Resolving the Limitations Illiteracy Places on the Human Spirit
WILLS POINT, TX — Gospel for Asia (GFA, www.gfa.org) issues an extensive Special Report on illiteracy, the dominant disabler to flourishing for millions around the world, and the miraculous potential of literacy that is able to change the lives of men, women and children for generations.
Few of us who have read all our lives understand the nearly miraculous potential of being able to read and write when illiteracy has been the dominant disabler to flourishing. Illiteracy is more dominant than poverty, more dominant than a chronic physical disability, and more dominant than even an oppressive social system.
We readers have long lost the joy of discovering that the squiggly marks on a page of paper can be interpreted or that the same kinds of marks can be learned and replicated with chalk, ink, pen or pencil. We don’t understand because we read and write and often take for granted the treacherous limitations illiteracy places on the human spirit as well as on human potential.
Perhaps one story from Gospel for Asia will help us again remember the wonder of our own unrecognized reading and writing capacities. This is about Mandeepa.
 This is Mandeepa. Her widowed mother was too poor to send her to school when she was younger, so she grew up illiterate. After she learned of God’s love as a teenager, she deeply desired to read God’s Word, but she couldn’t read or write.
This is Mandeepa. Her widowed mother was too poor to send her to school when she was younger, so she grew up illiterate. After she learned of God’s love as a teenager, she deeply desired to read God’s Word, but she couldn’t read or write.
Due to the early death of her father, Mandeepa and her five other siblings were raised by a struggling mother. None of these six children were able to attend school, and at the age of 13, Mandeepa started to work as a household maid to support her single parent. Eventually, as is frequently the case, a marriage was arranged for Mandeepa, which quickly produced a son and a daughter.
At the age of 16, Mandeepa started attending a local church where the young woman received a Bible of her own–but having never learned to read and write, she, of course, only saw strange markings on the page. Her heart was filled with a longing to read the words and to learn more about the Heavenly Father the book taught about, but this was impossible, and the young woman was disconsolate.
Mandeepa’s husband was also illiterate. Their daughter was fortunate to attend school, but her growing ability to read only pointed out the lack in her mother’s education. How Mandeepa wished she could help her daughter with her schoolwork. This parental lack only increased the woman’s desire to read and write like her children.
Then the GFA-supported Women’s Fellowship at her church initiated literacy learning classes.
Mandeepa was now 32 years old, and after a year of study, she could finally read the Bible she had received 16 long years before. One of the first things she did when this “great miracle cure” began to have effect on her, banishing the shame and frustration of ignorance caused by lack of education, was to memorize John 14:15: “If you love Me, keep my commandments.”
Gospel for Asia points out that there are more than 250 million women in Asia today who are illiterate. It’s impossible for them to help their children with schoolwork. In addition, the instructions on medicine bottles, road signs, notices from the government and legal papers are all indecipherable– and this in a society that is increasingly dependent upon the written word. Those who desire to read God’s Word can’t do so. Technology can’t be accessed unless a user is highly literate. One must be able to spell, to read commands, to type letters that form words if the digital world is to be accessed.
Illiteracy is more dominant than poverty, more dominant than a chronic physical disability, and more dominant than even an oppressive social system.
Illiteracy is a kind of intellectual limbo, and no matter how naturally intelligent a person might be, the very descriptor “illiterate” indicates inferior mental capability.
Worldwide, entire villages with increasing levels of literacy are making social and economic gains when even just a small percentage of the villagers learn to read and write. Much data (a preponderance of which is examined under the general category of education) gives good cause to make the assumption that learning to read and write is one of the “great miracle cures.”
UNESCO does a thorough job of establishing the difficulty of conducting evidence- based data gathering as to the specific impact of literacy on individuals and communities, but it makes a broad generalization by stating in one article, “The ‘multiplier effect’ of literacy empowers people, enables them to participate fully in society and contributes to improve livelihoods. Literacy is also a driver for sustainable development in that it enables greater participation in the labour market; improved child and family health and nutrition; reduces poverty and expands life opportunities.”
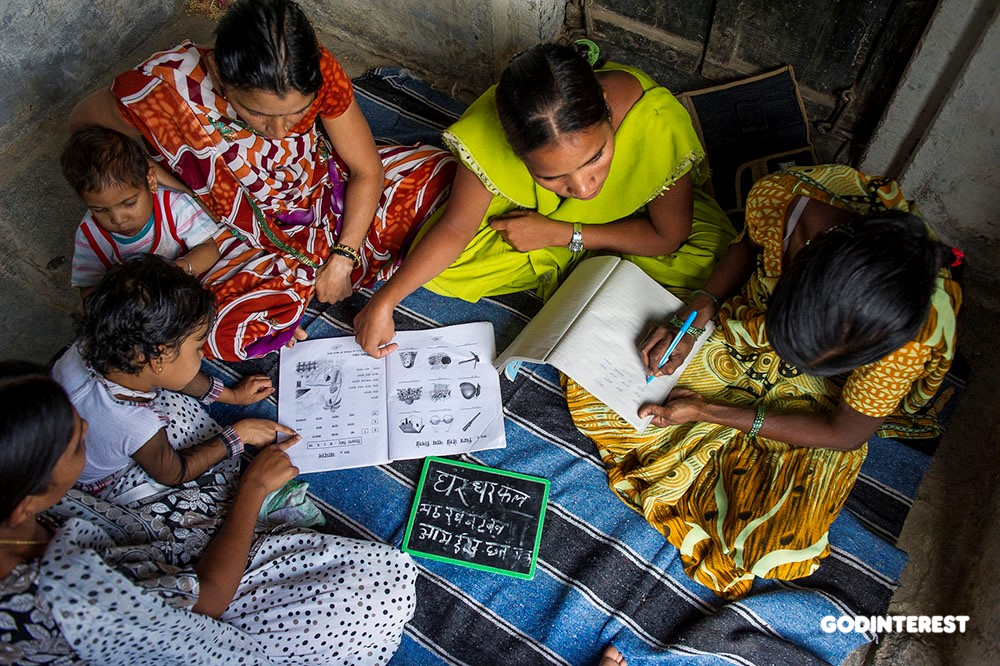 Asia: Manju is teaching several women how to read and write in a literacy class hosted in the women’s house in 2011. Illiteracy is often cured by an army of tutors like this. Opportunities to volunteer and serve to erase illiteracy, and spread the miracle of reading and writing, are numerous.
Asia: Manju is teaching several women how to read and write in a literacy class hosted in the women’s house in 2011. Illiteracy is often cured by an army of tutors like this. Opportunities to volunteer and serve to erase illiteracy, and spread the miracle of reading and writing, are numerous.
Why Is Literacy a Great Miracle Cure?
Hopefully, this article will inspire the reader about participating in some way in the joy of giving the gifts of reading and writing to other humans. The outcomes of such literacy initiatives are far beyond the investment of a few hours on the part of a tutor or of a volunteer week or some summer months overseas dedicated to literacy training and teaching. It is well worth considering teaching others how to read and write, or attending discussion groups at the local library where ESL (English as Second Language) learners are expanding their conversational skills, or volunteering with any of a multitude of organizations that welcome short-term teachers who are able to travel overseas. The opportunities for working literacy miracles are many and far-reaching.
Volunteering with NGOs (non-governmental organizations) overseas is, indeed, not only beneficial to individual learners who with literacy skills can obtain higher-paying jobs above menial labor and have the means to educate their own children, but also to whole villages and countries where the literacy aggregate continues to grow, or what has been referred to above as “the multiplier effect.”

All statistical evidence shows that one individual who is given reading and writing skills greatly improves his/her chances of success. Increasing literacy of individuals also greatly enhances the society in which those people live. A study conducted in Charleston, North Carolina, determined that “illiteracy is a multifaceted social equity and justice problem that results in less job opportunities and low income, often poverty.” The reporting continues to explain that employers are often careful not to allow low-skilled workers to work more than 30 hours at minimum wage, because hours accrued above this level must provide workers with benefits and paid time off. This limit means poverty or near-poverty for a certain demographic of workers, which then sets in motion the need for community government to provide welfare assistance. The Trident Literary Association of Charleston, South Carolina, notes that food and medical assistance are often necessary when someone lives below the poverty line, especially if children are present:
“Letting our people live in poverty can cost the Charleston community over $15,000 for ONE adult for only ONE year. This does not count the cost of any children each adult may have. When over 86,000 adults in the tri-county area don’t have a high school diploma or a GED, the community could incur costs of up to $1.3 BILLION in public assistance to help those people survive.”
If this is true in a mostly literate community, how does illiteracy impact countries with large demographics of people who can neither read or write? The consensus across the data is that illiteracy interferes with the flourishing of citizens within a community.
