completed that look into the success and failure rates of projects.
Below are 15 shocking statistics that reveal how project management has changed and is performing across various industries over the last 5 years.
- There is projected to be 15.7 million new project management roles to be added globally across seven project-intensive industries by 2020 reaching an economic impact of over $18 trillion, across seven project-intensive industries including Manufacturing, Finance & Insurance, Information Services, Utilities, Business Services, Oil & Gas and Construction (Project Management Institute)
- 75% of IT executives believe their projects are “doomed from the start. (Geneca)
- The healthcare industry is projected to increase project management roles by 30%, a higher growth rate than any current project intensive industry between 2010 and 2020. (Project Management Institute)
- A third of all projects were successfully completed on time and on budget over the past year. (Standish Group)
- 80% of “high-performing” projects are led by a certified project manager. (PricewaterhouseCoopers, Insights and Trends: Current Programme and Project Management Practices 2012)
- One in six IT projects have an average cost overrun of 200%. (Harvard Business Review 2004)
- 44% of project managers use no software, even though PWC found that the use of commercially available PM software increases performance and satisfaction. (Pricewaterhouse Coopers)
- More than 90% of organizations perform some type of project postmortem or closeout retrospective. (The Standish Group: CHAOS Research Report 2013)
- On average, it takes 7 years in the profession to go from entry-level to managing large, complex projects. (ESI International: Annual Salary Survey 2013)
- The average large IT project runs 45% over budget, 7% over time, and delivers 56% less value than expected. (Project Management Institute: Pulse of the Profession 2015)
- Only 64% of projects meet their goals. (Project Management Institute: Pulse of the Profession 2015)
- 60% of companies don’t measure ROI on projects. (KPMG New Zealand: Project Management Survey 2010)
- The United States economy loses $50-$150 billion per year due to failed IT projects. (Gallup Business Review)
- In just a 12 month period 49% of organizations had suffered a recent project failure. In the same period only 2% of organizations reported that all of their projects achieved the desired benefits. 86% of organizations reported a shortfall of at least 25% of targeted benefits across their portfolio of projects and many organizations failed to measure benefits so they are unaware of their true status in terms of benefits realization. (KPMG – Global IT Project Management Survey 2005)
- According to an IBM study, only 40% of projects meet schedule, budget and quality goals. (Harvard Business Review 2004)
If you have any other project management statistics please share them with us.
65% of Mega-projects Fail
There’s a reason why Mega-projects are simply called “Mega-projects.” Extremely large in scale with significant impacts on communities, environment and budgets, mega-projects attract a lot of public attention and often cost more than 1 billion. Because of its grandiose, a successful mega-project requires a lot of planning, responsibility and work. Likewise, the magnificence of such projects also creates a large margin for failure.
Mega-projects Come with Big Expectations. But a Project’s Success Is Often in the Eye of the Beholder
Despite their socio-economic significance mega-projects – delivering airports, railways, power plants, Olympic parks and other long-lived assets – have a reputation for failure. It is thought that over optimism, over complexity, poor execution, and weakness in organizational design and capabilities are the most common root causes of megaproject failure.
Blinded by enthusiasm for the project, individuals and organizations involved with mega-projects often miscalculate the complexity of the project. When a mega-project is pitched, its common for costs and timelines to be underestimated while the benefits of the project are overestimated. According Danish economist Bent Flyvbjerg, its not unusual for project managers who are competing for funding to massage the data until it is deemed affordable. After all, revealing the real costs up front would make a project unappealing, he said. As a result, these projects are destined for failure.
For example, building new railways spanning multiple countries could prove to be disastrous if plans are overly complex and over-optimized. Such a large-scale project involves national and local governments, various environmental and health standards, a wide range of skills and wages, private contractors, suppliers and consumers; therefore, one issue could put an end to the project. Such was the case when two countries spent nearly a decade working out diplomatic considerations while building a hydroelectric dam.
Complications and complexities of mega-projects must be considered thoroughly before launch. One way to review the ins and outs of a project is through reference-class forecasting. This process forces decision makers to look at past cases that might reflect similar outcomes to their proposed mega-project.
Poor execution is also a cause for failure in mega-projects. Due to the overoptimism and overcomplexity of a project, it’s easy for project managers and decision makers to cut corners trying to maintain cost assumptions and protect profit margins. Project execution is then overwhelmed by problems such as incomplete design, unclear scope, and mathematical errors in risk assessment and scheduling.
Researchers at McKinsey studied 48 struggling mega-projects and found that in 73 percent of the cases, poor execution was responsible for cost and time overruns. The other 27 percent ran into issues with politics such as new governments and laws.
Low productivity is another aspect of poor execution. Even though trends show that manufacturing has nearly doubled its productivity in the last 20 years, construction productivity remains flat and in some instances has even declined. However, wages continue to increase with inflation, leading to higher costs for the same results.
According to McKinsey studies, efficiency in delivering infrastructure can reduce total costs by 15 percent. Efficiency gains in areas like approval, engineering, procurement and construction can lead to as much as 25 percent of savings on new projects without compromising quality outcomes. This proves that planning before execution is worth its weight in gold.
We Tend to Exaggerate the Importance of Contracting Approach to Project Success or Failure
Finally, weaknesses in organizational design and capabilities results in failed megaprojects. For example, organizational setups can have multiple layers and in some cases the project director falls four or five levels below the top leadership. This can lead to problems as the top tier of the organizational chain (for example, subcontractors, contractors and construction managers) tend to focus on more work and more money while the lower levels of the chain (for example, owner’s representative and project sponsors) are focused on delivery schedules and budgets.
Likewise, a lack of capabilities proves to be an issue. Because of the large-scaled, complex nature of mega-projects, there is a steep learning curve involved and the skills needed are scarce. All the problems of megaprojects are compounded by the speed at which projects are started. When starting from scratch, mega-projects may create organizations of thousands of people within 12 months. This scale of work is comparable to the significant operational and managerial challenge a new start-up might face.
In the end, it seems that if organizations take the time to thoroughly prepare and plan for their mega-projects, problems like overcomplexity and overoptimism, poor execution, and weaknesses in organizational design and capabilities could be avoided. After all, mega=projects are too large and too expensive to rush into.
How To Deliver On The Promise of MegaProjects
Due to the large scale and outlook attached to them, mega-projects have a large opportunity for failure. Typically, the failure begins at the outset of the project, whether that be due to poor justification for the project, misalignment among stakeholders, insufficient planning, or inability to find and use appropriate capabilities.
Underestimated costs and overestimated benefits often offset the baseline for assessing overall project performance. This is why it is important for organizations to first establish social and economic priorities before even considering what projects will answer their needs. Once social and economic priorities are established, only then can a project be considered. Selecting projects must be fact-based and transparent in order to ensure accountability with stakeholders and the public.
Successful Megaprojects Must Have Robust Risk-analysis or Risk-management Protocols
It’s also important to maintain adequate controls. Successful megaprojects must have robust risk-analysis or risk-management protocols and provide timely reports on progress relative to budgets and deadlines. Typically, progress is measured on the basis of cash flow, which is less than ideal as data could be out of date and payments to contractors do not correlate construction progress. Instead, project managers should deliver real-time data to measure activity in the field. For example, cubic meters of concrete poured relative to work plans and budgets.
Overall, improving project performance requires better planning and preparation in three areas: doing engineering and risk analysis before construction, streamlining permitting and land acquisition, and building a project team with the appropriate mix of abilities.
Project developers and sponsors should put more focus into pre-planning such as engineering and risk analysis before the construction phase. Unfortunately, most organizations and sponsors are reluctant to spend a significant amount of money on early-stage planning because they often lack the necessary funds, they are eager to break ground and they worry the design will be modified after construction is underway, making up-front designs pointless.
However, it’s proven that if developers spend three to five percent of capital cost on early-stage engineering and design, results are far better in terms of delivering the project on-time and on-budget. This is because through the design process, challenges will be addressed and resolved before they occur during the construction phase, saving both time and money.
It’s not unusual for permits and approvals to take longer than the building of a megaproject. However, if developers look to streamline permitting and land acquisition, that would significantly improve project performance. Best practices in issuing permits involve prioritizing projects, defining clear roles and responsibilities and establishing deadlines.
In England and Wales, developers applied these approaches to cut the time needed to approve power-industry infrastructure from 12 months to only nine months. On average, timelines for approval spanned four years throughout the rest of Europe. Likewise, the state of Virginia’s plan to widen Interstate 495 in 2012 was able to cut costs and save hundreds of homes thanks to land acquisition planning by a private design company.
Investors and Owners Must Take an Active Role in Creating the Project Team
When it’s all said and done, projects cannot deliver the best possible return on investment without a well-resourced and qualified network of project managers, advisers and controllers. Investors and owners must take an active role in creating the project team.
It’s not enough to have a vague overview of what the project might look like in the end. Instead, it’s necessary to review risks and costs and draft a detailed, practical approach to tackle various issues. An experienced project manager cannot do it all alone. The project team must include individuals with the appropriate skills, such as legal and technical expertise, contract management, project reporting, stakeholder management, and government and community relations among others.
Failure to Properly Plan for These Projects Could Have a Negative Impact on Society
While mega-projects are important in filling economic and social needs, failure to properly plan for these projects could have a negative impact on society. Take Centro Financiero Confinanzas (Venezuela), the eighth tallest building in Latin America at 45 stories, located in the financial district of Venezuela’s capital, Caracas for example.
To those unaware of its history, the Centro Financiero Confinanzas is actually home to over 700 families, a “vertical slum” that is a truly fascinating example of reappropriation of space in an urban environment. An ironic symbol of financial failure that was intended to represent the unstoppable march of Venezuela’s booming economy.
It’s much more than an unbuilt building, bridge or tunnel, failed mega-projects are a blow to the economic growth and social improvements of communities around the world.
Small Projects Often Mean Greater Innovation
Small projects often embody more innovation than larger more costly or high profile ones.
Innovation is a wide concept that includes improvements in processes, products and services. It involves incorporating new ideas which generate changes that help solve the needs of a company and so increase its competitiveness. That’s hardly big news. But what may be surprising to some is that innovation has itself, well, innovated and it isn’t what it used to be.
New materials and energy, design approaches, as well as advances in digital technology and big data, are creating a wave of innovation within the construction industry. These new ideas are increasingly often tested and proven on smaller and agiler projects. Investing time and money is well spent on these ideas and technical improvements can then be used on large-scale developments.
Here are three exciting small projects:



