Mum Shocked After One Twin is Born with Albinism: Real Life Story
Albinism is the “congenital absence of any pigmentation or coloration in a person, animal or plant, resulting in white hair, feathers, scales and skin and pink eyes in mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians and fish and other small invertebrates as well.” Varied use and interpretation of the terms mean that written reports of albinistic animals can be difficult to verify.
For ages, Judith had a feeling that she would struggle to become pregnant. There wasn’t a medical explanation for this — it was simply a niggling fear.
She and her husband struggled to believe they would ever become parents after years went by without her becoming pregnant. “I found myself getting anxious and desperate,” Judith first wrote on Love What Matters.
“The fear remained no matter how hard I tried to stay positive. However, Eight years down the line, my husband and I decided to go for our second round of IVF. The first of which failed, as well as other various procedures and fertility treatments. Every ultrasound visit after that was horror”
Judith
The couple could hardly contain their joy when that second round of IVF proved successful.
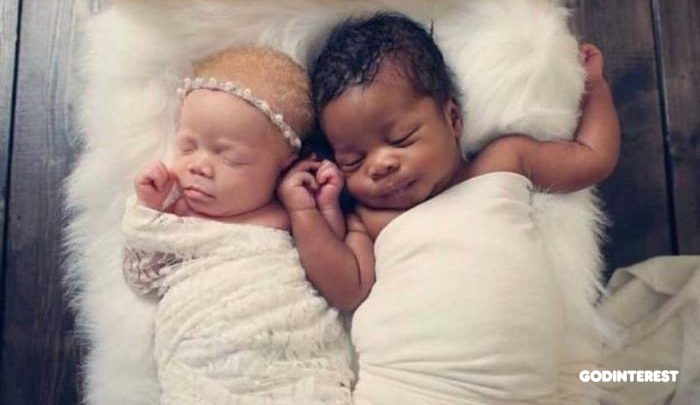
Judith was carrying twins — a boy, Kamis, and a girl, Kachi.
It felt remarkable that after all these years, their aspirations and dreams of a family were about to be real.
However, mum’s joy quickly turned to horror as doctors broke the news that Kachi was “at risk and might not make it”. “Every ultrasound visit after that was a nightmare as Kachi was far behind in growth whiles Kamsi did great.
“Finally, at 37 weeks, I had to be induced immediately because I was told that Kachi had stopped growing..” After the birth Nurses let Judith hold her daughter briefly before she was whisked to the NICU.
“The first time I saw her, I wondered if the nurse was handing me my baby, or someone else’s,” Judith said. “I waited a few seconds for someone to tell me there was a mix-up?” “Soon the joy of seeing them both healthy surpassed any other feeling at that instant.”
“How did I get black and white twins?”
Several days later Judith and her husband were told that their baby girl had albinism.
“I loved my princess like every mother would love her baby but worried about her condition,” Judith said.
“I worried about her future, how society would treat her, how she’ll be accepted.
“Gradually, worry turned to sadness and I started questioning “I envied other black babies and thought, ‘Why me? Why was I the one to have an albino baby?’
“How did I get black and white twins?”
“I threw the braille sheets in the garbage”
Unfortunately, medical professionals were quick to affirm Judith’s worst fears and told her that Kachi would struggle to see and would likely need to learn to read braille.
“I couldn’t imagine Kachi reading with braille and threw the braille sheets in the garbage.” She said
“She’s so smart and has a strong personality. She knows what she wants and will always go for it.
“I always tell her how beautiful she is, because she really is.“I’m not sure she`s aware of her uniqueness at the moment, but eventually she’ll know.”
“It’s my responsibility to educate her and teach her to love herself no matter what.
Albinism
Albinism affects the production of melanin, the pigment that colours skin, hair and eyes. It’s a lifelong condition, but it doesn’t get worse over time.
People with albinism have a reduced amount of melanin, or no melanin at all. This can affect their colouring and their eyesight.
Albinism is caused by faulty genes that a child inherits from their parents.
Symptoms of albinism
Hair and skin colour
People with albinism often have white or very light blonde hair, although some have brown or ginger hair. The exact colour depends on how much melanin their body produces.
Very pale skin that burns easily in the sun and doesn’t usually tan is also typical of albinism.
Eye colour
Someone with albinism can have pale blue, grey or brown eyes. Eye colour depends on the type of albinism and the amount of melanin. People from ethnic groups with darker pigmentation tend to have darker coloured eyes.
Eye problems
The reduced amount of melanin can also cause other eye problems. This is because melanin is involved in the development of the retina, the thin layer of cells at the back of the eye.
Possible eye problems linked to albinism include:
- poor eyesight — either short-sightedness or long-sightedness, and low vision (sight loss that can’t be corrected)
- astigmatism — where the cornea (clear layer at the front of the eye) isn’t perfectly curved or the lens is an abnormal shape, causing blurred vision
- photophobia — where the eyes are sensitive to light
- nystagmus — where the eyes move involuntarily from side to side, causing reduced vision; you don’t see the world as “wobbling” because your brain adapts to your eye movement
- squint — where the eyes point in different directions
Some young children with albinism may appear clumsy because problems with their eyesight can make it difficult for them to perform certain movements, such as picking up an object. This should improve as they get older.
How albinism is inherited
The two main types of albinism are:
- oculocutaneous albinism (OCA) — the most common type, affecting the skin, hair and eyes
- ocular albinism (OA) — a rarer type that mainly affects the eyes
Autosomal recessive inheritance
In most cases, including all types of OCA and some types of OA, albinism is passed on in an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern. This means a child has to inherit two copies of the faulty gene (one from each parent) to have the condition.
If both parents carry the gene, there’s a 1 in 4 chance that their child will have albinism and a 1 in 2 chance that their child will be a carrier. Carriers don’t have albinism but can pass on the faulty gene.
X-linked inheritance
Some types of OA are passed on in an X-linked inheritance pattern. This pattern affects boys and girls differently: girls who inherit the faulty gene become carriers and boys who inherit the faulty gene will get albinism.
When a mother is a carrier of an X-linked type of albinism, each of her daughters has a 1 in 2 chance of becoming a carrier and each of her sons has a 1 in 2 chance of having albinism.
When a father has an X-linked type of albinism, his daughters will become carriers, and his sons won’t have albinism and won’t be carriers.
Read more about how mutations are passed on.
Genetic counselling
If you have a history of albinism in your family or you have a child with the condition, you may want to talk to your GP about getting a referral for genetic counselling.
A genetic counsellor provides information, support and advice about genetic conditions. For example, you can discuss with them how you inherited albinism and the chances of passing it on.
Read more about genetic testing and counselling.
Diagnosing albinism
Albinism is usually obvious from a baby’s appearance when they’re born. Your baby’s hair, skin and eyes may be examined to look for signs of missing pigment.
As albinism can cause a number of eye problems, your baby may be referred to an eye specialist (ophthalmologist) for tests to check for conditions such as nystagmus, squint and astigmatism.
Electrodiagnostic testing is also sometimes used to help diagnose albinism. This is where small electrodes are stuck to the scalp to test the connections of the eyes to the part of the brain that controls vision.