Specific negative incomes of illiteracy on both individuals and society. For individuals, the impacts include:
- “A limited ability to obtain and understand essential information;
- “An unemployment rate two to four times higher among those with little schooling compared to those with bachelor’s degrees;
- “Lower income;
- “Lower-quality jobs;
- “Precarious financial position;
- “Little value given to education and reading within the family, often leading to intergenerational transmission of illiteracy;
- “Low self-esteem, which can lead to isolation;
- “More workplace accidents, longer recovery times and more misuse of medications due to not understanding health care resources and procedures.”
And for a community whose citizens have a high illiteracy rate, societal impacts include:
- “Since literacy is essential for individuals and states to be competitive in the new global knowledge economy, many positions remain vacant for lack of adequately trained personnel;
- “The higher the proportion of adults with low literacy proficiency, the slower the overall long-term GDP growth rate is;
- “Difficulty understanding societal issues lowers the level of community involvement and civic participation.”
Defining Literacy
Like many topics, the meaning of literacy has nuances: Someone might say they are illiterate about opera, meaning they are uninformed, uninterested or unexposed to this art form. The same implications could be attributed to a person who is “illiterate” about immigration. At its most elemental level, however, to be illiterate means that a person cannot read or write or can only decipher words in a minimal way. Literacy Advance says the definition is even more complex:
“Literacy is the ability to read, write, speak and listen, and use numeracy and technology, at a level that enables people to express and understand ideas and opinions, to make decisions and solve problems, to achieve their goals, and to participate fully in their community and in wider society.”
Illiteracy is most prevalent in developing countries. South Asian, Arab and Sub- Saharan African countries are regions with the highest illiteracy rates at about 40 to 50 percent. East Asia and Latin America have illiteracy rates in the 10—15 percent region, while developed countries have illiteracy rates of a few percent.
Within ethnically homogenous regions, literacy rates can vary widely from country or region to region. This often coincides with the region’s wealth or urbanization, though many factors play a role.
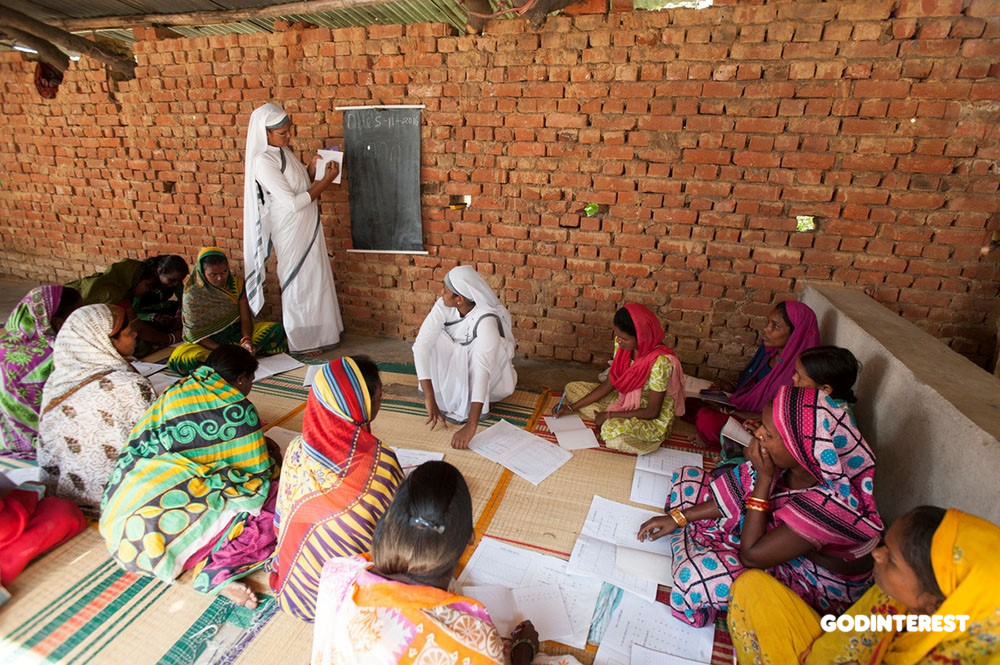 Odisha, India: Thirty-five ladies gather for a GFA-supported women’s literacy class three days a week. The class takes place Monday through Wednesday. Once they achieve their goal in teaching these ladies how to read and write, the Sisters of Compassion will begin another Adult Literacy Class elsewhere in the neighborhood.
Odisha, India: Thirty-five ladies gather for a GFA-supported women’s literacy class three days a week. The class takes place Monday through Wednesday. Once they achieve their goal in teaching these ladies how to read and write, the Sisters of Compassion will begin another Adult Literacy Class elsewhere in the neighborhood.
Illiteracy in the United States
Perhaps it is easier to examine literacy and illiteracy through the lens of one country, the one many of us know best and consider one of the most literate in the world.
ProLiteracy, a nonprofit that champions the power of literacy to improve the lives of adults and their families, communities and societies in the United States (and around the world), views illiteracy mostly through the lens of those who are foreign-born residents. The Center for Applied Linguistics reports that in 2006, some 13 years ago, there were 37.5 million foreign-born residents, or 12.5 percent of the total U.S. population.
Since that data was collected, there has been a surge in states that aren’t normally considered high foreign population centers such as California, Texas, New York and Florida. The Center for Applied Linguistics also reports that since 2005, some 14 other states experienced a 30 percent greater increase in foreign-born residency.
 They also state that the ESL (English as Second Language) population in the United States is diverse in terms of country of origin, education and individual language skills. In addition to Mexico and other Latin American countries, a growing number of non-native speakers of English come from China, the Philippines, India, Vietnam, Korea, Eastern Europe and African countries. Of these residents born outside the United States, 68 percent have a high school diploma in their native country or the U.S.
They also state that the ESL (English as Second Language) population in the United States is diverse in terms of country of origin, education and individual language skills. In addition to Mexico and other Latin American countries, a growing number of non-native speakers of English come from China, the Philippines, India, Vietnam, Korea, Eastern Europe and African countries. Of these residents born outside the United States, 68 percent have a high school diploma in their native country or the U.S.
With all this in mind, consider these additional facts on adult literacy in the U.S.:
- “36 million adults cannot read, write, or do basic math above a third-grade level.
- “68 percent of programs are struggling with long student waiting lists, and less than 10 percent of adults in need are receiving services.
- “Children whose parents have low literacy levels have a 72 percent chance of being at the lowest reading levels themselves. These children are more likely to get poor grades, display behavioral problems, have high absentee rates, repeat school years, or drop out.
- “One in six young adults–more than 1.2 million–drop out of high school every year.
- “2 million immigrants come to the U.S. each year, and about 50 percent of them lack high-school education and proficient English language skills
- “Low literacy costs the U.S. $225 billion or more each year in non-productivity in the workforce, crime, and loss of tax revenue due to unemployment.
- “43 percent of adults with lowest literacy levels live in poverty.
- “$232 billion a year in health care costs is linked to low adult literacy skills.
- “75 percent of state prison inmates did not complete high school or can be classified as low literate.”
According to the Barbara Bush Foundation for Family Literacy in the United States, research shows that the single greatest indicator of a child’s future success is the literacy level of his or her parents:
- “A child from a highly educated family will experience 30 million more words by the age of three than a child from a low-literate home.
- “Almost half of all children born to a mother lacking a high school diploma are not ready to start kindergarten.
- “Students who do not read proficiently by the third grade are four times more likely to leave high school without a diploma.”