Milan, Italy
1. Vanke Pavilion – Milan Expo 2015
The corporate pavilion for Vanke China explores key issues related to the theme of the Expo Milano 2015, “Feeding the Planet, Energy for Life”.
Situated on the southeast edge of the Lake Arena, the 800-square meter pavilion appears to rise from the east, forming a dynamic, vertical landscape.
The original tiling pattern would have resulted in thousands of ceramic tiles of different sizes and shapes. The resulting complexity and lack of repetition could have led to high costs and a longer erection time.
Working with Architects Studio Libeskind, Format Engineers (Engineering Designers with backgrounds in structural engineering, coding, mathematics, and architecture) changed the pattern from thousands of different tiles to less than a dozen and simplified the backing structure generating huge cost savings. Format Engineers also proposed ‘slicing’ of the building and then fabrication of the primary structure of steel ribs using low tech flat steel plate elements. These were then used in a series of long span portalised frames reminiscent of the ribs and spars in traditional boat building resulting in a column-free area for the display of Chinese Cultural Heritage.
The frame was built to a budget and without difficulty ahead of the neighboring Expo buildings.
Building Size
12 meters high
740 mq gross floor area (exhibition, service & VIP levels)
130 mq roof terrace
Architect: Studio Libeskind
Engineer: Format Engineers
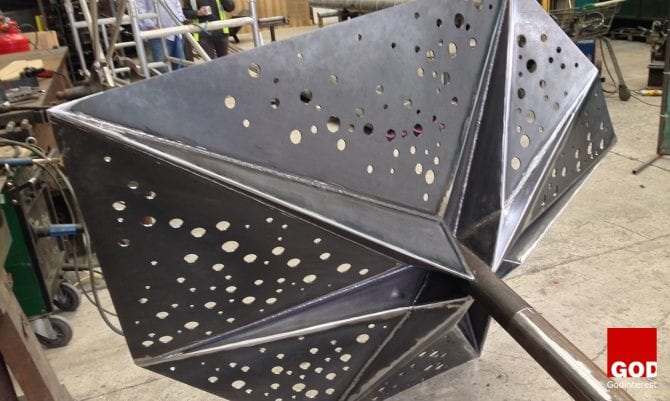