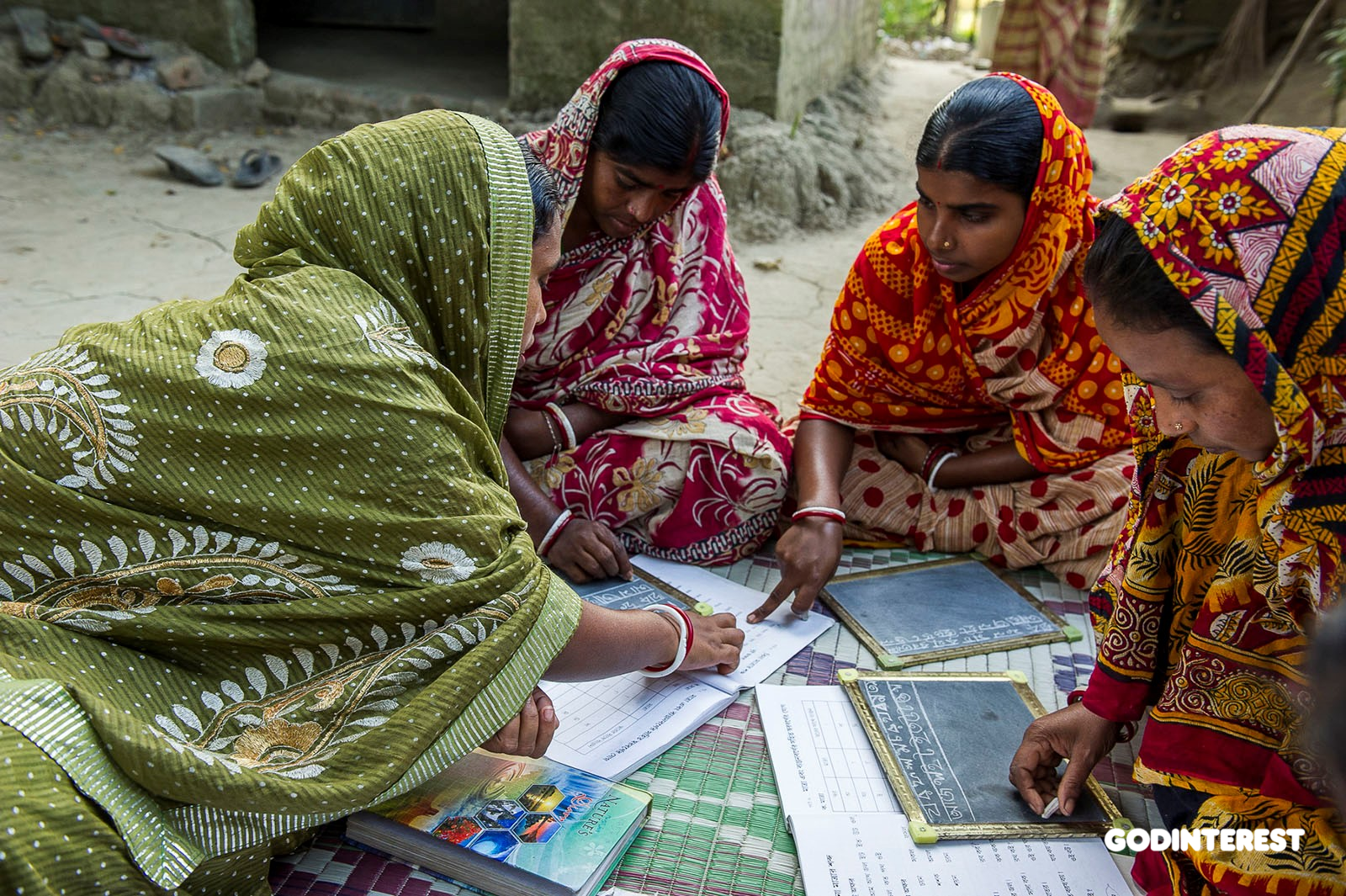 Sarada is teaching three women in a GFA-supported Women’s Literacy class. All statistical evidence shows that one individual who is given reading and writing skills greatly improves his/her chances of success. Increasing literacy of individuals also greatly enhances the society in which those people live.
Sarada is teaching three women in a GFA-supported Women’s Literacy class. All statistical evidence shows that one individual who is given reading and writing skills greatly improves his/her chances of success. Increasing literacy of individuals also greatly enhances the society in which those people live.
Literacy Efforts Around the World
The same results are evident in round-the-world data with many organizations working intensively to combat illiteracy. World Vision Ethiopia (WVE), for instance, is celebrating this year’s International Literacy Day with a campaign aimed at halting an alarming global trend: that of children graduating from primary school with reading deficiencies in their own mother tongue. Programs that emphasize reading proficiencies in five core reading skills are being implemented throughout 57 child-sponsorship Area Programs. Consequently, some 4,203 reading camps have been established across the Ethiopian nation. Nearly 1.5 million children are achieving reading and writing literacy in these camps; even more remarkable is that more than 15,000 youth are volunteering at these camps, helping serve not only children but also children’s parents.
Room to Read is a global non-profit promoting literacy and girl’s education, which asserts that “when children are educated, they are healthier. Their job opportunities improve. For every year that they stay in school, their earnings increase by 10 percent. They are more civically engaged and less dependent on social welfare. They are more likely to educate their own children and break the cycle of generational poverty.”
Their ambitious goal is to invest in the lives of at least 15 million children by 2020.
Although challenges of global illiteracy and gender inequality in education and their repercussions are enormous, Room to Read feels they have the tools to eradicate them.
According to their website,
“Children in grade two in our Literacy Program in India, Laos and Nepal can read three times as many words per minute and correctly answer more than twice as many comprehension questions as their peers. More than 4,800 girls have graduated from our Girls’ Education Program, and 78 percent of our 2016 graduates enrolled in tertiary education or found employment within one year post-graduation.”
Book Aid International is a UK based charity that provided nearly 1.3 million books in 2018 to people in 25 countries in Africa, the Middle east, the Caribbean, and other locations around the world. They are focused on addressing illiteracy by getting books to people who need them most through “thriving partnerships with library services and NGO’s who make books available to their communities.”
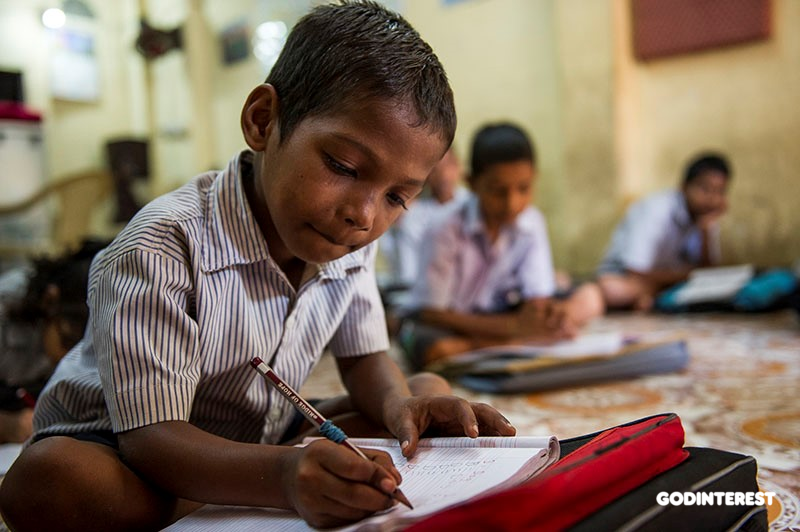 Shetal, an 8 year-old Bridge of Hope student, sits on the floor with his BOH book bag during the morning session. He attends from 9 to noon.Recognizing that 1 out of 5 people in the world cannot read or write, the World Literacy Foundation is operating in more than 80 countries worldwide to lift young people out of poverty through the power of literacy. Two mentionable projects they have in Australia alone include the Indigenous Learning App meant to close the literacy gap between indigenous and non-indigenous children, and the ROOP (Reading Out Of Poverty) Project designed to “enhance literacy skills and reading levels of children from low-income backgrounds.”
Shetal, an 8 year-old Bridge of Hope student, sits on the floor with his BOH book bag during the morning session. He attends from 9 to noon.Recognizing that 1 out of 5 people in the world cannot read or write, the World Literacy Foundation is operating in more than 80 countries worldwide to lift young people out of poverty through the power of literacy. Two mentionable projects they have in Australia alone include the Indigenous Learning App meant to close the literacy gap between indigenous and non-indigenous children, and the ROOP (Reading Out Of Poverty) Project designed to “enhance literacy skills and reading levels of children from low-income backgrounds.”
In The Enchanted Hour: The Miraculous Power of Reading Aloud in the Age of Distraction, author Meghan Cox Gurdon makes the point: “As we shall see, listening to stories while looking at pictures stimulates children’s deep brain networks, fostering their cognitive development. Further, the companionable experience of shared reading cultivates empathy, dramatically accelerates young children’s language acquisition and vaults them ahead of their peers when they get to school.”
After that premise, who wouldn’t want to read to their children or to their grandchildren or to their neighbor’s neglected kids on the block? But wait, according to Gurdon, there’s more.
“The rewards of early reading are astonishingly meaningful: toddlers who have lots of stories read to them turn into children who are more likely to enjoy strong relationships, sharper focus, and greater emotional resilience and self-mastery. The evidence has become so overwhelming that social scientists now consider read-aloud time one of the most important indicators of a child’s prospect in life.”
All well and good (and let’s admit it, also amazing), but what happens when the adults in a child’s life don’t read to them? What if they don’t read to their children because they can’t read? They can’t read books or newspapers or signs or legal documents or school papers or homework assignments or medical reports. Again: What if they don’t read to their children because they can’t read?