2. Oxford Brookes Rain Pavilion
The Rain Pavilion is an urban forest sculpture forming the front entrance to Oxford Brookes University’s Architecture Faculty.
“Rain Pavilion artwork is a sensory experience for the community.”
The complex form required extensive wind modeling and comprehensive structural analysis within a generative 3d model. This was allied with Format Engineers in-house code for the self-organization of voids and their subsequent redistribution.
.At each stage of the design process different modeling and analysis techniques were used to exploit the form and to optimise the structure. The considerable challenges posed by the slenderness of the structure and its dynamic behavior under wind were resolved by combining Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) (a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical analysis and algorithms to solve and analyze problems that involve fluid flows) with a generative design environment. Conceptual design introduced the ideas of tubular stems and folded steel canopies, both of which were perforated by circular holes arranged to allow the interplay of light and water through the structure. The voids were generated using a self-organizing process.
Grasshopper (a graphical algorithm computer 3-D modeling tool) was used to produce a mesh that could include the voids in both the stems and the petals.
The Rain Pavilion is designed to celebrate the sound of rain, and the noise of water interacting with different sections of the installation is part of the experience of passing through it. The structure has a design life of five years and can be transported to other locations.
Architect: Oxford Brookes University, Oxford, UK
Engineer: Format Engineers
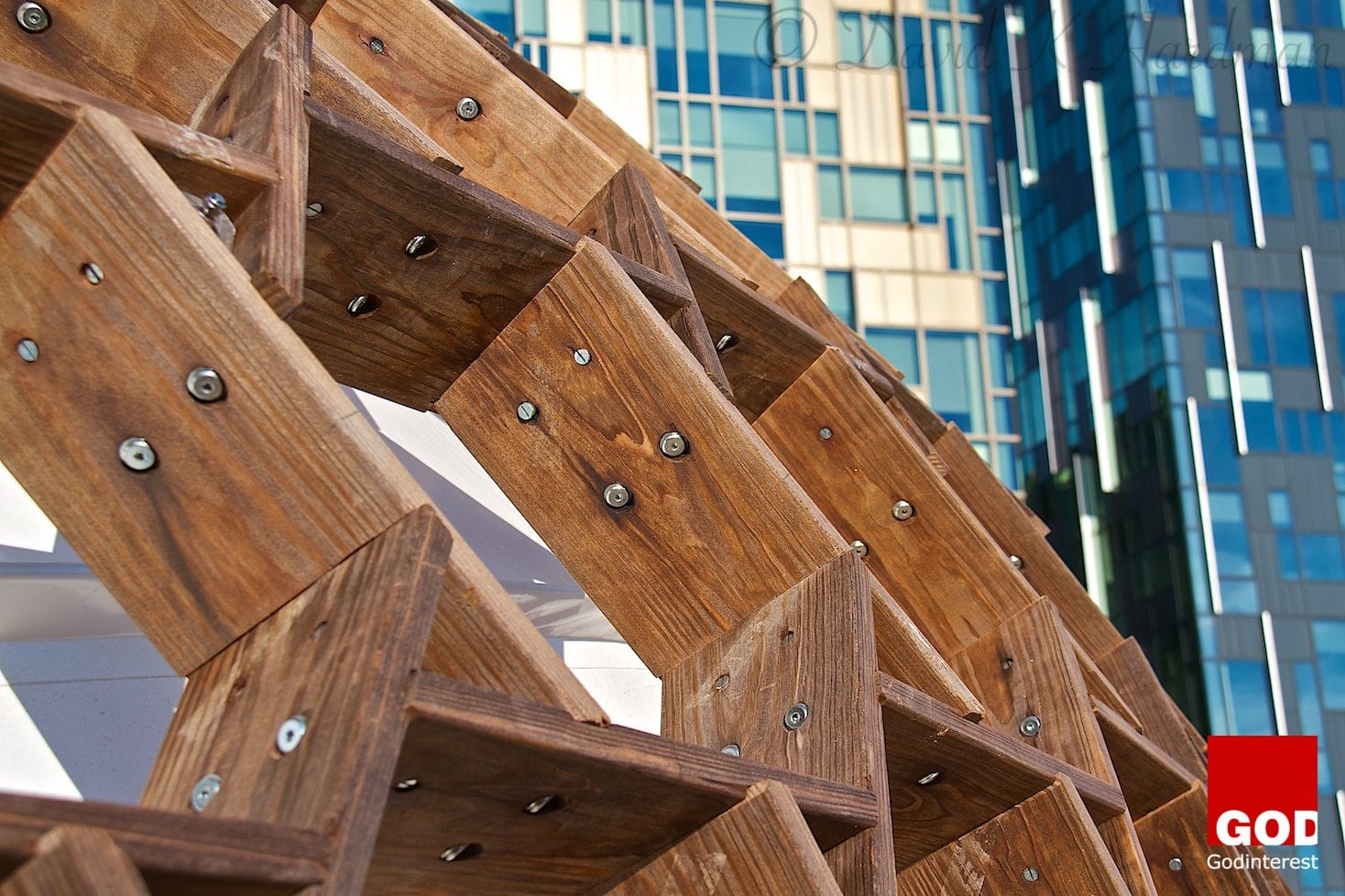