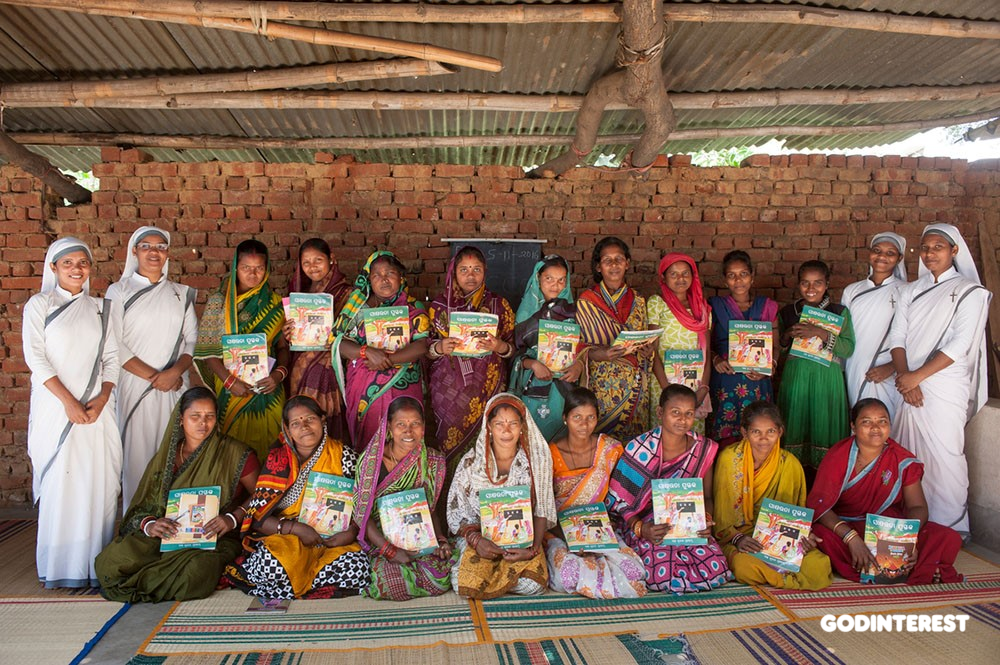 GFA-supported workers (like the Sisters of Compassion shown above) are helping to solve the literacy gap in Asia. In just one year, they taught 61,880 women how to read and write by providing free literacy classes. Many of those women had never had the opportunity to learn such a valuable skill because their families were either too poor to afford education or didn’t place importance on educating their daughters.
GFA-supported workers (like the Sisters of Compassion shown above) are helping to solve the literacy gap in Asia. In just one year, they taught 61,880 women how to read and write by providing free literacy classes. Many of those women had never had the opportunity to learn such a valuable skill because their families were either too poor to afford education or didn’t place importance on educating their daughters.
Solving the Literacy Gap
While searching for a significant role to champion while serving as First Lady of the United States, Barbara Bush decided that a whole society could be impacted for the better if enough folk were given the skills of literacy. There is less crime among the literate, more educational advancement and better opportunities for success. She not only started the Foundation for Family Literacy, but she pushed hard for the National Literacy Act, which was passed in 1991 while her husband was president.
Mostly, illiteracy is cured by an army of tutors. The opportunities to volunteer and serve to erase illiteracy (to spread the miracle of reading and writing) are numerous.
 GFA-supported workers are helping to solve the literacy gap in Asia. In just one year, they taught 61,880 women how to read and write by providing free literacy classes. Many of those women had never had the opportunity to learn such a valuable skill because their families were either too poor to afford education or didn’t place importance on educating their daughters. But now, they–like Mandeepa–have experienced the “great miracle cure,” and their families are thriving because of it.
GFA-supported workers are helping to solve the literacy gap in Asia. In just one year, they taught 61,880 women how to read and write by providing free literacy classes. Many of those women had never had the opportunity to learn such a valuable skill because their families were either too poor to afford education or didn’t place importance on educating their daughters. But now, they–like Mandeepa–have experienced the “great miracle cure,” and their families are thriving because of it.
According to UNICEF, literacy rates have shown a positive trend in recent years, due to the multitude of programs and outreaches around the world to erase one of the root causes–if not the major root cause–of illiteracy, which would be a lack of educational systems.
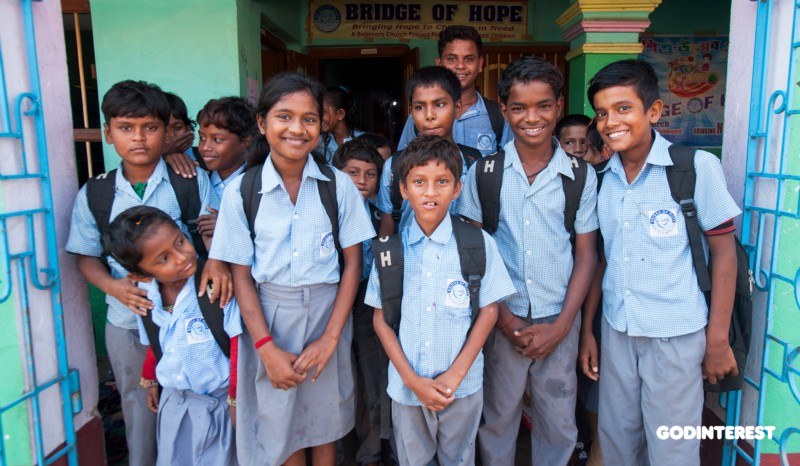
GFA-supported Bridge of Hope centers put an ax to this root cause by providing impoverished children free educational help. Staff at these centers provide each student with the academic tools they need to excel in their studies. If they see a student struggling in a specific area, they take measures to help them learn and overcome their challenges.
“Literacy rates among youth (aged 15 to 24) and adults are the test of an educational system, and the overall trend is positive, thanks to the expansion of educational opportunities,” reports UNICEF. “Globally, the youth literacy rate increased from 83 percent to 91 percent over two decades, while the number of illiterate youth declined from 170 million to 115 million. Regional and gender disparities persist, however. Literacy is lowest in least developed countries and higher among males than females. In the most recent years for which data are available, young women accounted for 59 percent of the total illiterate youth population.”
Personal Encounters with Illiteracy
I am an avid reader. It is nothing for me to go through some 35 books a month. Partly this is because of my writing profession; I am generally finishing a research deadline of some kind. The other part is that I just love to read. Reading has formed my character; exposed me to different kinds of thinking; enthralled me in the adventures of real and imaginary characters; improved my marriage and parenting capabilities; enhanced my housekeeping and gardening skills; and stimulated my intellectual, spiritual and psychological growth.
So in an attempt to have personal encounters with illiteracy, to develop an understanding I admittedly lack, I looked up literacy programs in my area for the purpose of considering what I, a solo person (who loves to read), could do to contribute to raising the literacy level of my hometown region, even if only by one or two individuals. I took a volunteer orientation class, an introductory evening of training to be followed by in-depth literacy tutor training this coming season. My $40 registration fee also bought the substantial workbook Teaching Adults: An ESL Resource Book, which I am reading. This, of course, deals with teaching those who are illiterate in writing and reading English. What gift could be more wonderful than coaching an eager English-language learner in the intricacies of speaking and writing English as a second language?
My husband and I live in the far western suburbs of Chicago. Our town is 52 percent non-white, mostly Hispanic. I can only relate to the immigrant experience of not knowing the language of an adopted country–e.g., not knowing how to read the road signs or the newspapers or the graphics that crawl across a television screen–by the times I have been plunged into a foreign culture overseas. Then I attempt to extrapolate those small and temporary situations into a lifetime of confusion due to the inability to read or write.
Obviously, knowing I would soon be returning home, or having a translator and guide shepherd me through the incomprehensible language and customs of a foreign country, renders these plunges only superficial. Due to our high Spanish-language speaking population, however, I run into literacy issues frequently enough–my own lack of Spanish-speaking facility as well as others’ lack of English comprehension. For instance, the name of the Lyft driver often sent to our door for a trip to the airport is Mariana. She makes sure we know she speaks “only little English.” I inevitably worry that she will take us to the wrong airport, but somehow, through a translation dispatcher system, we have so far been delivered to O’Hare or to Midway when needed.
While searching for a significant role to champion while serving as First Lady of the United States, Barbara Bush decided that a whole society could be impacted for the better if enough folk were given the skills of literacy. There is less crime among the literate, more educational advancement and better opportunities for success.
After my hairstylist’s departure to another state, I determined I would be part of the “new localism”–the grassroots effort of supporting the businesses and shops established by local entrepreneurs. “Oh, Lord,” I prayed. “Help me to find a decent stylist.” I walked into a hair salon in downtown West Chicago. There were five chairs and one person in the shop. “Do you cut hair?” I asked. “Si, si,” the woman responded. “Speak little English. Un pocito.”
“OK, OK,” I said, and signed an inch with my thumb and forefinger. “One inch off. All over.” Which is exactly what she did. She cut my hair one inch long all over my head. Without a doubt, it has been the easiest summer hairdo I have ever had. I wash it. Apply mousse. Then mess my hair up as it dries. No problem. But the experience gave me a baseline to imagine if every day and in every way these gaffes large and small would be part of the agony and effort of living. After time, one might just withdraw, choose silence, stop trying.
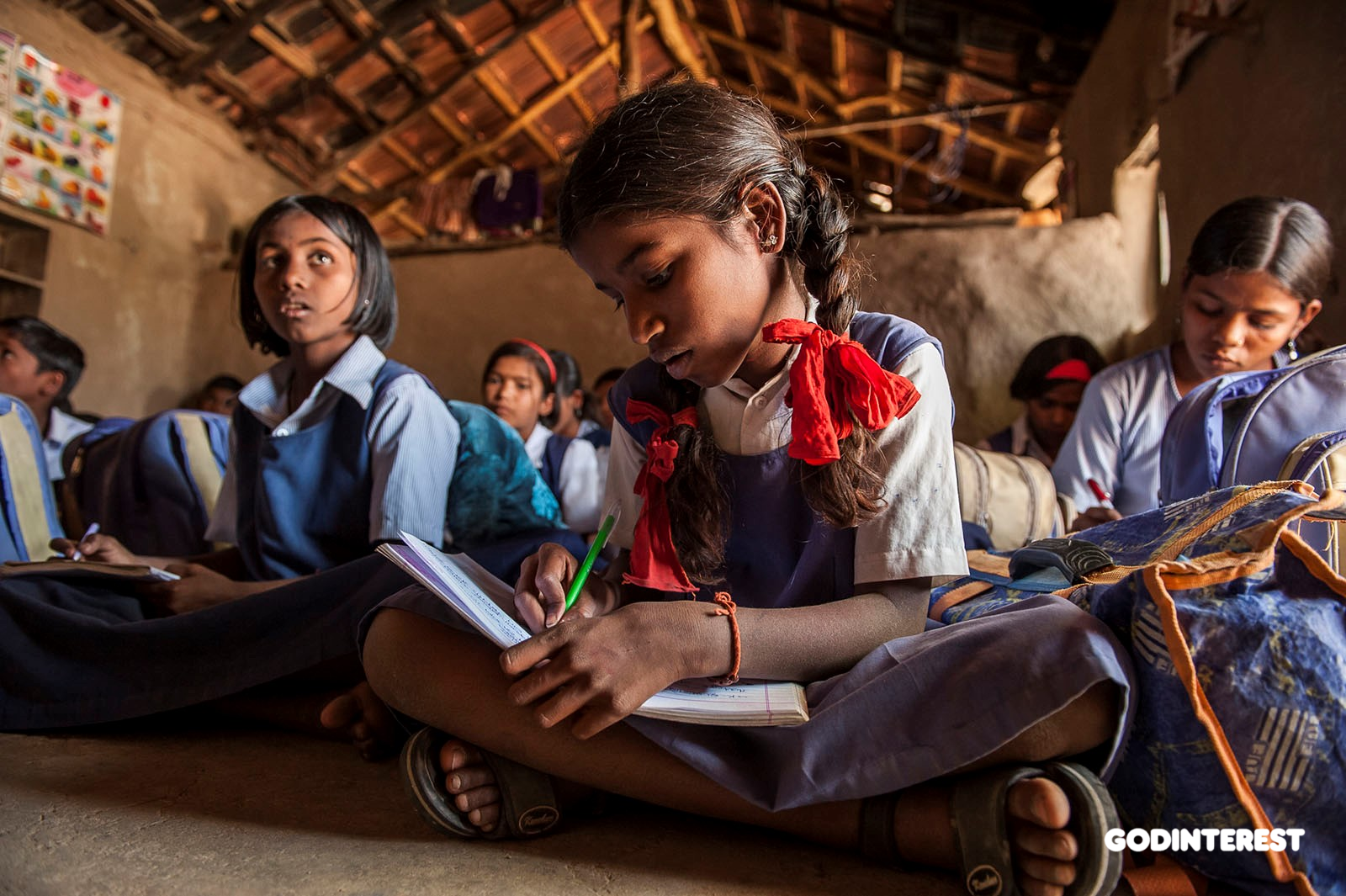 Maharashtra: Hkrishikesh, 11 years old, is in this class at her local Bridge of Hope Center. In the most recent years for which data are available from UNICEF, young women accounted for 59 percent of the total illiterate youth population.
Maharashtra: Hkrishikesh, 11 years old, is in this class at her local Bridge of Hope Center. In the most recent years for which data are available from UNICEF, young women accounted for 59 percent of the total illiterate youth population.
The Complexities of Gaining Literacy
The VeryWellFamily website teaches that the skills needed for reading and writing are not as simple as we so often assume. These skills include such things as the awareness of the sounds of language. These levels of learning will be the same for any culture. First is phonemic awareness: “the ability to hear and play with the individual sounds of language, to create new words using those sounds in different ways.” The article breaks down how this actually happens, a process that is quite complicated and mentions digraphs, onsets, rimes and phenomes. It is a process that occurs without intentional phonetically in the natural course of a child’s learning process.
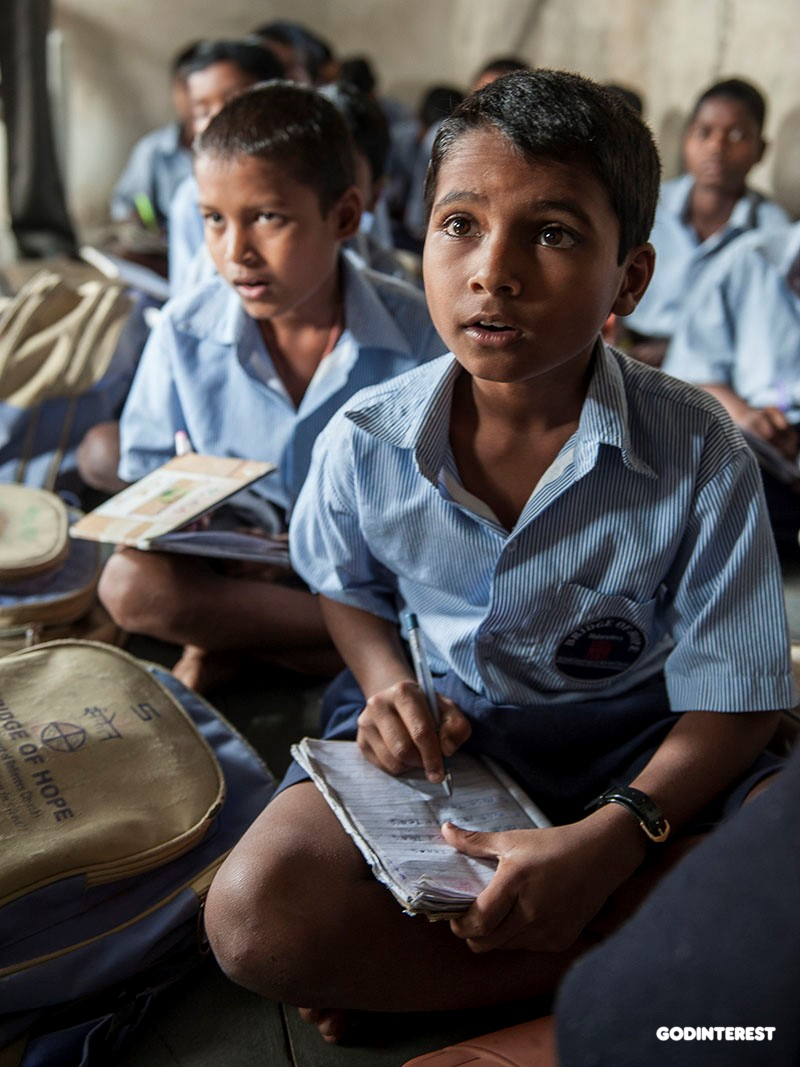 Avinash and Akshda are a brother and sister in the same class at their nearby Bridge of Hope Center.To read and speak fluently, a child must also develop an awareness of print; there’s a road sign, there’s a bathroom sign, here are words on cereal boxes, and, of course, there are books filled with print. The learner must develop an active vocabulary (words generally known and used in conversation, speech and writing) and a passive vocabulary (words that are known but the meanings of which are interpreted through context and use with others).
Avinash and Akshda are a brother and sister in the same class at their nearby Bridge of Hope Center.To read and speak fluently, a child must also develop an awareness of print; there’s a road sign, there’s a bathroom sign, here are words on cereal boxes, and, of course, there are books filled with print. The learner must develop an active vocabulary (words generally known and used in conversation, speech and writing) and a passive vocabulary (words that are known but the meanings of which are interpreted through context and use with others).