3. KREOD Pavilion
The KREOD pavilions were first erected on the London Greenwich Olympic site in 2012. Easily rearranged, three pod-like pavilions were formed with a wooden structural framework comprised of an open hexagonal composition.
Standing three meters tall, each double-curved wooden shell enclosed a footprint of 20 square meters, totaling 60 square meters. A waterproof tensile membrane sealed the interior from the elements fully portable with demountable joints, the individual components can be stacked for efficient transportation.
Chun Qing Li the architect required a temporary exhibition or function space that could be erected and demounted mostly by hand and by untrained staff. The quality of finish needed to echo that of handmade furniture and had to be low cost and quick to erect. The continuously changing double curved form of the enclosure meant that in theory, every nodal connection was different. A conventional bolted solution would have cost hundreds of pounds per fixing. Format Engineers suggestion of a ‘reciprocal’ jointed timber grid shell required standard bolts which equated to a fraction of the normal cost. It also allowed the structure to be built from simple and light flat timber elements.
The structure used Kebony timber throughout, a sustainable alternative to tropical hardwood. As this material had not previously been used in a structural context Format Engineers undertook load testing of the material and the connections at the University of Cambridge. The timber was fabricated using CNC routing (a computer controlled cutting machine) allowing a highly accurate fit between members and basic erection on site.
Architect: Chun Qing Li
Engineer: Format Engineers
9 Architectural Projects That Busted the Bank Vaults
Since the beginning of recorded time, construction projects have always been a major part of history. In fact, grandiose construction projects to erect the architectural visions of Pharaohs, Kings, Rulers, and Monarchs was used as a way to put the wealth and power of leaders on display for all of the people their lands to see.
Not surprisingly, all of these projects came at a great cost to the leaders that initiated them.
The Great Pyramid at Giza is one example of a grand architectural vision. This massive structure was built under the leadership of Egyptian pharaoh Khufu in the 26th century B.C.E. By the time work on the structure was completed, Knufu spent a great deal of his kingly fortunes on the project. According to sources, it is estimated that this project would cost more than $5 billion dollars to duplicate today.
Since then, there have been many other building projects that have cost significant amounts of money to build, some that were so grand in their scope they effectively broke the bank.
We will examine more of these projects here.