Achieving literacy for a child includes learning to spell (hence all those spelling tests). This means achieving a comprehension of irregular spelling, silent vowels, diphthongs, etc. He or she must not only be able to read words on a page (or a sign) but also comprehend the meaning of what has been read. This includes the ability to project meaning into the words, to pick up clues in the text, to visualize imaginatively what is occurring through the reading.
To read, to understand what one has read, to voice one’s inner thoughts, to comprehend and communicate the meaning of one’s being so that it can be heard either verbally or through thoughts committed to the page is not such a simple task as those of us who love reading might assume. But the joy, oh the gift of joy, that can be given to one other person or to a classroom of squirmy but nevertheless eager learners is incalculable.
[youtube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XK8YhTPwfNU?wmode=opaque&w=640&h=360]
A Lifetime of Illiteracy and the Onset of Leprosy
Gospel for Asia chronicles the tale of a woman named Kaavya. She was given this gift of literacy that filled a lifetime of longing when she was 64 years of age. What makes her story even more impelling was the fact that Kaavya also suffered from leprosy. Now, medical knowledge informs us that leprosy is a curable disease, but the stigma of this condition is implanted on the DNA of history, with a record of scorn and communal rejection that is recorded even in the New Testament stories of Christ’s healing encounters with lepers.
Kaavya’s father contracted leprosy with the result that the community ostracized the whole family. In time, the girl’s father died, and about then she began to experience symptoms of physical pain in her extremities and also a recurring fever. The crushing news from hospital staff indicated that the diagnosis of her difficulties was that she had developed leprosy also.
“It was the worst day and the saddest day in my life,” she said. “What to do? I could not die.”
Eventually, with treatment and medications, she procured a hospital job, but then, because she was illiterate, after 22 years of work, she was let go, unqualified in the eyes of the current staff. She married and settled into family life, but only a few years had passed when she discovered that her husband had a previous family. His first wife bore him eight daughters, and he was hoping some other woman would give him a son.
This is a chronicle of human misery, repeated in the hundreds of thousands of untold stories that exist around the world. But it does not have an unhappy ending.
“After years of hardships, Kaayva came to live in a leprosy colony, making her home with those who experienced the same kind of rejection she had,” the report states.
But here, the Sisters of Compassion, supported by Gospel for Asia, served the residents by practical needs. One of those expressions was in teaching the skills of reading and writing. Just imagine the meaning of this to a woman who had been expelled from a job of 22 years for being illiterate!
To become literate is exactly what miracle cures are about. To be able to read and write is a gift of immeasurable worth. It is, indeed, a miracle cure.
“When I joined the literacy class, I learned lots of things,” Kaavya explains. “I learned not only reading and writing; I learned good habits, roles of women, wife and mother in the family. Now I am very happy ”¦ I will not lose heart because I can read and write.”
GFA-supported literacy classes are taught by women missionaries who are trained in teaching reading and writing to adults. They write letters and words on chalk boards and carefully teach each student how to read and write those same letters and words. They guide their students’ hands, helping them become familiar with the feel and use of a pencil. Each woman enrolled in the literacy classes also receives a free literacy book in their local language. For tens of thousands of women across Asia, these free literacy classes have made a world of difference in their lives!
When the Word Became Flesh
I have often thought of Christ as the Great Translator who came to Earth to teach us Heaven’s language and ways.
“And the Word became flesh and dwelt among us, and we beheld His glory, the glory as of the only begotten Father, full of grace and truth” (John 1:14).
Jesus’ life lived on Earth, and now communicated to us existentially through the indwelling of the Holy Spirit, is the ultimate example of a superior language tutorial–one in spiritual literacy. By observing Him, by reading and inculcating His words, we learn to “read and write.” We become spiritually literate. And like those who conquer reading and writing in the everyday world, this too, this inexplicable capacity to know with the soul, brings light and opportunity and almost unbearable joy. Another kind of illiteracy has been overcome. To become literate is exactly what miracle cures are about. It is an intellectual healing, the acquisition of incalculable capabilities and the establishment of approval from others and from oneself. To be able to read and write is a gift of immeasurable worth. It is, indeed, a miracle cure.
WHAT CAN ONE READER DO?
 Consider giving to Gospel for Asia’s literacy efforts. GFA-supported workers have heightened personal exposure to the dilemmas caused by illiteracy and have daily witnessed the power of literacy training to spread Christ’s love, to lift individuals and families out of poverty, to change communities for the better. Undoubtedly, learning to read and write is one way the Word becomes flesh and dwells among us. This, indeed, is a spiritual miracle.
Consider giving to Gospel for Asia’s literacy efforts. GFA-supported workers have heightened personal exposure to the dilemmas caused by illiteracy and have daily witnessed the power of literacy training to spread Christ’s love, to lift individuals and families out of poverty, to change communities for the better. Undoubtedly, learning to read and write is one way the Word becomes flesh and dwells among us. This, indeed, is a spiritual miracle.
 Become intentional about the miracle of being able to read and write. Take some time to consider what it would be like if you were illiterate. Intentionally notice–even notate–the many times you read and write in a day. Then thank God that you were born in a literate culture with systemic educational programs in place to increase your reading and writing capacities.
Become intentional about the miracle of being able to read and write. Take some time to consider what it would be like if you were illiterate. Intentionally notice–even notate–the many times you read and write in a day. Then thank God that you were born in a literate culture with systemic educational programs in place to increase your reading and writing capacities.

Conduct an Internet exposure regarding the topic of illiteracy in your home country and then around the world. There is something about those online searches that embed the reality of illiteracy in your mind–more than just reading an article about illiteracy.

Conduct an Internet exposure regarding the topic of illiteracy in your home country and then around the world. There is something about those online searches that embed the reality of illiteracy in your mind–more than just reading an article about illiteracy.
Learn more about the Gospel for Asia: Women’s Literacy Program. Over 250 million women in Asia are illiterate. Even if they want to read, there is no way to learn. With your help, women in Asia can learn to read and will be equipped to tackle life’s hurdles.
This Special Report article originally appeared on GFA Special Reports.
Learn more about Gospel for Asia:
Facebook | YouTube | Instagram | SourceWatch | Integrity | Lawsuit Update | 5 Distinctives | 6 Remarkable Facts | Media Room | Endorsements | 40th Anniversary | Lawsuit Response |
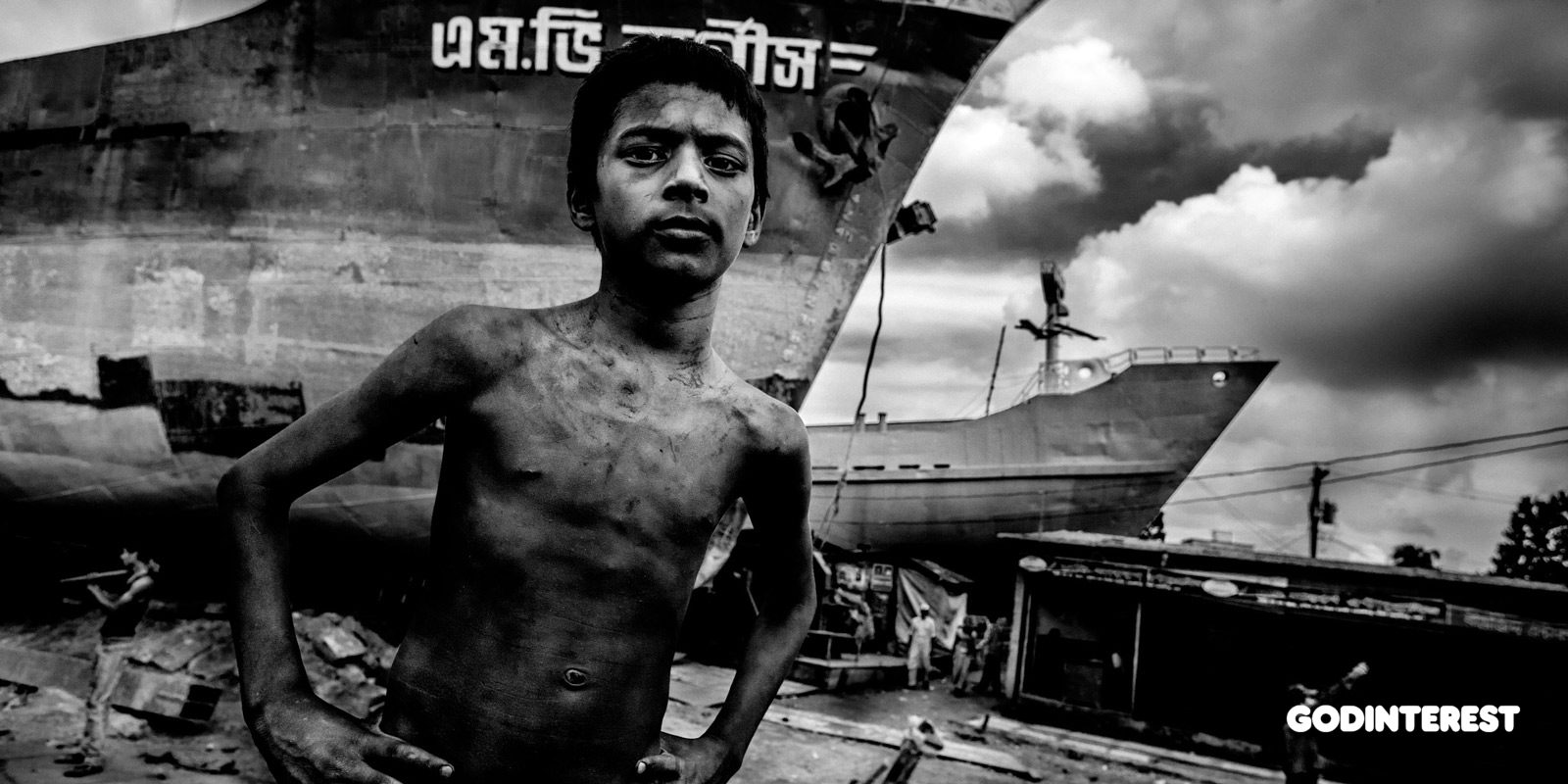




 The unconditional worst forms of child labor… defined as slavery, trafficking, debt bondage and other forms of forced labor, forced recruitment of children for use in armed conflict, prostitution and pornography, and illicit activities.
The unconditional worst forms of child labor… defined as slavery, trafficking, debt bondage and other forms of forced labor, forced recruitment of children for use in armed conflict, prostitution and pornography, and illicit activities.
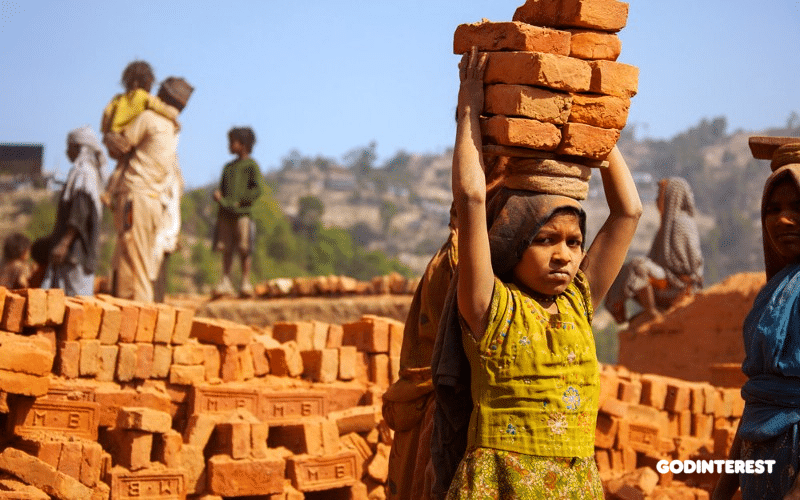
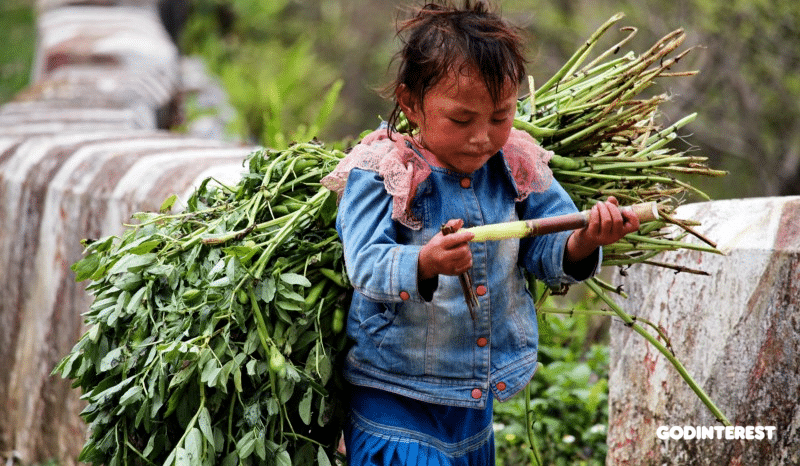
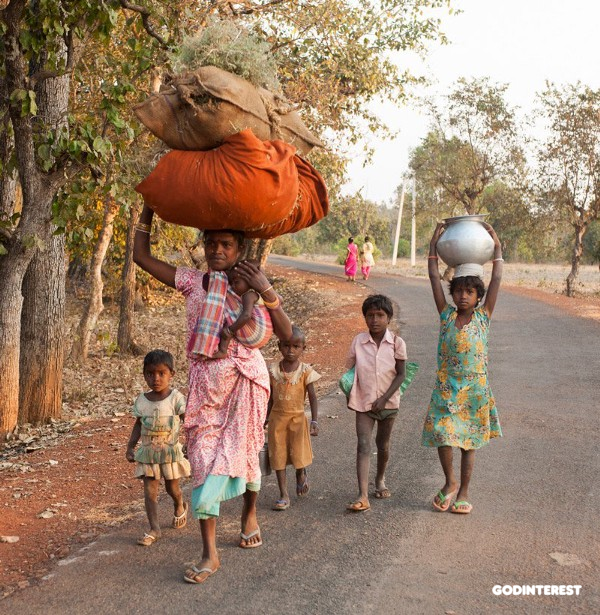







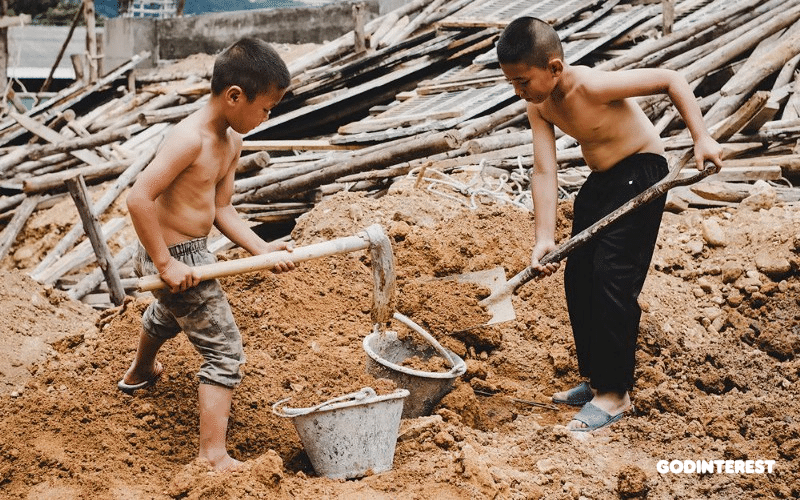
 When businesses throughout the chain fail to manage this dynamic, they go out of business. When they succeed, the two links at the far ends of the chain suffer the most. The first-touch laborers are destined to subsistence wages or less, and the consumers expend more for the final product. There are no winners at either end of the chain.