1. The Three Gorges Dam
This massive Chinese construction project took place over the Yangtze River in the Hubei province of Central China. This scope of this project was enormous and came with quite a bit of controversy due to the changes to the environment that were needed to make the project become a reality. When this project was approved in 1992, the Vice Premier at the time, Zoa Jiahua quoted the project cost at $8.35 billion to complete. In 2006, when the project was officially ended, the total cost ended up being closer to $37 billion dollars, or roughly four times more than the original estimate.

2. The Ryungyong Hotel
The ground broke for this 105 story luxury tourist hotel in 1987 in North Korea, despite the country being closed off to foreign visitors. After investing approximately $750 million dollars in the structure, the project came to an abrupt end when the Soviet Union, North Korea’s major economic supporter, collapsed. Today, the building remains unfinished and is recognised as being the tallest unoccupied structure in the entire world.



3. The MOSE Project
This building project was originally intended to help control flooding in Venice. However, it primarily served as a project to sink money into. The original budget for the project was $1.7 billion dollars but jumped to $8.1 billion over time. None of the work that was completed did anything to prevent flooding. Many people involved in the initial construction were arrested on bribery and corruption charges in connection with the project. Venice continues to have problems with flooding and sinking.

4. The Mirabel Airport
This airport was originally opened to serve Montreal, Canada in mid-1970. The Government seized 100,000 acres of land and displaced thousands of residents from their homes for the land that was needed to construct the airport. The cost of the land was $140 million dollars. This amount was eight times more than the costs that were originally projected. Once construction on the airport began, the price skyrocketed to a total cost of around $276 million dollars. Adding further pressure to the Mirabel Airport project was the fact that the Montreal-Dorval International Airport was located within a short driving distance away. While this airport did operate for a number of years, it ceased operations in 2004. In late 2014, demolition of the site began which added another $15 million dollars of cost to the failed project.



5. The Sagrada Familia
There is no doubt that building a Cathedral is no small undertaking. For the Sagrada Familia Cathedral, it is a project that has advanced at a snail’s pace and with a hefty price tag that can not even be calculated due to how slow the project has been to finish. Construction on the house of worship began in 1883. In 2015, it still needs to be completed. In 2011, the President of the Building Committee said that it might be completed in 2026 – 143 years after construction originally began.


6. The Millennium Dome
This is a London based project that has a happy ending, despite a shaky, and very expensive start. When construction of the Millennium Dome began in the 1990’s, the original budget of 758 million pounds was exceeded when it ended up costing 789 million pounds, so it lost money from day one, even without including maintenance costs. However, in 2007 the structure was sold to AEG and renamed the 02 Arena, so some of the initial investment money was recouped. This site is now a top venue for sporting events and concerts in the London, UK area.

7. The Channel Tunnel
Sometimes referred to as the “Chunnel” is a tunnel in the English Channel that links the United Kingdom with France. It’s not surprising that a project of this scope would cost a lot of money and time to complete successfully. In total, it took six years of work and $21 billion dollars to finish. In financial costs, it ended up being 80% more expensive than originally forecast. This privately funded project caused many of the initial investors to lose most of their investment due to over run costs. Today, their diligence to the project has made it widely successful. Hundreds of millions of people use the Chunnel trains to commute between France and the UK, with a travel time of around 35 minutes.


8. The Central Artery Tunnel Project
In 1991, Boston began construction of the Central Artery/Tunnel Project, also known as the Big D, to provide commuters with an alternative to using the main highway through the City. This project is one of the most expensive construction projects in the history of the United States with a ‘real’ cost of $22 billion dollars once interest on the funding for the project is paid off in 2038. The Central Artery/Tunnel Project included the construction of roads, bridges, and even a tunnel that was built under the Boston Harbor. While this project did have the original effect it was supposed to have by alleviating traffic congestion in parts of Boston, overall traffic in the areas where the Big D serves has also increased.

9. The Panama Canal
The Panama Canal is another example of a building project that came with many personal and financial losses during its construction in the early 1900’s. The project was hexed with obstacles including outbreaks of deadly malaria and mudslides that, according to hospital records, resulted in over 5,600 labourers deaths. Today, the Panama Canal remains a key part of the shipping industry between the Atlantic and the Pacific Ocean. In 2014, work at the Canal ground to a halt after a dispute between the Panama Canal Authority and a conglomerate of European construction companies disagreed who would pay for a $1.16 billion overrun in costs. All parties involved in the dispute agreed on stop-gap funding that put the project back in action. In 2015, expansion work on the Panama Canal continues and the overall costs of the project continue to rise.
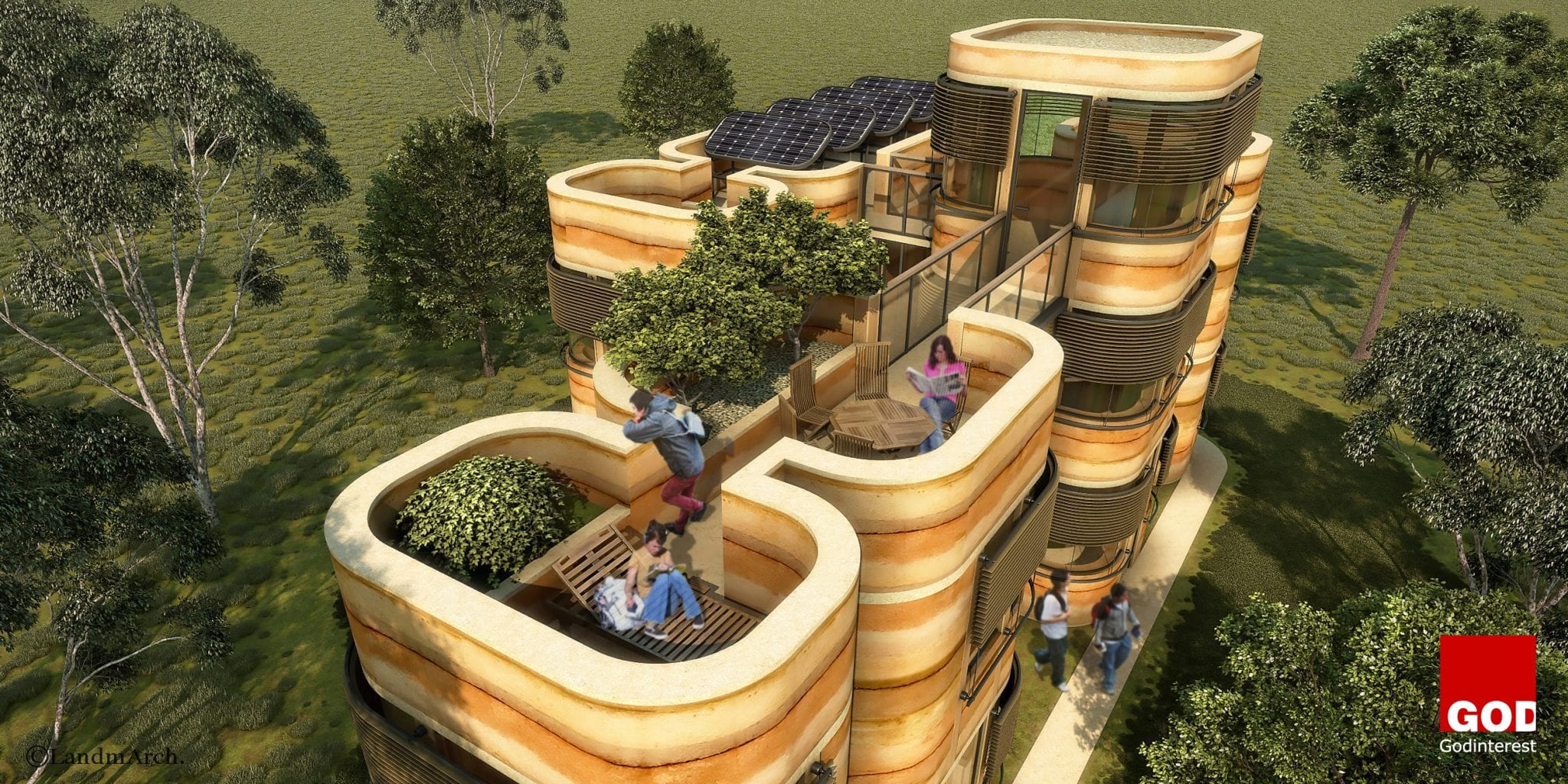
Modular Eco-house System
Top 10 Project Management Myths Debunked
Since the dawn of time, mankind has used myths to make sense of the uncertainty that surrounds us. In the early 1990s a lot of people believed that project management was the best kept secret in business. However, because project management was not seen as a prevailing profession at that time, it suffered from a lack of awareness which was in a sense, a double edged sword. Those who were knowledgeable in the practice of project management became extreamly valuable to organisations and pioneers for the profession.
These early adopters were able to convince organisations that project management practitioners were needed. Myths around project management began to form in the business community and as the role of the project manager was unclear, questions were raised as to what project management was and what it could offer organisations.
The definition of the word myth is a “widely held, but false belief or idea.” Here, we’re going to examine 10 of the most pervasive PM myths that have emerged.
Myth #1 – Contingency pool is redundant
This is one of the most ‘mythical’ myths that has plagued the industry for a long time. Coupled with the tendency to presume that ‘real work’ is tantamount to implementation or building something concrete and you have the perfect recipe for project disaster. The thought pattern behind this approach typically originates from budget constraints and/or having unrealistic expectations. As we all know, or should know, the unexpected happens quite regularly. An effective contingency plan is important as it aims to protect that which has value (e.g., data), prevent or minimise disruption (e.g., product lifecycle), and provide post-event feedback for analysis (e.g., how did we fare? did we allocate funds correctly?).
Myth #2 – Project Management software is too expensive
If your idea of project management software involves purchasing servers, and purchasing a software application from a major vendor for a small practice with 10 practitioners then, yes, it is too expensive. If, however, you have gone cloud and elected to use a powerful web-based project management solution (such as Smartsheet), then you are likely to save thousands of pounds while reaping the benefits of a pay-as-you-go price structure. The present, and future, lie in cloud solutions that provide equal, or superior, functionality at a fraction of the cost.
Myth #3 – Project Management methodologies will slow us down
Project managers have a reputation of using process-intensive methodologies that favour ideology over pragmatism. In some instances this may, indeed, be the case when there is a mismatch between a specific project management approach and the organisation’s acutall needs (e.g., a process-driven method, such as PRINCE2, may not be appropriate for a slightly chaotic environment that favours an adaptive approach, such as Scrum). So, in sum, put down the paint roller (“Project Management isn’t for us!”) and take out your fine-bristled brush (“The Critical-Chain method may not be our cup of tea, but Agile on the other hand”¦”).
Myth #4 – Facts and figures are more important than feelings and perceptions
While facts are very important, projects are often derailed and sabotaged because of false perceptions. The PM must pay attention to both fact and fiction to navigate through turbulent organisational change.
Myth #5 – Project managers need to be detail oriented and not strategic in nature
While it is of the utmost importance for the project manager to understand how to read the details of the project, they must also understand how the project supports organisational objectives. Having a strategic perspective adds great value to the skill-set of the project manager.
Myth #6 Rely on the experts in everything that you do
It is true, we do need to rely on the experts but our trust can not be a blind faith. The job of the project managers in this area is twofold. First we must extract information and second we must verify that the information is accurate. A good example of this is asking a planner to provide an estimate on the effort required to perform a task. In some instances team members forget to include tasks which ultimately results in a faulty estimate.
Myth #7 All the battles have to be fought and won so that we can succeed
Project managers sometimes make the assumption that they need to stand firm to get the job done, however, coming to compromise on a particular issue is often a better course of action in order to win the war.
Myth #8 Project Managers can wear multiple hats
Wearing different hats can be extremely confusing. This is especially true if the project manager is asked to be a business analyst or technical expert on top of serving in their PM role. They end up doing both roles with mediocrity. When we “wear two hats” we essentially tell ourselves that both hats fit on one head at the same time. However, what happens if the demands of two roles conflict and what assurances do we have that we’re managing the inherent conflict of multiple roles and the risks the roles introduce? Sadly, multiple roles become more common as we move up the management hierarchy in an organisation, and that’s exactly where potential conflicts of interest can do the most harm.
Myth #9 Once the risk register is created, it’s full speed ahead
Risk management provides a forward-looking radar. We can use it to scan the uncertain future to reveal things that could affect us, giving us sufficient time to prepare in advance. We can develop contingency plans even for so-called uncontrollable risks, and be ready to deal with likely threats or significant opportunities. Too often, it’s not until a catastrophic event occurs and significantly impacts project progress that ongoing risk reviews are conducted.
Myth #10 Project managers can not be effective in their role unless they have specific technical expertise in the given field that the project falls within
You don’t need to be an engineer to manage a construction project or a IT technician to manage a software development project. All you need is a fundamental understanding with strong PM skills to manage the team. Experience in the field helps but does not guarantee success.
Project management is challenging enough without the myths. The profession has come a long way since the 1990s and some of these myths are fading. However, we still see remnants of them in one form or another. Great projects cut through false assumptions and confusion, allowing their teams to make smart decisions based on reality.
These are just 10 project management myths, what are yours?
13 Basic Facts You Should Know about Modular Homes
Modular homes sometimes referred to as “factory-built construction“, encompass a category of housing built in sections typically at a factory location. These houses must conform to local and regional building codes for the country the buyer plans to situate the dwelling.
Just like site-built housing, construction teams build modular homes to last and increase in value over time. As the factory finishes building sections of the house, each piece is transported to the homeowners build site on large truck beds. Local building contractors then assemble the house and inspectors ensure the manufacturer has built your residence to code. Most customers find that modular housing is less expensive than site-built homes.
1. Benefits of Construction
One of the benefits of construction is that manufacturers build them indoors in an enclosed factory setting, where the materials used to build the homes are not subject to adverse weather during construction.
Most building contractors can finish erecting a house in as little as 1-2 weeks, though it may take up to 4 weeks or more for local contractors to finish building the dwelling on-site once it has been delivered.
2. Differences Between Modular and Site Built
Modular homes are not the same as site-built homes, which contractors create 100% at the build site. That means the
contractor must collect all the materials for a house and built it on-site. Like a modular home, the site-built home must conform to all regional, state and local building codes. Many refer to site-built construction as stick-built homes. Stick built housing is also well-built and designed to last a lifetime.
3. Difference Between Modular and Manufactured