When businesses throughout the chain fail to manage this dynamic, they go out of business. When they succeed, the two links at the far ends of the chain suffer the most. The first-touch laborers are destined to subsistence wages or less, and the consumers expend more for the final product. There are no winners at either end of the chain.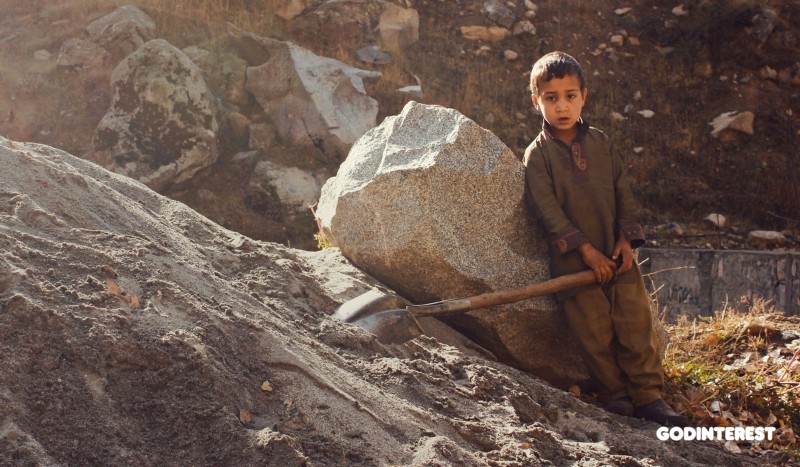
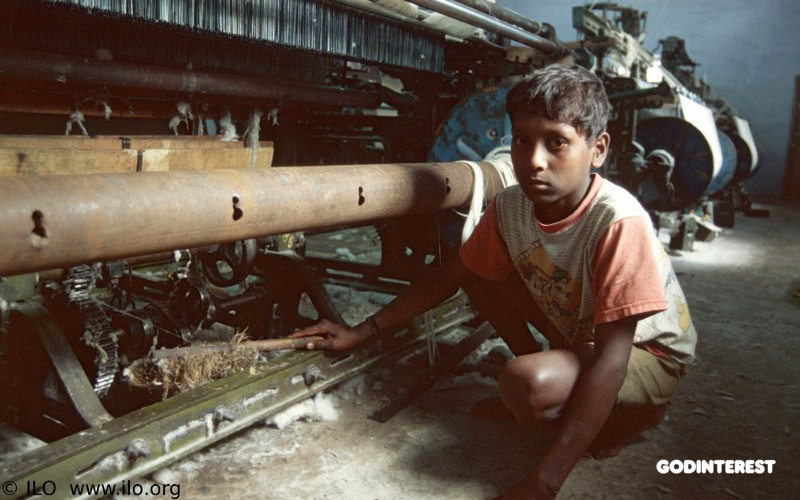


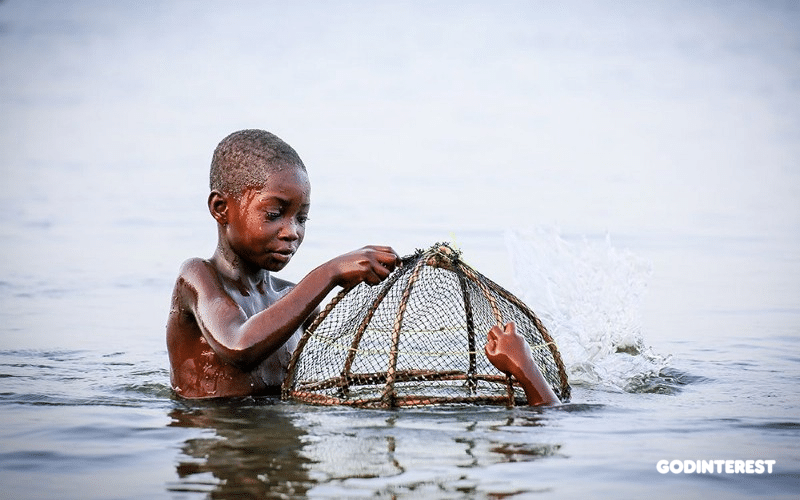
 A 2018 study by the Kyrgyzstan Federation of Trade Unions (KFTU) found that implementing and enforcing are inconsistent at best. Although it had been 10 years since the country ratified the International Labor Organization convention for the elimination of the worst forms of child labor, more than 250,000 children were still subjected to hazardous work. The
A 2018 study by the Kyrgyzstan Federation of Trade Unions (KFTU) found that implementing and enforcing are inconsistent at best. Although it had been 10 years since the country ratified the International Labor Organization convention for the elimination of the worst forms of child labor, more than 250,000 children were still subjected to hazardous work. The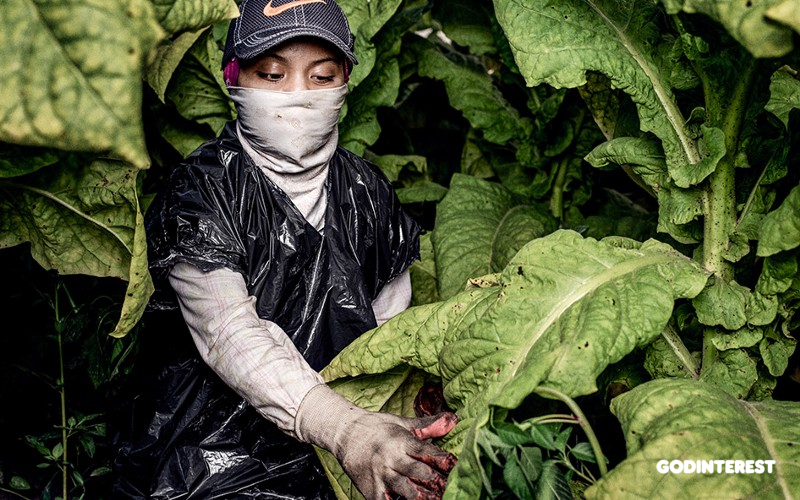 
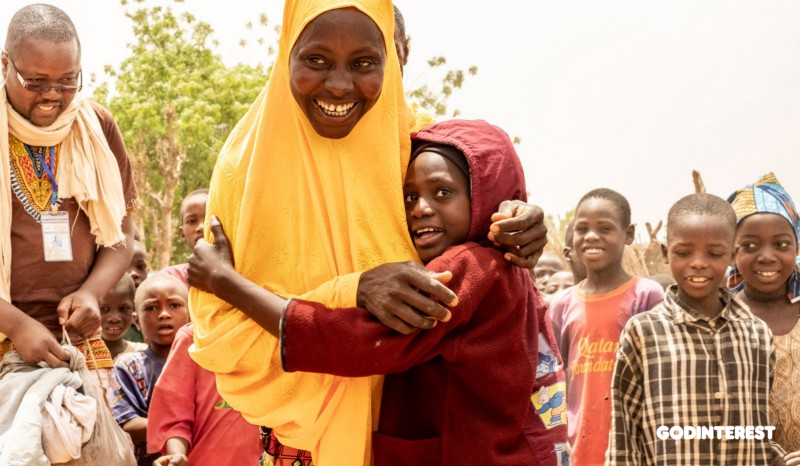
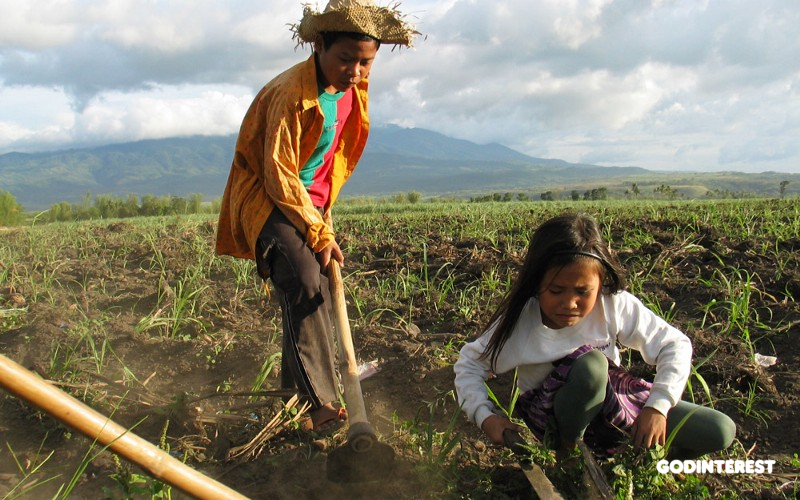


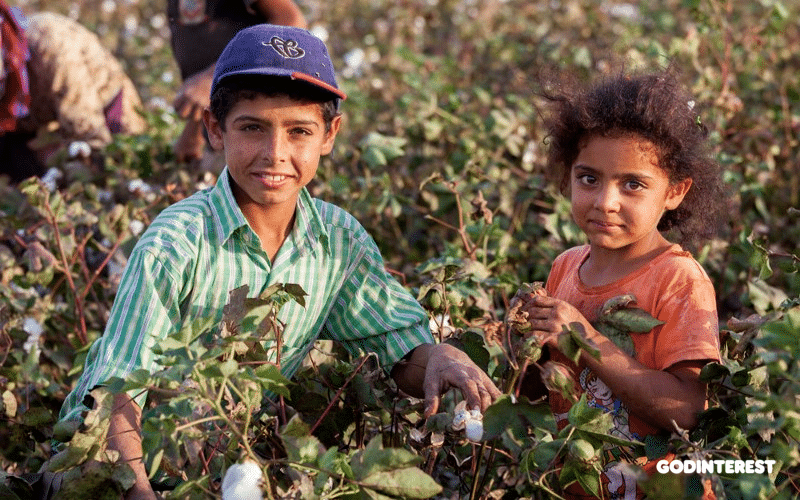
 While various and sundry organizations and institutions attempt to solve the child labor problem, the church's task remains what it has always been: Be the hands and feet of Jesus to "the least of these" (see Matthew 25:40).
While various and sundry organizations and institutions attempt to solve the child labor problem, the church's task remains what it has always been: Be the hands and feet of Jesus to "the least of these" (see Matthew 25:40).