Manufactured housing is another form of factory construction. Many consumers have mistakenly referred to these homes in the past as mobile homes. Others refer to manufactured homes as trailers. Manufacturers do build these houses in a factory like modular homes on a steel chassis.
The manufacturer then transports sections of the home to the building site as completed. These dwellings are usually less expensive than both modular housing and site built housing, in part because they don’t come with a permanent foundation. Trailers and mobile homes are more likely to depreciate than modular or site built homes.
4, Advantages of Modular Construction Over Site Built
Modular homes offer many advantages over traditional site built dwellings. Many consider modular homes a hybrid breed of housing. Not a manufactured house and not a site built house, these homes offer consumers multiple benefits including costs savings, quality and convenience. In many ways modular homes surpasses site built housing in quality and efficiency.
Modulars have grown up. They are more and more becoming a mainstream selection for first time and secondary homebuyers. Most people now realise they don’t’ have to give up design quality or customization to buy a prefabricated house. One of the biggest misconceptions people have of prefabricated housing is they are look alike. “Boxy” is not a word that can begin to describe prefab dwellings. In fact, more suitable descriptions of these buidlings would include: “Elegant, durable, customised and high-class”. Many people find they can afford to include more specialization and customization when they buy a factory built house over a traditional stick built construction.
5. Cutting-edge Designs
Looking for a building design with a little pizzazz? You need to check out the latest architectural designs associated with prefabricated buildings. Firms are now building more elegant and unique designs to meet the increasing demands of selective customers. People are selecting modular designs over stick built designs to build their dream homes.

6. Customised Design and Modification
There are hundreds of companies that offer modular prefabricated construction kits and plans, and most employ various architects and specialized designers to help customize your home. That means you have more choices and a wider selection of designers to choose from. If you don’t find a style you like with one designer you can often move onto another, without even switching manufacturers.

7. Huge Range of Selection
Its always best to select a home that matches your lifestyle and design preferences.
8. Rapid Customisation
These are often the ideal selection for homeowners in need of a speedily designed homes. You simply can’t build a dwelling faster. Site built housing can take months to design and build. A manufacturer can design and place a prefab house in a few short weeks. You can pick from just as many different styles as you would a site built home if not more, but don’t have to wait weeks for contractors to build your custom house.
9. Precise Budgeting and Timing
Yet another benefit of these designs is the lack of guesswork involved. You don’t have to worry about how something will look. You know that everything will arrive to the build site complete and you will know the exact outcome. You also don’t need to worry about unexpected expenses, which is commonly the case with site built homes. With a prefabricated house, you know exactly what your home will cost and can control that cost from the point of buying to final construction. This isn’t the case with stick built housing. With stick built housing you also have to worry about surprises in the middle of construction. It isn’t uncommon for example, for a contractor to quit in the middle of a project. If this happens you have few choices.
Your home will sit partially built until you are able to find a new construction team. This alone may cost you valuable time and money.
10. Improved Energy Efficiency
Many prefab houses also come with what manufacturers call the “Energy Star” certification. This is a national company that promotes energy efficiency. Buildings with this label use 30-40 percent less energy yearly than traditional stick built housing.
This saves you time and money. Some key features of prefabricated housing that help improve energy efficiency include tight installation, high performance and weather resistant windows, controlled air systems and duct systems, upgraded air-conditioning and heating units and use of efficient lighting and heating appliances. As a bonus, these features not only save on annual energy costs but also improve the quality of your indoor air. Think energy efficiency isn’t significant? Think again. Over the lifetime of your house you could save thousands of pounds in energy bills by buying a prefabricated dwelling.
11. Design Modification is Easier
Most prefab homemakers now use computer aided design systems when conducting operations. This adds to the efficiency of construction and improves the appearance and architecture of homes. Prefabricated construction ranges from plain vanilla styling to intricate and complex modern designs.
12. On Time and on Budget
Perhaps the two biggest features or benefits of prefabricated housing that manufacturers hone in on are the speed that they can be built with and the competitive pricing they can offer on the final product. This is one reason that modular homes are gaining popularity.
13. Appreciate in Value
These dwellings also appreciate much like site built housing designs. Most homeowners are interested in building value in their house over time. Prefab housing afford you the opportunity to do this (keep in mind however much appreciation is dependent on real estate location). Select a good build site and your house will gain significant value over time. Other factors may also affect appreciation including landscaping and how well the house is cared for year after year. These factors also affect site built housing. Unlike mobile homes, which depreciate, a modular homeowner can expect to gain value from their home year after year. Study after study suggests that modular homes appreciate just as well as site built homes. They are also just as easily insured and financed.
As far as risk goes, you are no more at risk buying prefabricated housing than site built construction.
Modular Home Facts
- Modular homes appraise the same as their on-site built counterparts do.
- Modular homes can be more easilly customised.
- Most modular home companies have their own in-house engineering departments that utilize CAD (Computer Aided Design).
- Modular home designs vary in style and size.
- Modular homes are permanent structures – “real property.”
- Modular homes are considered a form of “Green Building.”
- Modular homes are faster to build than a 100% site-built home.
- Home loans for modular are the same as if buying a 100% site-built home.
- Insuring your modular home is the same as a 100% site-built home.
- Modular homes can be built to withstand 175 mph winds.
- Modular homes can be built for accessible living and designed for future conveniences.
Would you consider a modular home for yourself, or are you more of a traditionalist?